Virginia State Tax Income

Virginia, located in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, has a robust economy and a diverse tax system. One of the key components of this system is the Virginia State Tax Income, which plays a significant role in funding public services and infrastructure across the state. Understanding the intricacies of this tax system is crucial for both residents and businesses operating within Virginia's borders.
Unraveling the Virginia State Tax Income System
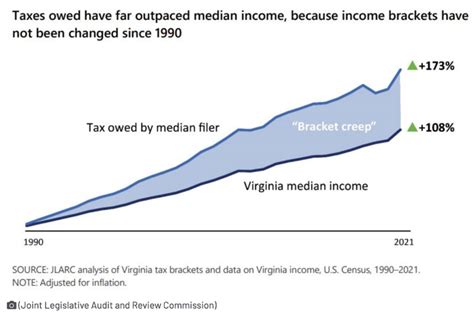
The Virginia State Tax Income, often referred to as the “Income Tax,” is a critical revenue source for the state government. It is imposed on the taxable income of individuals, businesses, and certain entities, with rates varying based on income brackets and tax classification.
For individuals, Virginia employs a progressive tax system, meaning that higher incomes are taxed at progressively higher rates. This approach ensures that those with greater financial means contribute a larger proportion of their income towards the state's fiscal responsibilities. The income tax rates for individuals range from 2.0% to 5.75%, with seven distinct tax brackets. These brackets are adjusted annually to account for inflation and changes in the cost of living.
| Tax Rate | Taxable Income Range |
|---|---|
| 2.0% | $0 - $3,000 |
| 3.0% | $3,001 - $5,000 |
| 4.0% | $5,001 - $17,000 |
| 5.0% | $17,001 - $50,000 |
| 5.5% | $50,001 - $100,000 |
| 5.75% | $100,001 and above |

Virginia's corporate income tax, on the other hand, operates on a flat rate structure. As of 2024, the corporate income tax rate stands at 6.0%, applying to the taxable income of corporations, limited liability companies, and other business entities. This rate has remained consistent for several years, providing a stable tax environment for businesses operating within the state.
Tax Credits and Incentives
To encourage economic growth and support various industries, Virginia offers a range of tax credits and incentives. These incentives are designed to attract businesses, stimulate job creation, and promote specific sectors such as renewable energy, technology, and manufacturing.
For instance, the Research and Development Tax Credit provides a credit of 7.5% of qualified research expenses for businesses engaged in research and development activities. Similarly, the Virginia Historic Tax Credit offers incentives for the rehabilitation of historic structures, encouraging the preservation of Virginia's rich architectural heritage.
Filing and Payment Processes
Virginia has streamlined its tax filing and payment processes to ensure convenience and efficiency for taxpayers. Individuals and businesses can file their tax returns electronically through the Virginia Tax Online Filing System, which provides a secure platform for data transmission. This system also allows for direct deposit of tax refunds, expediting the process for taxpayers.
For those who prefer traditional methods, paper returns are accepted, and taxpayers can choose to pay their taxes via check, money order, or electronic funds transfer. The Virginia Department of Taxation provides detailed guidelines and resources to assist taxpayers in navigating the filing and payment processes, ensuring compliance with state tax laws.
Impact of Virginia State Tax Income on Residents and Businesses

The Virginia State Tax Income has a profound impact on the lives of residents and the operations of businesses within the state. This section delves into the various ways in which the tax system influences economic decisions, shapes the business landscape, and contributes to the overall financial health of Virginia.
Resident’s Perspective: Balancing Tax Burden and Public Services
For Virginia residents, the state income tax is a key consideration in their financial planning. The progressive tax structure ensures that individuals with higher incomes contribute a larger share, reflecting the principle of ability to pay. This approach aims to distribute the tax burden equitably across the population.
However, the impact of the state income tax extends beyond the tax payment itself. The revenue generated from this tax is vital for funding essential public services, including education, healthcare, transportation, and public safety. Virginia residents directly benefit from these services, which are often financed through state tax revenues.
For instance, the state income tax plays a significant role in supporting Virginia's renowned public education system. It contributes to funding elementary, middle, and high schools, as well as institutions of higher learning, ensuring that residents have access to quality education. Similarly, the tax revenue supports healthcare initiatives, such as Medicaid and public health programs, providing essential healthcare services to those in need.
Business Perspective: Navigating Tax Obligations and Incentives
Businesses operating within Virginia face a unique set of challenges and opportunities when it comes to the state income tax. The corporate income tax, although at a flat rate, can impact business decisions, particularly for companies with substantial taxable income.
To mitigate the impact of the corporate income tax, Virginia offers a range of tax incentives and credits. These incentives are designed to attract businesses, encourage investment, and promote specific industries. For example, the Virginia Jobs Investment Program provides grants and tax credits to businesses that create new jobs and invest in employee training.
Furthermore, Virginia's tax system provides incentives for businesses to locate or expand within certain regions of the state. These incentives, often tied to economic development zones, offer reduced tax rates or tax credits to businesses that create jobs and stimulate economic growth in targeted areas. This strategic approach to tax incentives helps to promote balanced economic development across Virginia.
Additionally, the state's tax system considers the unique characteristics of different business entities. For instance, S-corporations and partnerships are taxed differently, with pass-through taxation that avoids double taxation at the entity level. This recognition of diverse business structures ensures that the tax system is adaptable and equitable for a wide range of businesses.
Economic Impact: Contributing to Virginia’s Fiscal Stability
The Virginia State Tax Income is a cornerstone of the state’s fiscal stability and economic prosperity. The revenue generated from this tax enables the state government to invest in critical infrastructure projects, such as road and bridge construction, public transportation, and utility improvements. These investments not only enhance the quality of life for residents but also attract businesses and contribute to long-term economic growth.
Moreover, the state income tax plays a vital role in supporting Virginia's robust business environment. The tax revenue funds initiatives aimed at business support and development, including small business grants, entrepreneurial programs, and industry-specific incentives. These efforts foster a thriving business community, which, in turn, creates jobs and drives economic growth.
In conclusion, the Virginia State Tax Income is a complex and multifaceted system that shapes the economic landscape of the state. It impacts residents' financial planning, businesses' operational strategies, and the overall fiscal health of Virginia. Understanding the nuances of this tax system is essential for individuals and businesses to navigate their tax obligations effectively and leverage the available incentives to their advantage.
When are Virginia state tax returns due?
+Virginia state tax returns are due on the same date as federal tax returns, typically April 15th. However, this date may be extended if certain conditions are met.
Are there any tax deductions available for residents of Virginia?
+Yes, Virginia offers various tax deductions, including deductions for medical expenses, charitable contributions, and certain education expenses. These deductions can help reduce the taxable income of individuals and provide some tax relief.
What is the sales tax rate in Virginia, and does it vary across the state?
+The general sales tax rate in Virginia is 4.3%, but it can vary depending on local jurisdictions. Some localities impose additional taxes, resulting in a higher sales tax rate. It’s important to check the specific sales tax rate for each locality.



