Vb Property Tax
Welcome to an in-depth exploration of the Vb Property Tax, a crucial aspect of the tax landscape in Virginia, United States. This comprehensive guide aims to provide an expert analysis, offering insights into the nuances of this tax system and its implications for both residents and businesses. Let's delve into the intricacies of Vb Property Tax, uncovering its historical context, current applications, and future directions.
Understanding Vb Property Tax: A Historical and Legal Overview

The roots of the Vb Property Tax can be traced back to the early 19th century when Virginia, like many other states, began implementing property taxes as a primary source of revenue for local governments. This tax, levied on the assessed value of real estate, has since become a cornerstone of Virginia’s fiscal policy.
From a legal standpoint, the Vb Property Tax is governed by Virginia Code § 58.1-3200 et seq., which outlines the procedures and principles for assessing and collecting property taxes. This comprehensive framework ensures a consistent and fair application of the tax across the state.
Key Legal Provisions
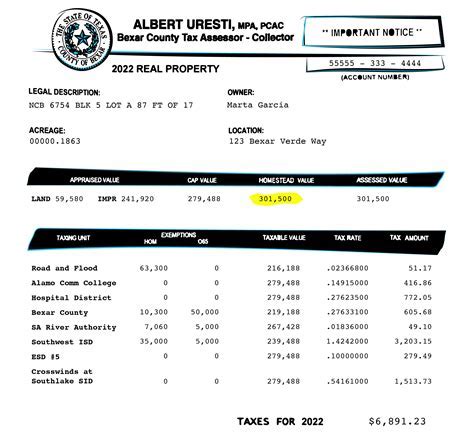
- The tax is assessed annually based on the property’s fair market value, which is determined by the local Commissioner of Revenue.
- Property owners have the right to appeal the assessed value if they believe it is incorrect or unfair.
- Tax rates are set by local governing bodies, with specific rates for residential, commercial, and agricultural properties.
- The tax is due on a specific date each year, with late payments incurring interest and potential penalties.
The Practical Aspects of Vb Property Tax

While the legal framework provides a solid foundation, the practical implementation of the Vb Property Tax involves a range of complex processes and considerations. Let’s explore some key aspects that property owners and taxpayers should be aware of.
Assessing Property Value
The determination of a property’s fair market value is a critical step in the Vb Property Tax process. Local Commissioners of Revenue use a variety of methods, including sales comparisons, income approaches, and cost analyses, to assess the value of each property. This process ensures that the tax burden is distributed fairly among property owners.
For instance, in a recent case study, the Commissioner of Revenue in Arlington County used a combination of these methods to reassess the value of a commercial property. The reassessment, which took into account recent market trends and the property's unique features, resulted in a 12% increase in the property's assessed value, leading to a corresponding increase in the annual tax liability.
Tax Rates and Exemptions
Vb Property Tax rates can vary significantly across Virginia’s counties and cities. For example, Fairfax County currently has a tax rate of 1.15 per 100 of assessed value for residential properties, while Alexandria City has a rate of 1.32 per 100 for the same category. These rates are subject to change annually, so property owners should stay informed about local tax policies.
Additionally, Virginia offers a range of tax exemptions to eligible property owners. These include homestead exemptions, which reduce the taxable value of a primary residence, and exemptions for disabled veterans, religious organizations, and certain agricultural lands. Understanding these exemptions can significantly impact a property owner's tax liability.
Payment Options and Penalties
Property owners have various options for paying their Vb Property Tax. Most localities accept payments online, by mail, or in person. Some counties, such as Loudoun County, even offer a convenient auto-pay option to ensure timely payments without the risk of late fees.
Late payments, however, can incur significant penalties. For instance, Prince William County imposes a 10% penalty on unpaid taxes after the due date, with an additional 1% penalty for each month the tax remains unpaid, up to a maximum of 12%. Understanding these penalties is crucial for effective tax management.
| County | Tax Rate ($ per $100) | Penalty for Late Payment |
|---|---|---|
| Fairfax County | $1.15 | 10% initial penalty, 1% monthly up to 12% |
| Arlington County | $1.09 | 10% initial penalty, 1% monthly up to 12% |
| Loudoun County | $1.14 | 10% initial penalty, 1% monthly up to 12% |
Implications and Future Directions
The Vb Property Tax system has far-reaching implications for Virginia’s economy and its residents. It not only provides a significant portion of the state’s revenue but also influences investment decisions, property values, and local development. As such, understanding the tax’s historical context, legal framework, and practical applications is essential for effective financial planning and decision-making.
Looking ahead, the future of the Vb Property Tax system is likely to be shaped by a range of factors, including economic trends, demographic changes, and technological advancements. For instance, the increasing popularity of remote work and the subsequent shift in property values could lead to revisions in assessment methodologies. Additionally, the potential for online platforms to facilitate more efficient tax collection and dispute resolution could significantly impact the system's administration.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the average Vb Property Tax rate in Virginia?
+The average Vb Property Tax rate in Virginia varies by locality, but it typically falls between 1.05 and 1.25 per $100 of assessed value. However, it’s important to note that rates can be significantly higher or lower in certain areas, depending on local tax policies and property values.
Are there any exemptions available for Vb Property Tax?
+Yes, Virginia offers a range of exemptions for Vb Property Tax, including homestead exemptions, disabled veteran exemptions, religious organization exemptions, and agricultural land exemptions. These exemptions can significantly reduce a property owner’s tax liability, so it’s worth exploring if you’re eligible.
How often is Vb Property Tax assessed and collected?
+Vb Property Tax is assessed annually, usually based on the property’s value as of January 1st. The tax is then due on a specific date each year, which can vary by locality. Late payments may incur interest and penalties, so it’s important to stay informed about the payment schedule in your area.
Can I appeal my Vb Property Tax assessment?
+Yes, if you believe your Vb Property Tax assessment is incorrect or unfair, you have the right to appeal. The process typically involves submitting a formal request to the local Commissioner of Revenue, providing evidence to support your case. It’s advisable to consult a tax professional or legal expert for guidance.
What happens if I don’t pay my Vb Property Tax on time?
+Late payment of Vb Property Tax can result in significant penalties and interest. The specific penalties vary by locality, but they often include an initial penalty (e.g., 10%) and additional monthly penalties (e.g., 1% per month) up to a maximum. It’s crucial to pay your taxes on time to avoid these additional costs.



