Tax Rate Marginal Vs Effective
Unraveling the Complexity: Understanding Marginal and Effective Tax Rates
In the intricate world of taxation, two key concepts often arise: marginal tax rate and effective tax rate. These terms, though seemingly similar, hold distinct meanings and play crucial roles in determining an individual's or entity's tax liability. As we delve into this discussion, we will explore the nuances between these rates, their practical implications, and how they influence financial planning and decision-making.
Taxation is an essential aspect of modern economies, serving as a primary source of revenue for governments to fund public services and infrastructure. However, the complexity of tax systems can often be a challenge for taxpayers, especially when navigating the differences between marginal and effective tax rates. Understanding these concepts is vital for effective financial management and ensuring compliance with tax laws.
Marginal Tax Rate: A Step-by-Step Understanding
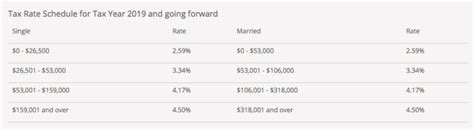
The marginal tax rate represents the tax percentage applied to an individual's or entity's taxable income, specifically the portion that falls within a particular tax bracket. It is the tax rate that applies to the next dollar earned and can vary depending on the income level and the tax system in place. For instance, consider a progressive tax system, where tax rates increase as income rises. In such a system, the marginal tax rate would be higher for higher income brackets, reflecting the progressive nature of the tax structure.
Let's illustrate this with an example. Imagine an individual named Alex, who has a taxable income of $100,000. If the tax system has three tax brackets: 10% for income up to $50,000, 20% for income between $50,001 and $100,000, and 30% for income above $100,000, Alex's marginal tax rate would be 20%. This means that the next dollar earned beyond $50,000 would be taxed at a rate of 20%, as it falls within the second tax bracket.
| Tax Bracket | Income Range | Marginal Tax Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Bracket 1 | $0 - $50,000 | 10% |
| Bracket 2 | $50,001 - $100,000 | 20% |
| Bracket 3 | $100,001 and above | 30% |
The marginal tax rate is a crucial factor in financial planning, especially for high-income earners. It influences decisions such as investing strategies, retirement planning, and the timing of income recognition. For instance, an individual with a high marginal tax rate may opt for tax-advantaged investment accounts or explore strategies to reduce their taxable income to fall into a lower tax bracket.
Effective Tax Rate: The Bigger Picture
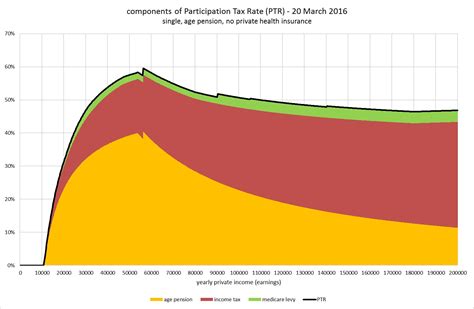
While the marginal tax rate focuses on a specific income bracket, the effective tax rate provides a broader perspective, representing the actual percentage of tax paid relative to the total income. It is calculated by dividing the total tax liability by the total income. This rate offers a more comprehensive view of an individual's or entity's tax burden and can vary significantly from the marginal tax rate.
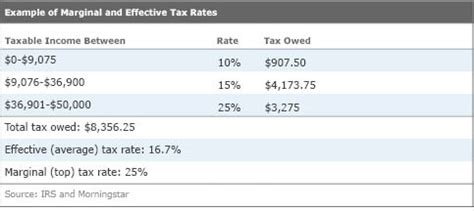
To illustrate this, let's consider another example. Imagine Sarah, who has a taxable income of $75,000. If her total tax liability for the year is $15,000, her effective tax rate would be 20% ($15,000 / $75,000). This means that, on average, she pays 20% of her income in taxes. However, her marginal tax rate might be different, depending on the tax brackets and her income distribution throughout the year.
The effective tax rate is a valuable metric for assessing the overall tax burden and can be used to compare the tax efficiency of different entities or individuals. It is often a key consideration for businesses when evaluating the financial viability of different jurisdictions for operations.
For instance, a multinational corporation might assess the effective tax rates of various countries to determine the most tax-efficient location for a new facility. This analysis would consider not only the marginal tax rates but also other factors such as tax incentives, deductions, and the overall tax structure.
Comparative Analysis: Marginal vs. Effective Tax Rates
While both marginal and effective tax rates provide valuable insights, they serve different purposes and should be considered in conjunction with one another. The marginal tax rate is a forward-looking metric, guiding financial decisions and tax planning strategies. On the other hand, the effective tax rate offers a retrospective view, allowing individuals and entities to assess their past tax liabilities and make adjustments for future planning.
For individuals, understanding the effective tax rate can help in evaluating the overall impact of tax liabilities on their financial well-being. It can highlight areas where tax efficiency can be improved, such as through strategic tax planning or exploring tax-efficient investment options. For businesses, the effective tax rate is a key performance indicator, reflecting the company's financial health and its ability to manage tax obligations effectively.
Tax Planning and Strategy
The knowledge of marginal and effective tax rates is essential for developing sound tax planning strategies. By understanding these rates, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions to optimize their tax liabilities. This may involve adjusting income levels, exploring tax-efficient investment options, or taking advantage of available tax incentives and deductions.
For instance, a business might decide to restructure its operations to take advantage of a lower effective tax rate in a different jurisdiction. Alternatively, an individual might choose to contribute to a tax-advantaged retirement account to reduce their taxable income and potentially lower their marginal tax rate.
Effective tax planning often involves a comprehensive approach, considering not only the current tax year but also future tax obligations. This may include strategies such as income splitting, deferring income, or accelerating deductions to maximize tax benefits.
The Future of Taxation: Implications and Considerations
As tax systems continue to evolve, the role of marginal and effective tax rates will remain pivotal in financial planning and decision-making. With the increasing complexity of global tax landscapes, individuals and businesses must stay informed and adaptable to navigate these changes effectively.
The ongoing debate around tax reform and the potential for a global minimum tax rate highlights the dynamic nature of taxation. Understanding how these changes may impact marginal and effective tax rates is crucial for staying ahead of the curve and ensuring compliance with evolving tax laws.
Furthermore, advancements in technology and the increasing use of data analytics are transforming the tax landscape. From automated tax filing systems to predictive analytics for tax planning, the future of taxation is increasingly digital and data-driven. Staying abreast of these developments is essential for optimizing tax strategies and ensuring efficient tax management.
In conclusion, the concepts of marginal and effective tax rates are fundamental to understanding the intricacies of taxation. By unraveling the differences between these rates and their practical implications, individuals and entities can make informed financial decisions, optimize their tax liabilities, and navigate the complex world of taxation with confidence.
How does the marginal tax rate impact investment decisions?
+The marginal tax rate can significantly influence investment decisions, especially for high-income earners. A higher marginal tax rate may encourage individuals to explore tax-advantaged investment options, such as contributing to retirement accounts or investing in tax-efficient mutual funds. Understanding your marginal tax rate can help you make informed choices to optimize your investment strategy and minimize tax liabilities.
What factors can affect the effective tax rate for businesses?
+The effective tax rate for businesses can be influenced by various factors, including the industry, location, and tax planning strategies. Businesses may utilize tax incentives, deductions, and tax-efficient structures to reduce their effective tax rate. Additionally, the choice of business entity (e.g., corporation, partnership, LLC) can impact tax liabilities and, consequently, the effective tax rate.
How can individuals lower their effective tax rate?
+Individuals can lower their effective tax rate through strategic tax planning. This may involve maximizing tax deductions and credits, contributing to tax-advantaged accounts, and exploring income-splitting options. Additionally, understanding the tax implications of different investment vehicles and retirement planning strategies can help individuals optimize their tax liabilities and, consequently, their effective tax rate.