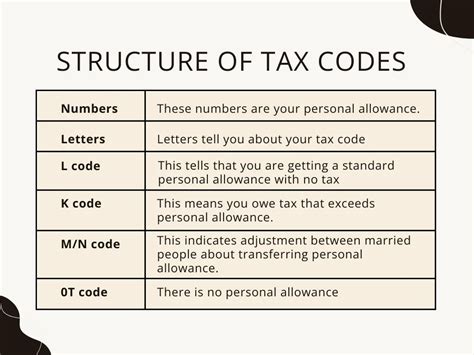
Tax Airfreight

In the ever-evolving world of logistics and international trade, understanding the intricacies of tax regulations for airfreight is paramount. This comprehensive guide delves into the complex landscape of airfreight taxes, offering a deep insight into the challenges and strategies that businesses face when navigating this critical aspect of global commerce.
The Complexity of Airfreight Taxation

Airfreight taxation is a multifaceted issue, influenced by a myriad of factors including international tax laws, import-export regulations, and the unique characteristics of the goods being transported. This complexity often presents significant challenges for businesses, especially those engaged in cross-border trade.
Key Considerations in Airfreight Taxation
When it comes to airfreight taxes, several critical factors come into play:
- International Tax Laws: These laws vary greatly from country to country, making it essential for businesses to have a comprehensive understanding of the tax regulations in both the country of origin and the destination country.
- Import Duties and Taxes: Import duties and taxes are a significant aspect of airfreight taxation. These can include customs duties, value-added taxes (VAT), and other specific levies imposed by the destination country.
- Goods Classification: The classification of goods is crucial as it determines the applicable tax rates. Different goods are subject to different tax treatments, and misclassification can lead to significant financial penalties.
- Freight Forwarders’ Role: Freight forwarders play a vital role in the airfreight process, often handling the complex task of tax compliance. However, it is crucial for businesses to ensure that their forwarders are well-versed in the latest tax regulations to avoid potential issues.
| Tax Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Customs Duties | Tariffs imposed on imported goods to protect domestic industries and raise revenue. |
| Value-Added Tax (VAT) | A consumption tax added to the cost of a product at each stage of the supply chain. |
| Excise Duties | Taxes on specific goods like alcohol, tobacco, and fuel, often used to discourage consumption or generate additional revenue. |
Case Study: Tax Challenges in International Airfreight
Consider a scenario where a European tech company, TechGadgets Ltd., ships a consignment of electronic devices to its distributor in the United States. The complexity arises when determining the applicable taxes. The shipment’s value, the type of goods, and the specific tax laws of both the EU and the US come into play. This includes understanding the US’ Harmonized Tariff Schedule for import duties and the potential application of state-specific sales taxes.
Strategies for Effective Airfreight Tax Management

Given the intricate nature of airfreight taxation, businesses must adopt strategic approaches to ensure compliance and minimize costs.
Expert Insights: Strategies for Airfreight Tax Optimization
Implementing an effective airfreight tax management strategy requires a deep understanding of the tax landscape and a proactive approach. Here are some key strategies that businesses can employ:
- Comprehensive Tax Planning: Develop a detailed tax strategy that accounts for all potential tax liabilities. This should involve a thorough analysis of the tax laws in both the exporting and importing countries, including any specific tax incentives or penalties.
- Choose the Right Freight Forwarder: Select a freight forwarder with a strong understanding of international tax laws. Ensure they provide accurate and up-to-date tax advice and can efficiently manage the tax-related aspects of the airfreight process.
- Accurate Goods Classification: Ensure that goods are correctly classified according to the Harmonized System (HS) codes. Misclassification can lead to overpayment of taxes or legal issues, so it’s crucial to get this right.
- Utilize Tax Incentives and Free Trade Agreements: Research and take advantage of any tax incentives or preferential rates offered by free trade agreements between the countries involved. These can significantly reduce the tax burden on your shipments.
- Stay Updated on Tax Law Changes: Tax laws are dynamic and often subject to change. Stay informed about any updates or amendments to ensure continued compliance and avoid potential penalties.
The Impact of Airfreight Taxation on Global Trade
Airfreight taxation is a critical factor influencing the dynamics of global trade. It can significantly impact the cost and efficiency of cross-border transactions, shaping the strategies and decisions of businesses engaged in international commerce.
Economic Implications of Airfreight Taxes
The economic impact of airfreight taxes is profound. These taxes directly influence the cost structure of international trade, often adding a substantial burden to the overall expense of doing business globally. For instance, a higher tax rate on imported goods can make a product less competitive in the market, impacting its sales and profitability.
Competitive Advantage and Tax Strategies
Businesses that effectively navigate the complex landscape of airfreight taxation can gain a significant competitive advantage. By optimizing their tax strategies, companies can reduce their tax liabilities, making their products more affordable and attractive to consumers. This, in turn, can lead to increased market share and profitability.
Future Outlook: Navigating the Evolving Tax Landscape
As the world of international trade continues to evolve, so too does the landscape of airfreight taxation. With ongoing negotiations on trade agreements and the potential for new tax policies, staying ahead of the curve is more critical than ever.
Key Trends and Predictions
Here are some key trends and predictions for the future of airfreight taxation:
- Increased Digitalization: The trend towards digital tax management platforms and online tax filing is expected to continue, offering greater efficiency and transparency in tax processes.
- Focus on Sustainability: With a growing emphasis on environmental sustainability, there may be a shift towards taxing airfreight based on its carbon footprint, encouraging the adoption of greener logistics solutions.
- Changing Trade Dynamics: As global trade patterns evolve, so will the tax landscape. Businesses will need to stay agile and adaptable to navigate these changes effectively.
Conclusion: Empowering Businesses with Knowledge

In the complex world of international trade, understanding and effectively managing airfreight taxation is crucial for businesses’ success and sustainability. By staying informed, adopting strategic tax management practices, and leveraging the latest tools and technologies, companies can navigate the tax landscape with confidence, ensuring compliance, reducing costs, and gaining a competitive edge.
FAQs
What are the main types of taxes associated with airfreight?
+The primary taxes associated with airfreight include customs duties, value-added tax (VAT), and excise duties. Customs duties are tariffs imposed on imported goods, VAT is a consumption tax, and excise duties are taxes on specific goods like alcohol and tobacco.
How can businesses ensure compliance with airfreight tax regulations?
+Businesses should invest in comprehensive tax planning, choose reputable freight forwarders with tax expertise, and stay updated on tax law changes. Additionally, accurate goods classification and utilizing tax incentives can help ensure compliance.
What is the role of free trade agreements in airfreight taxation?
+Free trade agreements can offer preferential tax rates or exemptions for goods traded between member countries. By understanding and utilizing these agreements, businesses can reduce their tax liabilities and enhance their competitive position.
How can businesses stay updated on the latest airfreight tax regulations and changes?
+Businesses can stay informed by subscribing to tax news services, following industry associations and government websites, and consulting with tax advisors or freight forwarders who specialize in international trade.



