Sales Tax Hawaii

In Hawaii, sales tax is an important aspect of the state's revenue system, contributing significantly to its overall economic landscape. The unique nature of Hawaii's sales tax system, including its rates, exemptions, and collection methods, is worth exploring to understand its impact on both local businesses and consumers.
Understanding Sales Tax in Hawaii
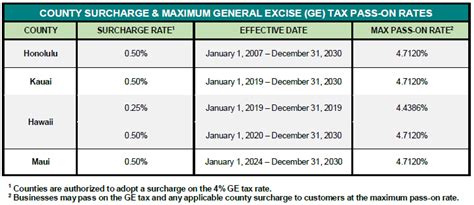
Sales tax in Hawaii is a consumption tax levied on the sale of goods and certain services. Unlike many other states, Hawaii operates a unique tax system with specific rules and rates. The state’s General Excise Tax (GET) serves as a primary source of revenue, with a base rate of 4% applicable to most transactions. This base rate, however, can be subject to additional surcharges, resulting in a composite rate that varies across the state.
The Hawaii General Excise Tax
The General Excise Tax is a broad-based tax applied to the privilege of doing business in Hawaii. It’s important to note that GET is levied on the gross income of businesses, including sales, receipts, and even compensation. This differs from a traditional sales tax, as it’s not solely applied to the end consumer.
While the base rate for GET is 4%, there are specific industries and locations in Hawaii that operate under different tax structures. For instance, the Transitory Accommodation Tax (TAT) applies to lodging rentals and carries a rate of 10.25%. This tax is often included in the room rates quoted to tourists, making it a significant contributor to the state's tourism revenue.
Furthermore, certain counties in Hawaii have the authority to impose additional surcharges on the GET. For example, the County of Hawaii (Big Island) levies a 0.5% surcharge on the GET, bringing the total tax rate to 4.5% for most transactions within the county.
| Tax Type | Rate | Description |
|---|---|---|
| General Excise Tax (GET) | 4% | Base rate applicable to most transactions. |
| Transitory Accommodation Tax (TAT) | 10.25% | Applies to lodging rentals. |
| County Surcharges | Varies (e.g., 0.5% on Big Island) | Additional charges imposed by certain counties. |
Exemptions and Special Considerations
Hawaii’s sales tax system also includes a range of exemptions and special considerations. Certain goods and services are exempt from the GET, such as:
- Prescription drugs
- Medical devices
- Residential rent
- Educational and training services
- Some agricultural products
Additionally, Hawaii has specific provisions for tourist-related purchases. The state offers a Temporary Visitor's VAT Refund Program, which allows visitors to claim a refund on the GET paid for certain goods. This program aims to make Hawaii a more attractive destination for international tourists by reducing the effective tax rate on their purchases.
The Impact of Sales Tax on Businesses and Consumers

The sales tax system in Hawaii has significant implications for both businesses and consumers. For businesses, understanding and managing sales tax obligations is crucial for financial planning and compliance. The complexity of Hawaii’s tax structure, with its various rates and exemptions, can pose challenges, especially for new businesses or those unfamiliar with the state’s unique system.
Business Implications
Businesses operating in Hawaii must navigate the intricacies of the General Excise Tax and its variations. This includes accurately calculating tax rates, maintaining proper records, and ensuring compliance with reporting requirements. Failure to do so can result in penalties and interest charges.
From a strategic perspective, businesses must consider the impact of sales tax on their pricing. While a higher tax rate can increase the final cost to the consumer, it also affects the business's profit margin. Therefore, businesses often need to strike a balance between competitive pricing and covering their costs, including the GET.
Consumer Perspective
For consumers, understanding the sales tax landscape in Hawaii is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. The state’s composite tax rates can vary significantly depending on the location and type of purchase, which can impact a consumer’s budget and perception of value.
For instance, a consumer buying groceries in Hawaii might face a lower tax rate than someone purchasing lodging or certain services. This variability can influence consumer behavior, with some individuals choosing to make larger purchases in areas with lower tax rates or timing their purchases to take advantage of tax-free events or periods.
Furthermore, the Transitory Accommodation Tax can significantly impact travelers' budgets, especially for those on extended stays. This tax is often a significant component of the total cost of lodging, making it a notable expense for tourists and a key consideration when planning a trip to Hawaii.
Sales Tax and the Hawaii Economy
Sales tax plays a vital role in the economic health of Hawaii. As a significant source of revenue for the state, it funds essential services and infrastructure projects. The unique structure of Hawaii’s sales tax system, with its GET and various surcharges, allows for a more flexible and responsive approach to revenue generation.
Revenue Generation and Allocation
The General Excise Tax is a primary driver of revenue for Hawaii’s government. The tax is applied across a broad range of transactions, ensuring a steady stream of income. This revenue is then allocated to various state and county programs, including education, healthcare, and infrastructure development.
The ability to impose additional surcharges on the GET provides Hawaii with a tool to address specific economic needs or emergencies. For instance, during times of economic downturn or natural disasters, these surcharges can be a crucial source of additional funding for recovery efforts.
Economic Impact and Consumer Behavior
The sales tax system in Hawaii also influences consumer behavior and the overall economic climate. Higher tax rates can lead to reduced spending, especially on non-essential items, which can impact businesses and potentially lead to a decrease in tax revenue. On the other hand, certain tax exemptions or refunds, like the Temporary Visitor’s VAT Refund Program, can stimulate consumer spending and attract more tourists to the state.
Additionally, the variability in tax rates across the state can lead to economic disparities. Areas with higher tax rates might see a slowdown in economic activity, while those with lower rates might experience a boost in consumer spending and business growth. This highlights the importance of a well-balanced and equitable tax system for the overall economic health of Hawaii.
How often does Hawaii review and adjust its sales tax rates?
+Hawaii’s sales tax rates are typically reviewed and adjusted on a periodic basis, often in response to economic conditions or the need for additional revenue. While the base rate of the General Excise Tax has remained at 4% for many years, additional surcharges and tax programs can be introduced or modified by the state legislature or county governments as needed.
Are there any efforts to simplify Hawaii’s sales tax system for businesses and consumers?
+Simplifying Hawaii’s sales tax system is an ongoing discussion. While the state’s unique tax structure serves specific purposes, there have been proposals to streamline the system, particularly for businesses. These proposals often aim to reduce the administrative burden on businesses while ensuring a fair and sustainable revenue system for the state.
How does Hawaii’s sales tax compare to other states in the US?
+Hawaii’s sales tax system is distinct from most other states in the US. While many states have a traditional sales tax model, Hawaii’s General Excise Tax is a broader-based tax applied to the privilege of doing business. This means that Hawaii’s tax structure is often more complex but also provides a more diverse revenue stream for the state.