Salary After Taxes California

When it comes to understanding your salary after taxes in California, there are several factors to consider. The state of California has a progressive tax system, which means that your income tax rate increases as your income rises. Additionally, various deductions and credits can impact your final take-home pay. Let's delve into the specifics and explore how these elements interplay to determine your salary after taxes in the Golden State.
Understanding California’s Income Tax System

California employs a graduated income tax structure, which is divided into several tax brackets. As of the 2023 tax year, these brackets and their corresponding tax rates are as follows:
| Income Bracket | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| $0 - $9,999 | 1% |
| $10,000 - $25,999 | 2% |
| $26,000 - $36,999 | 4% |
| $37,000 - $59,999 | 6% |
| $60,000 - $77,999 | 8% |
| $78,000 - $107,999 | 9.3% |
| $108,000 - $267,999 | 10.3% |
| $268,000 and above | 11.3% |

It's important to note that these tax rates are applied to your taxable income, which is your total income minus any deductions and credits. The state also offers various tax credits, such as the California Earned Income Tax Credit (CalEITC) and the Child and Dependent Care Credit, which can further reduce your taxable income.
Federal Income Tax and Other Deductions
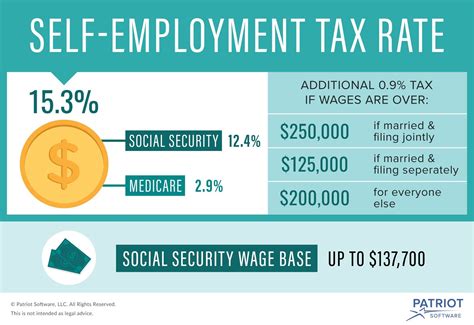
In addition to California’s income tax, your salary will also be subject to federal income tax. The federal tax system is similar to California’s, with its own set of tax brackets and rates. Moreover, your salary will be impacted by other deductions, such as Social Security and Medicare taxes, which are typically withheld from your paycheck.
Social Security tax is levied at a rate of 6.2% on earnings up to $147,000 (as of 2023), while Medicare tax is 1.45% with no income limit. These deductions, along with any federal and state tax credits you may qualify for, will influence your take-home pay.
The Impact of Local Taxes
California is a diverse state with various counties and municipalities, each with its own set of local taxes. These local taxes can include sales taxes, property taxes, and even additional income taxes. For instance, the city of San Francisco imposes a 1.5% surcharge on state income tax for residents earning over $500,000.
Therefore, your salary after taxes can vary significantly depending on your specific location within California. It's crucial to research and understand the local tax landscape to get an accurate picture of your take-home pay.
Net Salary Calculator: A Handy Tool
Given the complexity of tax calculations, utilizing a net salary calculator can be immensely helpful. These calculators take into account your gross salary, federal and state tax rates, deductions, and any applicable credits to provide an estimate of your take-home pay. Many online resources offer these calculators, often with the option to input specific details such as your location, marital status, and number of dependents.
While these calculators provide a useful estimate, it's essential to remember that they are just that - estimates. Actual tax liabilities can vary based on individual circumstances and changes in tax laws.
Tips for Maximizing Your Take-Home Pay

Understanding your salary after taxes is just the first step. To maximize your take-home pay, consider the following strategies:
- Review your tax withholdings: Ensure that the amount of tax withheld from your paycheck aligns with your expected tax liability. Adjusting your withholdings can result in a larger refund or reduce the risk of owing money at tax time.
- Explore tax credits and deductions: Familiarize yourself with the various tax credits and deductions you may qualify for. For instance, if you have dependent children, the Child Tax Credit can significantly reduce your tax burden.
- Consider retirement contributions: Contributing to a retirement plan, such as a 401(k) or IRA, can lower your taxable income and provide long-term financial benefits. Consult a financial advisor to determine the best strategy for your situation.
Future Outlook and Tax Reforms
California’s tax landscape is subject to change, and keeping abreast of potential reforms is crucial. Currently, there are discussions about potential tax reforms aimed at making the system more progressive and equitable. While the specifics are yet to be determined, these reforms could impact tax rates and brackets in the future.
Additionally, with the rise of remote work, the concept of digital nomad taxes has gained prominence. As more individuals work remotely across state lines, the allocation of tax liability becomes a complex issue. California, like many other states, is exploring ways to address this evolving challenge.
Conclusion: Your Take-Home Pay in California
Determining your salary after taxes in California involves navigating a complex web of state, federal, and local tax laws, deductions, and credits. While the process can be daunting, utilizing tools like net salary calculators and staying informed about tax reforms can help you better understand your financial situation.
Remember, your salary after taxes is just one aspect of your financial health. It's essential to consider other factors, such as cost of living, benefits, and long-term financial goals, when evaluating job opportunities and planning your financial future.
What is the average income tax rate in California for 2023?
+The average income tax rate in California for 2023 is approximately 8.85%, taking into account the state’s progressive tax structure.
Are there any cities in California with unique tax structures?
+Yes, cities like San Francisco and Los Angeles have additional local taxes, which can increase the overall tax burden for residents.
How often do California’s tax laws change?
+California’s tax laws can change annually, with new tax brackets, rates, and credits being introduced or modified. It’s essential to stay updated with these changes to accurately calculate your take-home pay.