Maine State Income Tax Rate

Maine, known for its picturesque landscapes and vibrant communities, has a robust tax system that contributes significantly to the state's fiscal health and local development. The state income tax, a crucial component of this system, varies based on several factors, including individual income levels and tax brackets. Understanding the intricacies of Maine's state income tax rate is essential for both residents and businesses operating within the state.
Understanding Maine's State Income Tax Rate
Maine's income tax structure is designed to be progressive, meaning that higher income earners are taxed at a higher rate. This approach ensures that the tax burden is distributed fairly across different income levels. The state income tax rate is applied to taxable income, which is the amount left after certain deductions and exemptions are taken into account.
The tax rate in Maine is divided into tax brackets, with each bracket representing a specific income range. As an individual's income increases, they move into higher tax brackets, resulting in a corresponding increase in the tax rate. This system ensures that those with higher incomes contribute a larger share to the state's revenue.
Tax Brackets and Rates for Individuals
The following table outlines the current tax brackets and corresponding rates for Maine's individual income tax as of the 2023 tax year:
| Tax Bracket (Taxable Income) | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| $0 - $21,950 | 5.8% |
| $21,951 - $36,583 | 6.75% |
| $36,584 - $83,166 | 7.15% |
| $83,167 and above | 7.15% |

It's important to note that these rates are subject to change annually and are influenced by various economic factors and legislative decisions. For instance, in recent years, there have been discussions about introducing additional tax brackets to accommodate higher income earners and provide a more progressive tax structure.
Taxation for Businesses and Corporations
Maine also imposes income taxes on businesses and corporations operating within the state. The tax rate for businesses varies based on the type of business entity and its taxable income. Here's a simplified breakdown of the corporate income tax rates:
| Business Entity | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| C Corporations | 8.93% |
| S Corporations | 3.5% |
| Limited Liability Companies (LLCs) | 3.5% (pass-through taxation) |
Unlike individual income tax, business income tax is not structured in brackets. Instead, the applicable rate is determined by the nature of the business and its income level. For instance, C Corporations are taxed at a flat rate of 8.93%, while S Corporations and LLCs enjoy a lower rate of 3.5% due to pass-through taxation, where the business income is taxed at the individual level rather than the corporate level.
Factors Influencing Maine's State Income Tax Rate
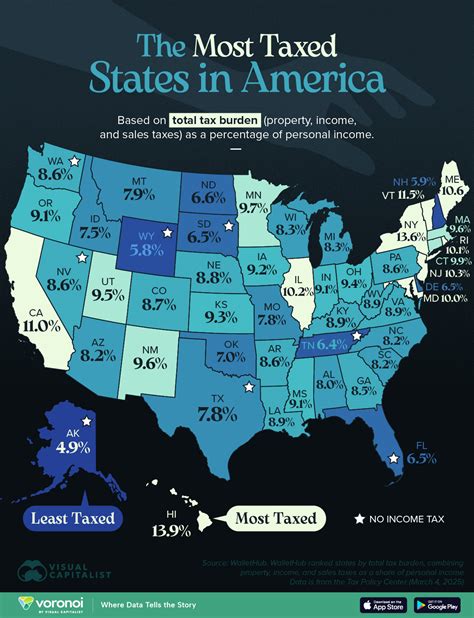
The state income tax rate in Maine is influenced by a multitude of factors, including economic conditions, political ideologies, and revenue needs. These factors collectively shape the tax landscape and can lead to changes in tax rates and brackets over time.
Economic Conditions and Tax Policy
Maine's economy, like any other, experiences cycles of growth and recession. During periods of economic prosperity, the state may consider increasing tax rates to capitalize on higher incomes and generate more revenue. Conversely, in times of economic downturn, tax rates might be reduced to stimulate economic activity and provide relief to taxpayers.
The state's tax policy is also shaped by political ideologies and party affiliations. For instance, a conservative government might prioritize lower taxes to encourage business growth and investment, while a more progressive government might advocate for higher taxes to fund social programs and infrastructure development.
Revenue Needs and Budget Constraints
The state's revenue needs play a crucial role in determining tax rates. Maine, like many other states, relies on tax revenue to fund essential services, such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure projects. When the state faces budget deficits or increased spending requirements, it may consider raising tax rates to bridge the gap.
Additionally, the state's budget constraints can influence the tax structure. For instance, if the state is facing financial constraints, it might consider introducing new tax brackets or increasing existing rates to generate additional revenue. This approach ensures that the tax burden is distributed more evenly across different income levels.
The Impact of State Income Tax on Maine's Economy
The state income tax rate has a significant impact on Maine's economy, influencing investment decisions, business growth, and the overall financial well-being of residents. Understanding these impacts is crucial for policymakers, businesses, and individuals alike.
Attracting Investment and Business Growth
A competitive tax environment is essential for attracting investment and fostering business growth. Maine's state income tax rate, when compared to other states, plays a pivotal role in shaping the state's attractiveness to businesses and investors. A lower tax rate can make Maine a more appealing destination for businesses, leading to increased economic activity and job creation.
Conversely, a higher tax rate might deter businesses from setting up operations in Maine, especially if they perceive the tax burden as excessive. Therefore, striking the right balance between generating revenue and maintaining a competitive tax environment is crucial for the state's economic development.
Resident Tax Burden and Disposable Income
The state income tax directly affects the disposable income of Maine residents. Higher tax rates can reduce the amount of income available for spending and saving, potentially impacting the local economy. On the other hand, lower tax rates can provide residents with more disposable income, leading to increased consumer spending and a boost in local businesses.
Moreover, the progressive nature of Maine's tax system ensures that higher-income earners contribute a larger share of their income to the state's revenue. This approach not only maintains fairness but also allows the state to provide essential services and support to those who need it most.
Future Implications and Tax Reform
Looking ahead, the state income tax rate in Maine is likely to undergo further adjustments to meet evolving economic and social needs. The state's commitment to fiscal responsibility and its desire to remain competitive in the regional and national market will continue to drive changes in the tax landscape.
Potential future developments might include the introduction of new tax brackets to accommodate higher incomes, the expansion of tax credits and deductions to provide relief to specific groups, or even the exploration of alternative tax structures to enhance revenue generation. These changes will be guided by the state's economic priorities and the need to balance revenue generation with taxpayer affordability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How often are Maine’s state income tax rates updated?
+
Maine’s state income tax rates are typically updated annually to align with economic conditions and legislative decisions. These updates ensure that the tax system remains responsive to the state’s fiscal needs and competitive in the regional market.
Are there any tax credits or deductions available in Maine?
+
Yes, Maine offers a range of tax credits and deductions to provide relief to taxpayers. These include credits for education expenses, property taxes, and energy-efficient home improvements, among others. Deductions are also available for certain medical expenses and retirement contributions.
How does Maine’s state income tax rate compare to other states?
+
Maine’s state income tax rate is relatively moderate compared to some other states. While it has a progressive structure, the top tax bracket is lower than in many other states. This competitive rate can make Maine an attractive destination for businesses and individuals alike.
Are there any tax incentives for specific industries in Maine?
+
Yes, Maine offers tax incentives to encourage investment and growth in specific industries. These incentives include tax credits for research and development, manufacturing, and renewable energy projects. The state also provides tax abatements for certain business expansions and improvements.