Indiana State Tax Payment

Indiana, the "Hoosier State," is known for its rich history, diverse industries, and vibrant communities. One essential aspect of living and doing business in Indiana is understanding the state's tax system, especially when it comes to tax payment obligations. Indiana's tax structure includes various taxes, such as income tax, sales and use tax, property tax, and excise taxes, each serving a specific purpose in funding public services and infrastructure.
For individuals and businesses, staying compliant with Indiana's tax laws is crucial to avoid penalties and ensure smooth financial operations. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the process of paying state taxes in Indiana, providing a step-by-step breakdown, real-world examples, and valuable insights to make tax payment a more manageable task.
Understanding Indiana’s Tax Landscape

Indiana’s tax system is designed to support the state’s economic growth and development while ensuring fairness and transparency. Here’s an overview of the key taxes and their purposes:
Income Tax
Indiana imposes an individual income tax on residents and non-residents with income sourced from the state. The tax rate varies based on income brackets, with a standard deduction and personal exemptions available to reduce taxable income. For example, as of [Tax Year 2022], the state’s income tax rates range from 3.23% to 6.45% for individuals and from 3.23% to 6.25% for estates and trusts.
Businesses, including sole proprietorships, partnerships, and corporations, are also subject to Indiana's corporate income tax. The corporate tax rate is currently 4.9% for the first $250,000 of taxable income and 6.5% for income exceeding $250,000.
Sales and Use Tax
Indiana’s sales and use tax is a consumption tax levied on the sale or lease of tangible personal property and certain services. The state sales tax rate is 7%, but local jurisdictions may add additional taxes, resulting in a combined rate that varies across the state. For instance, in Indianapolis, the total sales tax rate is 7%, while in Fort Wayne, it’s 7.5%.
Use tax is applicable when items are purchased from out-of-state vendors and used, stored, or consumed in Indiana. This ensures that all purchases, regardless of origin, contribute to the state's revenue.
Property Tax
Indiana’s property tax is a local tax levied by counties, townships, and municipalities to fund public services like schools, fire departments, and road maintenance. The tax rate varies by location and is typically expressed as a percentage of a property’s assessed value. Property tax bills are usually sent out annually, and the due date may differ based on the jurisdiction.
Excise Taxes
Indiana imposes excise taxes on specific goods and activities, such as gasoline, tobacco, alcohol, and motor vehicle purchases. These taxes are often used to fund infrastructure projects and specific programs related to the taxed items. For instance, the gasoline excise tax in Indiana is 18 cents per gallon.
The Tax Payment Process

Navigating Indiana’s tax payment process can be streamlined with the right information and tools. Here’s a detailed guide to ensure a smooth payment experience:
Registering for an Indiana Tax Account
Before making any tax payments, individuals and businesses must register with the Indiana Department of Revenue (DOR) to obtain a taxpayer account number. This unique identifier is essential for all tax-related transactions.
For individuals, the registration process involves providing personal information, such as name, address, and social security number. Businesses, on the other hand, need to furnish details like the legal name, business address, and employer identification number (EIN) during registration.
Determining Taxable Income and Liabilities
Calculating taxable income and the resulting tax liability is a crucial step. Individuals and businesses should carefully review their financial records and use the appropriate tax forms to determine their tax obligations.
For instance, individuals can use Form IT-40 to report their income and calculate their tax liability, while businesses may need to complete Form IT-20 or Form IT-6, depending on their entity type and income source.
Making Tax Payments
Indiana offers various payment methods to accommodate different preferences and needs:
- Online Payments: The Indiana DOR's website provides a secure portal for making electronic payments using a credit or debit card, electronic check, or direct bank account transfer. This method is convenient and can be done 24/7.
- Mail-In Payments: Taxpayers can mail their payment along with the appropriate tax form to the address specified by the DOR. It's crucial to include the correct taxpayer account number and ensure the payment arrives before the due date to avoid penalties.
- In-Person Payments: For those who prefer a personal touch, Indiana DOR offices accept cash, check, or money order payments during business hours. Taxpayers should verify the location and hours of their nearest office before visiting.
- Payment Plans: If taxpayers are unable to pay their full tax liability, the DOR offers installment agreements to help manage the debt. These plans require an application and may involve a fee and interest charges.
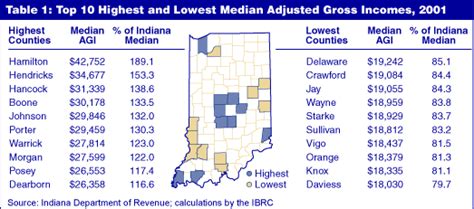
Tax Payment Due Dates
Understanding the tax payment due dates is essential to avoid late fees and penalties. Here are some key dates to keep in mind:
| Tax Type | Due Date |
|---|---|
| Individual Income Tax | April 15th of each year |
| Corporate Income Tax | April 15th for calendar year taxpayers; varies for fiscal year taxpayers |
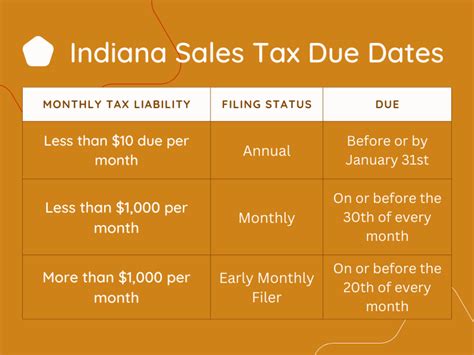
| Sales and Use Tax | Monthly, quarterly, or annually, depending on filing frequency |
| Property Tax | Varies by county; typically due in two installments |
| Excise Taxes | Varies based on the specific tax; for example, gasoline excise tax is due monthly |
Tips and Strategies for Effective Tax Management
Managing Indiana’s tax obligations can be made more efficient with the right strategies and tools:
- Stay Informed: Regularly check the Indiana DOR's website for updates, announcements, and changes to tax laws and regulations. Being aware of any modifications can help taxpayers plan and adjust their strategies accordingly.
- Use Tax Software: Tax software can simplify the process of calculating tax liabilities, preparing tax returns, and making payments. These tools often provide accurate calculations and guide users through the process step by step.
- Seek Professional Help: For complex tax situations or when in doubt, consulting a tax professional or accountant can provide valuable guidance and ensure compliance with Indiana's tax laws.
- Understand Deductions and Credits: Indiana offers various deductions and tax credits to reduce taxable income or the tax liability. Staying informed about these incentives can help taxpayers optimize their tax positions and potentially reduce their overall tax burden.
Conclusion: A Smooth Tax Payment Experience
Understanding and navigating Indiana’s tax payment process is essential for individuals and businesses operating in the state. By following the steps outlined in this guide and utilizing the available resources, taxpayers can ensure timely and accurate tax payments, contributing to the state’s economic growth and development while maintaining compliance with Indiana’s tax laws.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I estimate my Indiana income tax liability?
+
To estimate your Indiana income tax liability, you can use the Indiana Department of Revenue’s tax estimator tool available on their website. This tool provides a rough estimate based on your income and filing status. For a more accurate calculation, it’s recommended to use tax software or consult a tax professional.
What happens if I miss the tax payment deadline?
+
Missing a tax payment deadline can result in late payment penalties and interest charges. The Indiana Department of Revenue may assess a penalty of up to 5% of the unpaid tax, and interest accrues daily on the outstanding balance. It’s best to make payments on time to avoid these additional costs.
Are there any tax incentives or credits available in Indiana?
+
Yes, Indiana offers various tax incentives and credits to individuals and businesses. These include credits for research and development, film production, historic preservation, and more. It’s important to research and understand the eligibility criteria and application processes for these incentives.
How can I pay my Indiana taxes if I live out of state?
+
If you live out of state but have tax obligations in Indiana, you can still make payments online through the Indiana Department of Revenue’s website. You can also mail your payment to the appropriate address, ensuring you include your taxpayer account number and any required forms.
Can I make partial payments for my tax liability?
+
Yes, the Indiana Department of Revenue allows taxpayers to make partial payments for their tax liabilities. However, it’s important to note that interest and penalties may still accrue on the outstanding balance. Setting up a payment plan with the DOR may be a better option if you’re unable to pay the full amount.



