Income Tax Rate In Ma
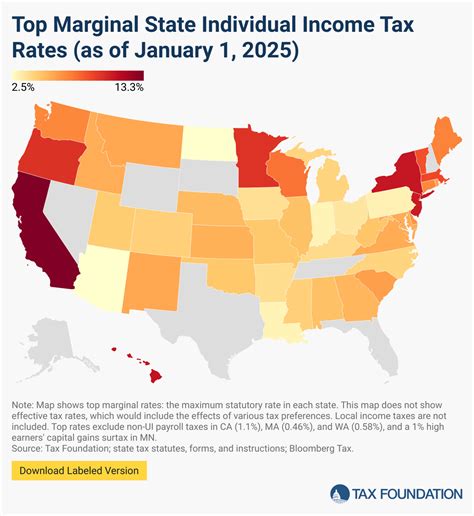
Income taxes are a significant part of financial planning and understanding the tax landscape in different regions is crucial for individuals and businesses alike. Massachusetts, often referred to as "The Bay State," has its own unique tax structure. Let's delve into the specifics of income tax rates in this historic and vibrant state.
Understanding Income Tax Rates in Massachusetts

Massachusetts operates under a progressive tax system, which means that the income tax rate increases as taxable income rises. This approach ensures that individuals with higher incomes contribute a larger share of their earnings to the state’s revenue. The income tax rates in Massachusetts are divided into brackets, and each bracket is associated with a specific tax rate.
Tax Brackets and Rates
As of my last update in January 2023, the income tax brackets and rates in Massachusetts are as follows:
| Tax Bracket | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Up to $8,850 | 5.05% |
| $8,851 - $15,300 | 5.50% |
| $15,301 - $51,750 | 5.95% |
| $51,751 - $111,400 | 6.25% |
| Over $111,400 | 5.10% |

It's important to note that these tax rates are applicable to Massachusetts residents. Non-residents who earn income in the state may be subject to different tax rules and rates, depending on their home state's reciprocity agreements with Massachusetts.
Factors Influencing Taxable Income
The taxable income for an individual in Massachusetts is determined by various factors. Firstly, any income earned within the state, including wages, salaries, commissions, and bonuses, is taxable. Additionally, income from investments, such as interest, dividends, and capital gains, is also subject to state income tax. Certain types of income, like Social Security benefits, may be partially or fully exempt from taxation, depending on the individual’s circumstances.
Taxpayers in Massachusetts can also benefit from various deductions and credits, which can reduce their taxable income and, consequently, their overall tax liability. These include deductions for medical expenses, charitable contributions, and certain education-related costs. Additionally, Massachusetts offers a variety of tax credits, such as the Earned Income Tax Credit and the Low and Moderate Income Homeowner Tax Credit, which can provide significant relief to eligible taxpayers.
Taxable Entities and Exemptions

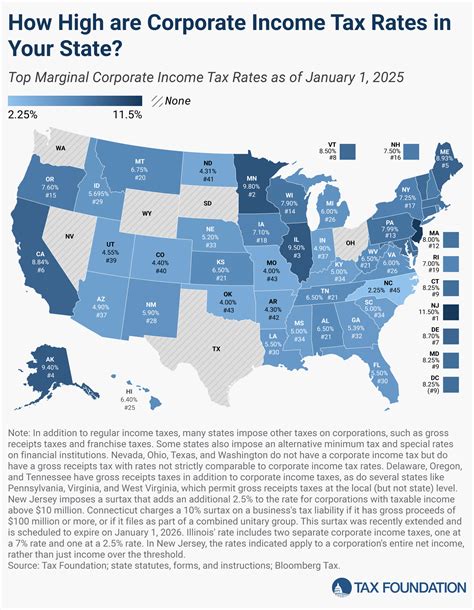
In addition to individuals, various entities, such as corporations, partnerships, and trusts, are also subject to income tax in Massachusetts. The tax rates for these entities can vary depending on their legal structure and the nature of their operations.
Corporations and Business Entities
Corporations, limited liability companies (LLCs), and other business entities are taxed on their net income in Massachusetts. The tax rate for corporations is generally 8.80%, while LLCs and other pass-through entities may be taxed at the individual income tax rates of their owners or members. It’s important for businesses to consult with tax professionals to ensure they are compliant with the state’s tax regulations.
Tax Exemptions and Nonprofits
Certain entities in Massachusetts are exempt from income tax. These include religious, charitable, educational, and certain governmental organizations. To qualify for tax-exempt status, these organizations must meet specific criteria set forth by the state and the IRS. Additionally, some types of income, such as interest earned on municipal bonds, are exempt from taxation for both individuals and entities.
Tax Filing and Payment
Massachusetts residents and entities have several options for filing their tax returns and making payments. The Department of Revenue (DOR) provides an online filing system, MassTaxConnect, which allows taxpayers to file their returns electronically and make payments using a credit card, debit card, or electronic check. Traditional paper filing and payment by check are also options.
The deadline for filing income tax returns in Massachusetts is typically April 15th, aligning with the federal tax deadline. However, the DOR may extend this deadline in certain circumstances, such as during natural disasters or other emergencies. It's crucial for taxpayers to stay informed about any changes to the filing deadline to ensure compliance and avoid penalties.
Recent Tax Reforms and Updates
Massachusetts, like many other states, periodically reviews and reforms its tax system to address budgetary needs and changing economic conditions. In recent years, the state has implemented several significant tax reforms and updates, which have impacted both individuals and businesses.
The 2018 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act
The federal Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2018 brought about several changes that impacted state tax systems, including Massachusetts’. One notable change was the limitation on state and local tax (SALT) deductions, which reduced the amount of state and local taxes that could be deducted from federal taxable income. This change had a significant impact on high-tax states like Massachusetts, as many residents faced higher federal tax bills.
In response, Massachusetts introduced legislation to address this issue. The state passed a law allowing residents to make charitable contributions to certain state-designated funds, which could then be deducted from their state taxable income. This workaround, known as the "charitable deduction bill," provided a way for residents to continue benefiting from the SALT deduction, albeit in a more limited form.
Recent Updates and Proposals
In addition to addressing the SALT deduction issue, Massachusetts has proposed and implemented other tax reforms. For instance, the state has considered and, in some cases, enacted changes to its corporate tax structure, including the introduction of a corporate minimum tax. These reforms aim to ensure a fair and stable tax system for businesses operating in the state.
Furthermore, discussions around tax relief for middle- and low-income earners have been ongoing. Proposals have included expanding the state's Earned Income Tax Credit and introducing a new Child Tax Credit. These measures aim to provide financial relief to families and individuals facing economic challenges.
Conclusion: Navigating the Massachusetts Tax Landscape
Understanding the income tax rates and regulations in Massachusetts is crucial for individuals and businesses operating in the state. The progressive tax system ensures a fair distribution of tax liability, while the availability of deductions and credits provides much-needed relief for taxpayers. Staying informed about recent tax reforms and updates is essential to ensure compliance and take advantage of any available benefits.
As the tax landscape continues to evolve, it's important for taxpayers to seek professional guidance and stay connected with reliable sources of tax information. By staying informed and proactive, individuals and businesses can navigate the complexities of Massachusetts' tax system with confidence.
How often are Massachusetts income tax rates updated?
+Massachusetts income tax rates are typically updated annually to account for inflation and budgetary needs. The Department of Revenue announces any changes to the tax rates before the start of the new fiscal year.
Are there any tax incentives for businesses in Massachusetts?
+Yes, Massachusetts offers various tax incentives to attract and support businesses. These include tax credits for research and development, film production, and certain types of job creation. Businesses should consult with tax professionals to understand the specific incentives available to them.
What is the penalty for late tax filing in Massachusetts?
+Late tax filing in Massachusetts can result in penalties and interest charges. The penalty for late filing is typically 5% of the unpaid tax for each month the return is late, up to a maximum of 25%. Additionally, interest is charged on the unpaid tax at a rate of 12% per year.
Are there any income tax reciprocity agreements with other states?
+Yes, Massachusetts has income tax reciprocity agreements with several states, including New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. These agreements allow residents who work in one state but live in another to pay income tax only to their resident state. The specific rules and rates vary by state.
How can I stay updated on tax changes in Massachusetts?
+To stay informed about tax changes in Massachusetts, it’s recommended to regularly check the official website of the Department of Revenue (DOR). The DOR provides updates, announcements, and guidance on tax-related matters. Additionally, consulting with tax professionals and staying engaged with industry publications can help keep you informed.



