Idaho Tax Return
Welcome to this in-depth exploration of the Idaho Tax Return process. As a resident of the Gem State, understanding the ins and outs of tax filing is crucial. Idaho's tax landscape is unique, offering its residents a straightforward system with a few nuances. In this article, we'll delve into the specifics, providing you with all the information you need to navigate your tax obligations with confidence.
Understanding Idaho's Tax Structure
Idaho's tax system is primarily based on an individual's income and business activities. The state imposes a flat tax rate on personal income, meaning all taxpayers, regardless of their income bracket, pay the same percentage of tax. This simplicity makes the tax system more predictable and easier to understand.
However, Idaho also has a corporate income tax system in place for businesses operating within the state. This tax is levied on the net income of corporations, S corporations, and limited liability companies (LLCs) doing business in Idaho. Additionally, the state imposes various sales and use taxes, property taxes, and excise taxes on specific goods and services.
Key Tax Rates and Thresholds
Idaho's personal income tax rate is currently set at 6.925%, which applies to all taxable income. This rate is relatively low compared to many other states, making Idaho an attractive location for businesses and individuals alike. The state does not differentiate tax rates based on income brackets, which means the tax burden remains consistent across different income levels.
For businesses, the corporate income tax rate stands at 6.925% as well. This rate is applied to the net income of corporations, including those that are S corporations and LLCs. It's important to note that Idaho offers tax incentives for certain business activities, which can significantly reduce the tax burden for eligible entities.
In terms of sales tax, Idaho has a base rate of 6%, which is applied to most goods and some services. However, the state also allows local governments to impose additional sales taxes, resulting in varying effective rates across different regions. These local sales taxes can add up to an additional 2% to 5% of the purchase price, so it's crucial to be aware of the specific rates in your area.
| Tax Type | Rate |
|---|---|
| Personal Income Tax | 6.925% |
| Corporate Income Tax | 6.925% |
| Base Sales Tax | 6% |
| Local Sales Tax (Varies) | 2% - 5% |

Filing Your Idaho Tax Return

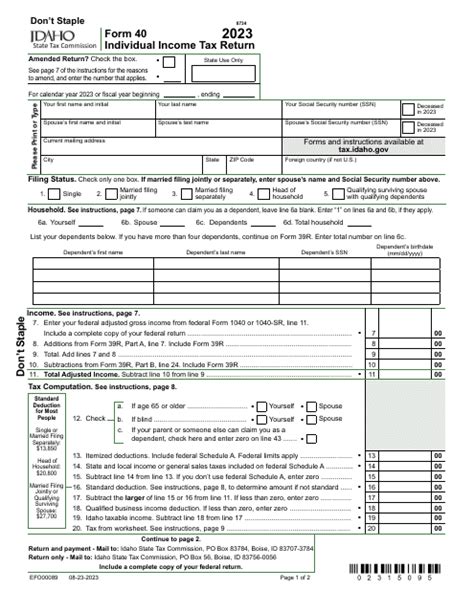
Filing your Idaho tax return is a straightforward process, thanks to the state's user-friendly tax system. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you through the process.
Step 1: Determine Your Tax Liability
Start by calculating your tax liability for the year. This involves adding up all your taxable income sources, such as wages, self-employment income, interest, and dividends. Then, apply the 6.925% tax rate to this total to determine your tax liability.
For businesses, the process is similar. Calculate your net income for the year and apply the 6.925% corporate tax rate. Remember to account for any tax incentives or credits you may be eligible for.
Step 2: Gather Necessary Documents
Collect all the necessary documents to support your tax return. This includes W-2 forms for wage earners, 1099 forms for self-employment income, and any other income-related documents. If you have business income, you'll need financial statements and records to support your calculations.
Step 3: Choose Your Filing Method
Idaho offers several filing methods to suit different preferences and needs. You can choose to file your tax return electronically through the Idaho Tax Commission's online portal or use paper forms if you prefer a more traditional approach.
Step 4: Prepare and Submit Your Return
If you're filing electronically, follow the instructions on the Idaho Tax Commission's website to complete and submit your return. Ensure you have all the required information and documents ready before starting the process.
For paper filers, download and print the appropriate tax forms from the Idaho Tax Commission's website. Fill out the forms carefully, ensuring all information is accurate and complete. Then, mail your completed return to the address specified on the forms.
Step 5: Payment and Refunds
If you owe taxes, you can pay online through the Idaho Tax Commission's website or by mailing a check along with your return. Ensure you include the correct payment amount and any necessary payment vouchers.
If you're due a refund, the Idaho Tax Commission will process your return and issue your refund via direct deposit or check, depending on your preference.
Tax Deadlines and Extensions
Understanding the tax deadlines is crucial to avoid penalties and interest charges. Here's a breakdown of the key deadlines for Idaho tax returns.
Personal Income Tax Deadlines
The general deadline for filing your Idaho personal income tax return is April 15th of the year following the tax year. For example, for the tax year 2023, the deadline would be April 15, 2024.
If you're unable to meet this deadline, you can request an automatic six-month extension by filing Form 40EXT. However, it's important to note that an extension only extends the filing deadline, not the payment deadline. If you owe taxes, you must pay them by the original deadline to avoid penalties and interest.
Corporate and Business Tax Deadlines
For corporate and business tax returns, the filing deadline is typically the 15th day of the third month following the close of the tax year. For example, for a corporation with a tax year ending on December 31, the deadline would be March 15.
Similar to personal income tax returns, corporations and businesses can request an extension by filing the appropriate forms. However, it's crucial to remember that extensions only extend the filing deadline and not the payment deadline.
Common Tax Deductions and Credits in Idaho
Idaho offers a range of tax deductions and credits to help reduce your tax liability. Understanding these can be beneficial when preparing your tax return.
Standard Deduction
Idaho allows taxpayers to claim a standard deduction, which reduces their taxable income. The standard deduction amount varies based on your filing status. For the 2023 tax year, the standard deduction amounts are:
- Single: $2,400
- Married Filing Jointly: $4,800
- Head of Household: $3,600
Itemized Deductions
In addition to the standard deduction, Idaho taxpayers can also claim itemized deductions. This includes deductions for medical expenses, charitable contributions, state and local taxes, and mortgage interest. To claim itemized deductions, your total deductions must exceed the standard deduction amount for your filing status.
Tax Credits
Idaho offers several tax credits to eligible taxpayers. These include:
- Earned Income Tax Credit: A refundable credit for low- to moderate-income taxpayers.
- Child and Dependent Care Credit: A credit for expenses incurred for child or dependent care.
- Education Tax Credits: Credits for eligible educational expenses, such as tuition and fees.
- Research and Development Credit: A credit for businesses engaged in research and development activities.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I file my Idaho tax return electronically?
+Yes, Idaho offers electronic filing through its online portal. This method is secure, convenient, and often faster than traditional paper filing. You can access the online filing system on the Idaho Tax Commission's website.
Are there any tax incentives for businesses in Idaho?
+Yes, Idaho provides various tax incentives for businesses. These include tax credits for research and development, job creation, and investment in certain industries. The Idaho Economic Development Association can provide more information on these incentives.
Can I file an amended tax return if I made a mistake?
+Absolutely. If you discover an error on your tax return, you can file an amended return to correct it. In Idaho, you use Form 40X to amend your personal income tax return. Ensure you have all the necessary documentation to support your amendments.
What happens if I miss the tax filing deadline?
+If you miss the tax filing deadline, you should file your return as soon as possible to minimize penalties and interest. Idaho imposes penalties for late filing and late payment. However, the amount of the penalty can be reduced if you can demonstrate reasonable cause for the delay.
Where can I find more information on Idaho's tax laws and regulations?
+The Idaho Tax Commission's website is a comprehensive resource for all things related to Idaho's tax system. You can find detailed information on tax rates, deadlines, forms, and specific tax topics. Additionally, you can contact the Tax Commission directly for further assistance.
Filing your Idaho tax return doesn’t have to be daunting. With a basic understanding of the tax system, the right resources, and a step-by-step approach, you can ensure a smooth and efficient filing process. Remember, staying informed and seeking professional advice when needed can help you navigate the complexities of tax filing and make the most of the available deductions and credits.



