Georgia State Income Tax Rate 2025
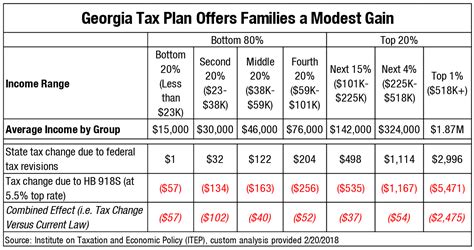
As of 2023, Georgia's state income tax structure is a progressive system, meaning the tax rate increases as income levels rise. This system ensures that individuals with higher incomes contribute a larger share of their earnings towards the state's revenue. Understanding the state income tax rate is crucial for residents and businesses alike, as it directly impacts their financial planning and budgeting.
The Progressive Nature of Georgia’s Income Tax

Georgia’s income tax brackets for the tax year 2023 illustrate the progressive nature of its tax system. These brackets determine the applicable tax rate based on an individual’s taxable income.
| Tax Bracket | Tax Rate | Taxable Income Range |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1% | $0 - $1,000 |
| 2 | 2% | $1,001 - $2,000 |
| 3 | 3% | $2,001 - $3,000 |
| ... | ... | ... |
| 6 | 5.75% | $7,001 and above |
For the year 2025, these tax brackets are subject to adjustments to keep pace with inflation and changing economic conditions. The state typically announces any changes in the tax rates for the upcoming year by the end of the current tax season, offering taxpayers sufficient time to adjust their financial strategies.
Factors Influencing Tax Rate Adjustments

The determination of tax rates for the upcoming year is a complex process that considers various factors. These include the state’s economic performance, budget requirements, and the need to maintain a competitive tax environment relative to other states.
Economic factors such as inflation, which erodes the purchasing power of money, often necessitate adjustments to the tax brackets. If the taxable income ranges remain static, more taxpayers could find themselves in higher tax brackets due to increased costs of living, despite their real income remaining relatively unchanged.
Additionally, the state's budgetary needs play a crucial role. If the state requires additional revenue for public services, infrastructure development, or debt servicing, it may consider raising tax rates or widening the taxable income ranges to capture more revenue from higher-income earners.
Potential Scenarios for the 2025 Tax Rates
While it is challenging to predict exact tax rates for 2025 at this juncture, we can anticipate several possible scenarios based on historical trends and current economic indicators.
Scenario 1: Inflation-Adjusted Rates
In a typical year, the tax brackets are adjusted to account for inflation. This ensures that taxpayers are not inadvertently pushed into higher tax brackets due to rising costs of living. The Consumer Price Index (CPI), a measure of the average change in prices over time, is often used as a reference for these adjustments.
Scenario 2: Tax Reform and Structural Changes
Georgia’s legislature could also implement more significant changes to the tax structure. This could involve broadening the tax base, introducing new tax brackets, or altering the tax rates to encourage economic growth or alleviate the tax burden on specific income groups.
For instance, the state might consider lowering tax rates for lower- and middle-income earners to stimulate consumer spending, which could lead to economic growth. Conversely, it might opt to raise tax rates for higher-income earners to address budget deficits or fund specific public initiatives.
Scenario 3: Impact of Economic Conditions
The economic climate in 2025 will also significantly influence tax rate decisions. If the state experiences robust economic growth, it may have less need to increase tax rates. Conversely, a downturn could lead to considerations for tax hikes to boost revenue.
Preparing for the 2025 Tax Season
While the specific tax rates for 2025 remain uncertain, individuals and businesses can take proactive steps to prepare for the upcoming tax season.
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of any announcements or proposals related to tax changes. This information is often available on the official websites of the Georgia Department of Revenue or through local news outlets.
- Financial Planning: Consider consulting a financial advisor to ensure your financial strategies are aligned with the potential tax rate scenarios. This could involve adjustments to savings plans, investment strategies, or even business operational costs.
- Review Past Returns: Analyze your tax returns from previous years to identify areas where you can optimize deductions, credits, or other tax-saving opportunities.
- Consider Tax-Efficient Investments: Explore investment options that offer tax benefits, such as retirement accounts or tax-exempt municipal bonds.
Conclusion: A Forward-Looking Perspective

As we navigate the uncertainties of future tax rates, it’s essential to maintain a forward-looking perspective. While we cannot predict the exact tax landscape for 2025, staying informed and adaptable is key. By understanding the factors that influence tax rates and being proactive in our financial planning, we can ensure we are prepared for whatever the future holds.
Stay tuned for official announcements from the state regarding the 2025 tax rates, and continue to explore strategies to optimize your financial position, regardless of the tax environment.
When will the 2025 tax rates be announced?
+
The specific timeline for announcing the 2025 tax rates is not set in stone, but typically, the state provides updates on tax rates during the preceding tax season. It’s best to keep an eye on official announcements from the Georgia Department of Revenue or consult tax professionals for the most up-to-date information.
How do I prepare for potential tax rate changes?
+
To prepare for potential tax rate changes, consider these steps: stay informed about proposed tax reforms, adjust your financial plans and savings strategies accordingly, and explore tax-efficient investment options. Regularly reviewing your tax returns can also help identify areas for optimization.
What factors influence tax rate adjustments in Georgia?
+
Tax rate adjustments in Georgia are influenced by various factors, including economic performance, budget requirements, and the need to maintain a competitive tax environment. The state may adjust tax rates to account for inflation, encourage economic growth, or address budget deficits.



