Ein Vs Tax Id

Understanding the differences between an EIN and a Tax ID is crucial for businesses, especially when it comes to navigating the complex world of tax obligations and legal requirements. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the nuances of these identifiers, their purposes, and how they impact various aspects of business operations.
EIN: The Employer Identification Number

The Employer Identification Number (EIN), also known as a Federal Employer Identification Number (FEIN) or simply a Federal Tax ID Number, is a unique nine-digit identifier assigned to businesses by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) in the United States. It serves as a vital tool for the IRS to track and manage tax-related activities and is an essential component of the US tax system.
Purpose of an EIN
The primary purpose of an EIN is to identify a business entity for tax purposes. It is required for various transactions and filings, ensuring that the IRS can effectively monitor and regulate business activities. Here are some key reasons why businesses need an EIN:
- Employment Taxes: If a business has employees, an EIN is necessary to report and pay employment taxes, such as Social Security and Medicare taxes, federal income tax withholding, and federal unemployment (FUTA) tax.
- Business Tax Returns: An EIN is required when filing business tax returns, including partnerships, corporations, and certain trusts and estates.
- Opening Business Bank Accounts: Many financial institutions require an EIN to open a business bank account, as it helps verify the legitimacy of the business and facilitates easier tracking of financial transactions.
- Applying for Business Licenses and Permits: In some cases, an EIN may be required when applying for specific business licenses or permits, as it serves as a unique identifier for the business.
- Establishing Business Credit: An EIN is often used by credit reporting agencies to create and maintain a business credit report, which can impact a company's ability to secure loans and lines of credit.
How to Obtain an EIN
Obtaining an EIN is a straightforward process, typically done online through the IRS website. The IRS offers an online EIN application, which allows businesses to receive their EIN immediately upon submission. Alternatively, businesses can also apply by fax or mail, but these methods may take longer to process.
EIN Structure and Format
EINs follow a specific format, consisting of nine digits arranged in two groups: the first two digits indicate the assigning office, while the last seven digits are the business’s unique identifier. The structure can vary based on the business type, with some common examples including:
| Business Type | EIN Structure |
|---|---|
| Corporations | XX-XXXXXXX |
| Partnerships | XX-XXXXXXX |
| Limited Liability Companies (LLCs) | XX-XXXXXXX |
| Sole Proprietorships | XX-XXXXXXX |
Using an EIN
Once a business obtains its EIN, it becomes a critical identifier for various business operations. Here are some common scenarios where an EIN is used:
- Tax Forms and Filings: EINs are required on various tax forms, including Form 941 (Employer's Quarterly Federal Tax Return), Form 940 (Employer's Annual Federal Unemployment (FUTA) Tax Return), and Form 1099 (Miscellaneous Income) for independent contractors.
- Payroll and Employee Benefits: EINs are used for payroll processing, employee benefit plans, and reporting employee compensation to the IRS.
- Business Licenses and Permits: As mentioned earlier, an EIN may be required when applying for certain business licenses or permits.
- Business Credit and Loans: Lenders and credit reporting agencies often request an EIN to verify the legitimacy of a business and assess its creditworthiness.
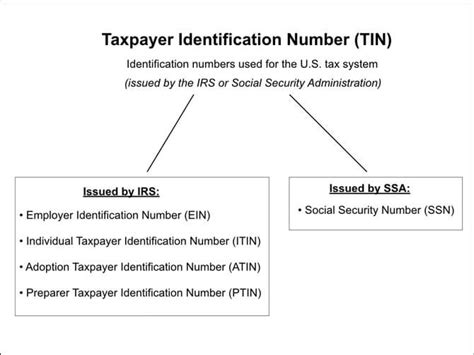
Tax ID: A Broader Term

The term “Tax ID” is often used interchangeably with “EIN” but can also refer to other types of tax identification numbers. While the EIN is specific to businesses, there are other Tax IDs used by individuals and entities for various tax purposes.
Types of Tax IDs
Here are some common types of Tax IDs:
- Social Security Number (SSN): A nine-digit number issued to individuals by the Social Security Administration. It is used for personal identification and tax reporting purposes.
- Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN): A processing code issued by the IRS to individuals who are required to have a US taxpayer identification number but are not eligible for an SSN. It is often used by foreign nationals and their dependents living in the US.
- Prepared Settlement Code (PSC): A unique identifier assigned to individuals who have received a court-ordered settlement or judgment and need to report the income to the IRS.
- Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN): A broader term that encompasses various types of tax identification numbers, including the SSN, EIN, ITIN, and PSC. It is used to identify taxpayers for tax reporting and compliance purposes.
When to Use a Tax ID
The use of a Tax ID depends on the specific circumstances and requirements. For individuals, a Tax ID is primarily used for personal tax filings and reporting income. For businesses, the EIN is the primary Tax ID, as discussed earlier.
Obtaining a Tax ID
The process of obtaining a Tax ID varies depending on the type. For an SSN, individuals typically apply through the Social Security Administration either online, by mail, or in person at a local SSA office. For an ITIN, the IRS has a specific application process, often requiring the completion of Form W-7 (Application for IRS Individual Taxpayer Identification Number) and providing supporting documentation.
Differences Between EIN and Tax ID
While the terms “EIN” and “Tax ID” are often used synonymously, there are distinct differences between them. Here’s a breakdown of the key differences:
| Aspect | EIN | Tax ID |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Business Identification and Tax Reporting | Individual and Entity Identification and Tax Reporting |
| Issuing Authority | Internal Revenue Service (IRS) | Internal Revenue Service (IRS) and Social Security Administration (SSA) |
| Format | Nine-digit number, XX-XXXXXXX | Varies based on type: SSN (nine digits), ITIN (nine digits with a suffix), PSC (four digits), TIN (various formats) |
| Applicability | Businesses, including corporations, partnerships, LLCs, and sole proprietorships | Individuals, foreign nationals, court-ordered settlements, and various entities |
EIN and Tax ID: A Comprehensive Overview
Understanding the distinctions between an EIN and a Tax ID is crucial for businesses and individuals alike. While an EIN is specific to businesses and serves as a critical identifier for tax and legal purposes, a Tax ID encompasses a broader range of identifiers used by individuals and entities for tax reporting and compliance.
By recognizing the unique roles and applications of these identifiers, businesses can navigate the complex world of tax obligations and legal requirements with confidence. Whether it's filing taxes, opening a business bank account, or applying for licenses, the EIN and Tax ID play integral roles in ensuring compliance and facilitating smooth business operations.
Can I use my Social Security Number (SSN) as my EIN for my business?
+No, a Social Security Number is an individual identifier and should not be used as an EIN for a business. An EIN is specifically assigned to businesses by the IRS and is required for various business-related transactions and filings.
Do I need an EIN if I’m a sole proprietor with no employees?
+While it’s not mandatory for sole proprietors to have an EIN, obtaining one can simplify tax reporting and provide certain benefits. For example, it allows you to open a business bank account, apply for business loans, and establish business credit.
Can I apply for an EIN if my business is not yet operational?
+Yes, you can apply for an EIN even if your business is in the planning stages or not yet operational. The EIN is a prerequisite for many business activities and can be obtained well in advance of your business’s official launch.
What happens if I lose my EIN or Tax ID information?
+If you lose your EIN or Tax ID information, you can retrieve it by contacting the relevant issuing authority. For an EIN, you can contact the IRS, and for a Social Security Number or Individual Taxpayer Identification Number, you can reach out to the Social Security Administration or the IRS, respectively.
Are there any fees associated with obtaining an EIN or Tax ID?
+No, there are no fees for obtaining an EIN or most types of Tax IDs. The IRS and Social Security Administration provide these identifiers free of charge. However, certain specialized Tax IDs, such as Employer Identification Numbers for certain trusts, may require a fee.



