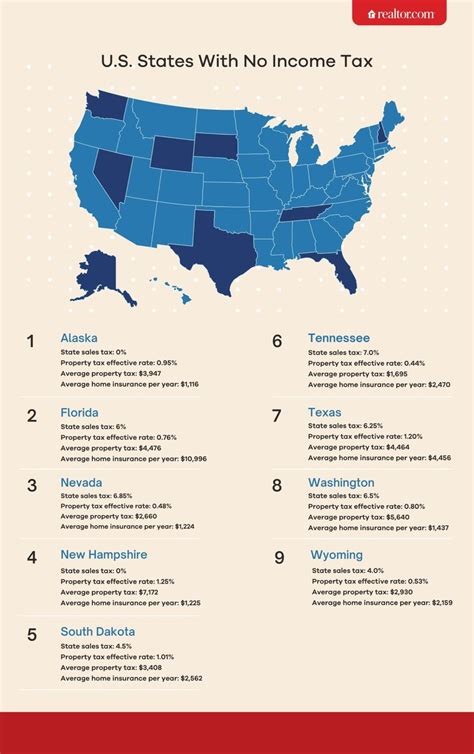
Does Alaska Have State Income Tax

When it comes to tax systems, each state in the United States has its own unique set of rules and regulations. Alaska, the largest state in the US by area, boasts a diverse economy and a distinct tax landscape. Let's delve into the specifics of Alaska's tax system and explore whether the state imposes an income tax on its residents.
The Alaskan Tax System: An Overview

Alaska’s tax system stands out as one of the most intriguing and least common across the nation. Unlike many other states, Alaska has opted for a tax structure that heavily relies on revenue streams other than personal income tax. This unique approach has garnered attention and curiosity from tax experts and individuals alike.
The state's decision to forego personal income tax is a strategic move that aims to encourage economic growth and attract businesses and individuals. By doing so, Alaska has created a tax environment that is often viewed as business-friendly and attractive to investors.
Revenue Sources in Alaska: Beyond Income Tax

So, if Alaska doesn’t collect income tax from its residents, where does the state derive its revenue? The answer lies in a combination of diverse tax sources and unique natural resources.
Resource-Based Revenue
One of the primary revenue streams for Alaska is its abundant natural resources. The state is home to vast oil and gas reserves, which contribute significantly to its overall income. The Alaska Permanent Fund, a state-run investment fund, receives a portion of the revenue generated from oil and gas production, providing a stable and substantial income source for the state.
Additionally, Alaska benefits from its vast mineral resources, including gold, silver, and other precious metals. The mining industry plays a crucial role in the state's economy, generating revenue through taxes and royalties.
Other Tax Sources
Apart from resource-based revenue, Alaska relies on various other tax streams to fund its operations and provide services to its residents. Here’s a breakdown of some key tax sources:
- Corporate Income Tax: Alaska does impose an income tax on corporations doing business within the state. This tax contributes to the state's revenue, although the rates are relatively low compared to other states.
- Sales and Use Tax: While Alaska does not have a state-wide sales tax, many municipalities and boroughs within the state have implemented their own sales and use taxes. These taxes vary across different regions, with rates ranging from 1% to 7.5%.
- Property Tax: Property taxes are a significant source of revenue for Alaska. The state's property tax system is complex, with assessments based on the value of the property and varying tax rates across different municipalities.
- Severance Tax: Alaska levies a severance tax on the extraction of natural resources, such as oil, gas, and minerals. This tax is designed to capture a portion of the profits generated from these valuable resources.
- Hunting and Fishing Licenses: Alaska's vast wilderness and abundant wildlife attract hunters and anglers from across the country. The state generates revenue by charging fees for hunting and fishing licenses, as well as through the sale of tags and permits.
The Impact on Residents and Businesses
Alaska’s decision to abstain from personal income tax has both advantages and disadvantages for its residents and businesses.
Advantages
For individuals, the absence of personal income tax means more disposable income and the potential for higher take-home pay. This can be particularly beneficial for those with higher earnings, as they would typically pay a significant portion of their income in taxes in other states.
Businesses also stand to gain from Alaska's tax system. The lack of personal income tax can make the state an attractive destination for companies looking to reduce their tax liabilities. Additionally, the state's resource-based economy offers unique opportunities for industries related to oil, gas, and mining.
Disadvantages
However, there are also potential drawbacks to Alaska’s tax structure. The reliance on a limited number of revenue streams, particularly natural resources, can make the state vulnerable to economic downturns and fluctuations in commodity prices. Additionally, the absence of personal income tax may lead to reduced funding for public services and infrastructure, potentially impacting the quality of life for residents.
Performance Analysis and Future Implications
Analyzing the performance of Alaska’s tax system is essential to understanding its long-term sustainability and impact on the state’s economy. While the absence of personal income tax has its advantages, it is crucial to consider the potential risks and challenges.
Economic Growth and Stability
Alaska’s economy has experienced significant growth and development over the years, largely driven by its natural resource industries. The state’s tax system has played a role in attracting businesses and investors, contributing to job creation and economic prosperity. However, the state’s reliance on a few key industries can pose risks, as economic downturns or changes in global markets can have a significant impact.
To mitigate these risks, Alaska has implemented various strategies to diversify its economy. Efforts have been made to promote tourism, technology, and small business development, reducing the state's dependence on a single industry. Additionally, the Alaska Permanent Fund, which receives a portion of the state's oil revenue, provides a stable source of income and acts as a financial buffer during economic downturns.
Public Services and Infrastructure
The absence of personal income tax has led to a reliance on other revenue sources to fund public services and infrastructure. While Alaska has made significant investments in these areas, there are ongoing debates about the adequacy of funding and the potential impact on the quality of life for residents.
To address these concerns, Alaska has implemented various initiatives to improve efficiency and maximize the impact of its revenue streams. For example, the state has explored innovative financing options, such as public-private partnerships, to fund large-scale infrastructure projects. Additionally, the state has focused on developing its tourism industry, which can generate revenue through visitor spending and contribute to the overall economic growth of the state.
Comparative Analysis with Other States
When compared to other states, Alaska’s tax system stands out as unique and often debated. While the absence of personal income tax can be seen as a competitive advantage, it also sets the state apart from the majority of states that rely heavily on this tax stream.
States with a broader tax base, including personal income tax, often have more stable and diversified revenue streams. This can provide a level of economic stability and the ability to invest in a wider range of public services and infrastructure. However, Alaska's tax system, with its focus on natural resources and limited tax burden on residents, has its own set of advantages and challenges.
Conclusion: Alaska’s Tax Landscape
In conclusion, Alaska’s decision to forego personal income tax has shaped a unique tax landscape within the state. The absence of this tax stream has both positive and negative implications for residents and businesses, impacting economic growth, public services, and the overall quality of life.
While Alaska's tax system offers advantages such as a reduced tax burden and a business-friendly environment, it also presents challenges in terms of economic stability and the funding of essential public services. The state's ongoing efforts to diversify its economy and maximize its revenue streams are crucial for long-term sustainability and the well-being of its residents.
As the state continues to navigate its tax landscape, the impact of its decisions will be closely monitored, providing valuable insights into the complex relationship between tax systems and economic development.
Does Alaska have a state sales tax?
+
Alaska does not have a state-wide sales tax. However, many municipalities and boroughs within the state have implemented their own sales and use taxes, with rates varying across different regions.
How does Alaska fund its public services without personal income tax?
+
Alaska relies on a combination of tax sources, including corporate income tax, property tax, severance tax, and revenue from natural resources like oil and gas. Additionally, the state has made efforts to diversify its economy and maximize its revenue streams.
What are the potential risks of Alaska’s tax system?
+
The state’s reliance on a limited number of revenue streams, particularly natural resources, can make it vulnerable to economic downturns and fluctuations in commodity prices. Additionally, the absence of personal income tax may lead to reduced funding for public services and infrastructure.
How does Alaska compare to other states in terms of tax systems?
+
Alaska’s tax system is unique compared to most states, as it does not rely on personal income tax. While this offers certain advantages, it also sets the state apart from the majority of states that have a broader tax base and more stable revenue streams.