Dallas Tax Rate
The tax landscape in Dallas, Texas, is a complex and dynamic system that plays a significant role in the city's economic framework. Understanding the Dallas tax rate is essential for both residents and businesses, as it directly impacts financial planning and decision-making. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to the various taxes applicable in Dallas, offering insights into the tax structure, rates, and their implications.
Navigating the Dallas Tax Landscape

Dallas, a bustling metropolis in the heart of Texas, boasts a vibrant economy and a diverse tax structure. The city’s tax system is multi-faceted, encompassing a range of taxes that contribute to its overall revenue generation. From property taxes to sales taxes, each component serves a specific purpose, shaping the financial framework of the city.
The Dallas tax rate is a crucial aspect for individuals and businesses alike, as it influences financial strategies and planning. Whether it's a homeowner calculating their annual property tax bill or a business owner assessing the cost of doing business in Dallas, understanding the tax landscape is essential.
Property Taxes in Dallas
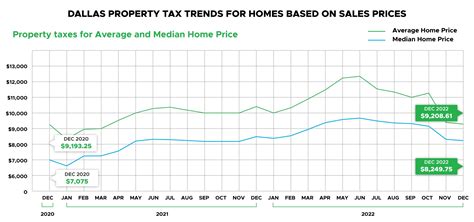
One of the most significant tax contributions in Dallas comes from property taxes. The city’s property tax system is a key revenue generator, with rates varying based on the location and type of property. Dallas County, which includes the city of Dallas, is renowned for its diverse property tax landscape, with rates influenced by factors such as school districts, municipalities, and special districts.
| Taxing Entity | Tax Rate (Per $100 Valuation) |
|---|---|
| Dallas County | 0.3718 |
| Dallas ISD | 1.4715 |
| City of Dallas | 0.6327 |
| Dallas Community College District | 0.1494 |
| Dallas County Hospital District | 0.0833 |
| Dallas County Community College District | 0.0883 |
The property tax rate in Dallas is calculated by multiplying the property's appraised value by the corresponding tax rate for each taxing entity. For instance, a homeowner with a property valued at $200,000 would pay approximately $4,944.20 in taxes, assuming a 20% homestead exemption.
The Dallas Central Appraisal District (DCAD) plays a pivotal role in this process, determining property values annually. Property owners have the right to appeal their appraised values if they believe they are inaccurate. The DCAD's appraisal process is a critical aspect of the property tax system, ensuring fairness and transparency.
In addition to the standard property tax, Dallas also imposes a local option homestead exemption for qualifying homeowners. This exemption, typically ranging from 20% to 25%, reduces the taxable value of a property, providing relief to homeowners. The availability and percentage of this exemption vary by school district, with some districts offering more generous exemptions.
Sales and Use Taxes
Dallas, like the rest of Texas, is known for its lack of state income tax, making sales and use taxes a significant revenue source for the city. The sales tax in Dallas is levied on most retail sales, rentals, and leases of tangible personal property, as well as certain services.
| Taxing Entity | Sales Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| State of Texas | 6.25% |
| Dallas County | 0.50% |
| City of Dallas | 1.00% |
| Total Combined Rate | 8.25% |
The combined sales tax rate in Dallas is 8.25%, which includes the state, county, and city sales taxes. This rate is applicable to most goods and services, with certain exceptions and exemptions, such as groceries, prescription drugs, and some services.
In addition to sales taxes, Dallas also imposes a use tax on tangible personal property purchased outside the city and brought into Dallas for use. The use tax rate mirrors the sales tax rate, ensuring that transactions occurring outside the city's jurisdiction are still subject to taxation.
Franchise Taxes and Business Levies
For businesses operating in Dallas, understanding the franchise tax is crucial. The franchise tax, also known as the margin tax, is a privilege tax imposed on certain entities doing business in Texas. The tax is calculated based on a business’s taxable margin, which is generally derived from its total revenue.
The franchise tax rate in Texas is currently set at 0.375% for most entities. However, certain entities, such as professional service businesses, are subject to a lower rate of 0.75%. The taxable margin is determined by subtracting various deductions and allowances from the entity's total revenue.
In addition to the franchise tax, Dallas imposes various business taxes and fees. These include the Business Personal Property Tax, which is levied on tangible personal property used in business operations, and the City of Dallas Occupational License Tax, which is a flat fee based on the business's gross receipts.
Other Taxes and Fees
Dallas, like many cities, has a range of other taxes and fees that contribute to its revenue stream. These include:
- Hotel Occupancy Tax: A tax levied on guests occupying hotel rooms, typically ranging from 6% to 17%.
- Mixed Beverage Tax: A tax on the sale of mixed alcoholic beverages, with rates varying based on the location.
- Motor Vehicle Rental Tax: A tax on the rental of motor vehicles, with rates typically around 10%.
- Local Sales Tax: Dallas County and some municipalities impose additional local sales taxes, increasing the overall sales tax rate.
Implications and Financial Planning

The Dallas tax rate has significant implications for both individuals and businesses. For homeowners, understanding the property tax system and applying for exemptions can lead to substantial savings. Businesses, on the other hand, must navigate a complex web of taxes and fees, ensuring compliance with all applicable regulations.
Financial planning in Dallas requires a comprehensive understanding of the city's tax landscape. Whether it's budgeting for annual property taxes, factoring in sales tax rates for pricing strategies, or navigating the franchise tax, being well-informed is crucial. Professionals in the financial industry, such as accountants and tax advisors, play a vital role in helping individuals and businesses navigate the complexities of the Dallas tax system.
The tax rates in Dallas are subject to change, and staying updated on any legislative or regulatory shifts is essential. The city's tax structure is a dynamic and evolving system, and keeping abreast of these changes ensures that financial plans remain aligned with the latest tax regulations.
In conclusion, the Dallas tax rate is a multifaceted and intricate system that impacts the financial decisions of its residents and businesses. From property taxes to sales taxes, each component plays a vital role in the city's revenue generation. Understanding this tax landscape is key to effective financial planning and compliance.
How are property taxes determined in Dallas?
+Property taxes in Dallas are determined by multiplying the property’s appraised value by the applicable tax rate for each taxing entity. The appraised value is set by the Dallas Central Appraisal District (DCAD), and property owners can appeal if they believe their value is inaccurate.
What is the local option homestead exemption, and how does it benefit homeowners in Dallas?
+The local option homestead exemption is a tax relief measure that reduces the taxable value of a homeowner’s primary residence. It is offered by certain school districts in Dallas and can range from 20% to 25%. This exemption provides significant savings on annual property tax bills.
How does the franchise tax affect businesses in Dallas?
+The franchise tax, or margin tax, is a privilege tax imposed on certain entities doing business in Texas. It is calculated based on a business’s taxable margin, which is derived from its total revenue. Businesses must understand this tax to ensure compliance and accurate financial planning.



