Car Sales Tax

The sales tax landscape in the automotive industry is a complex web of regulations, varying from state to state and often involving intricate calculations and exemptions. This guide aims to demystify the intricacies of car sales tax, providing an in-depth analysis of its mechanisms, variations, and potential impact on the industry and consumers alike.
Understanding Car Sales Tax: A Comprehensive Overview
Car sales tax is a critical component of the automotive retail ecosystem, influencing everything from dealership profitability to consumer affordability. It is a tax levied on the sale of vehicles, typically calculated as a percentage of the vehicle’s total price. However, the devil is in the details, and these taxes can vary significantly depending on a multitude of factors.
State-by-State Variations
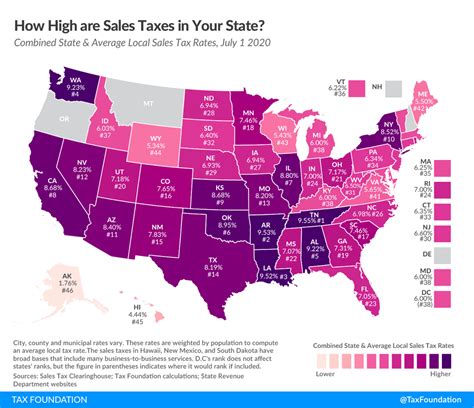
One of the most notable aspects of car sales tax is its diverse nature across different states in the U.S. Each state has its own set of rules and regulations, often resulting in vastly different tax rates and calculations. For instance, while some states like Delaware and Montana do not impose a statewide sales tax on vehicle purchases, others like California and Texas have relatively high sales tax rates.
These variations can significantly impact the final cost of a vehicle. For example, a $30,000 car purchased in Texas might attract a sales tax of around $2,400 (assuming a 8% sales tax rate), while the same car purchased in Delaware would not be subject to any statewide sales tax. This could make a substantial difference in the overall affordability of the vehicle for consumers.
| State | Sales Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| California | 7.25% |
| Texas | 6.25% |
| New York | 4% |
| Florida | 6% |
| Delaware | 0% |

Calculating Car Sales Tax: A Step-by-Step Guide
Calculating car sales tax involves more than just multiplying the vehicle’s price by the applicable tax rate. Several factors can influence the final tax amount, including the vehicle’s purchase price, any additional fees, and potential exemptions.
- Base Price Calculation: The first step involves calculating the base price of the vehicle. This includes the manufacturer's suggested retail price (MSRP) and any additional fees or costs, such as destination fees, dealer preparation fees, and optional equipment.
- Tax Rate Determination: Once the base price is established, the applicable tax rate needs to be determined. This is influenced by the state, county, and sometimes even the city where the vehicle is purchased.
- Exemptions and Deductions: Not all vehicle purchases are subject to the full sales tax rate. Certain exemptions and deductions might apply, such as trade-in allowances, military discounts, or tax holidays. These can significantly reduce the overall tax liability.
- Final Tax Calculation: With the base price, tax rate, and any applicable exemptions determined, the final tax amount can be calculated. This involves multiplying the base price by the tax rate and then subtracting any applicable exemptions.
The Impact on the Automotive Industry
Car sales tax has a profound impact on the automotive industry. It influences dealership profitability, as the tax amount is typically passed on to the consumer, impacting their purchasing power and willingness to spend. Higher tax rates can lead to a slowdown in sales, particularly for high-end vehicles, while lower tax rates can stimulate demand.
Furthermore, the complexity of car sales tax regulations can present challenges for dealerships in terms of compliance and administration. Keeping up with constantly changing tax laws and regulations requires significant resources and expertise, which can be a burden for smaller dealerships.
Consumer Perspectives: Navigating Car Sales Tax
For consumers, understanding car sales tax is crucial when making vehicle purchase decisions. It can significantly affect the overall cost of ownership, influencing their choice of vehicle, financing options, and even the timing of their purchase. Being aware of the applicable tax rates and potential exemptions can help consumers negotiate better deals and make more informed choices.
Additionally, consumers can explore strategies to minimize their tax liability, such as negotiating a lower purchase price, taking advantage of tax holidays or incentives, or considering leasing options which might offer more flexibility in terms of tax implications.
Future Implications and Industry Trends

The landscape of car sales tax is constantly evolving, influenced by economic, political, and technological factors. Here are some potential future implications and industry trends to consider:
- Digitalization and E-Commerce: With the rise of online car sales platforms, the traditional dealership model might undergo significant changes. This could lead to shifts in tax regulations, with potential for more streamlined and centralized tax collection processes.
- Electric Vehicle (EV) Incentives: As the adoption of electric vehicles accelerates, governments might introduce new tax incentives or rebates to encourage EV purchases. This could significantly alter the tax landscape for consumers and dealerships alike.
- Tax Reform and Simplification: There is a growing push for tax reform and simplification in many states. This could lead to more standardized tax rates and regulations, making it easier for dealerships and consumers to navigate the tax landscape.
- Consumer Advocacy and Awareness: As consumers become more informed about car sales tax, there might be increased pressure on dealerships and policymakers to provide greater transparency and clarity on tax implications. This could lead to more consumer-friendly tax policies and practices.
Conclusion: A Complex Yet Navigable Landscape
Car sales tax is a complex web of regulations, varying significantly across states and often involving intricate calculations and exemptions. While it can present challenges for both the automotive industry and consumers, understanding its intricacies is crucial for informed decision-making.
By staying informed about the latest tax regulations, leveraging available incentives and exemptions, and exploring alternative purchasing strategies, consumers can navigate the car sales tax landscape more effectively. Similarly, dealerships can stay ahead of the curve by investing in tax compliance expertise and adapting to evolving industry trends.
FAQs
Are there any ways to reduce my car sales tax liability?
+
Yes, there are several strategies to consider. Negotiating a lower purchase price, taking advantage of trade-in allowances, military discounts, or tax holidays, and exploring leasing options can all help reduce your sales tax liability. Additionally, staying informed about state-specific tax incentives and exemptions can provide further opportunities for savings.
How do dealerships handle the complexity of car sales tax regulations?
+
Dealerships typically employ tax experts or utilize specialized software to navigate the complex web of car sales tax regulations. This ensures compliance with the latest tax laws and helps dealerships offer accurate tax estimates to their customers. However, staying updated with constantly changing regulations can be a challenge, particularly for smaller dealerships.
Can I negotiate the sales tax on my car purchase?
+
No, sales tax is a mandatory charge determined by the state and local tax authorities. Dealerships do not have the authority to negotiate or waive sales tax. However, you can negotiate the purchase price of the vehicle, which can indirectly impact your sales tax liability.
Are there any states with no sales tax on car purchases?
+
Yes, as of [current year], there are a few states that do not impose a statewide sales tax on vehicle purchases. These include Delaware, Montana, New Hampshire, and Oregon. However, it’s important to note that local jurisdictions within these states might still levy their own taxes.



