California State Sales Tax Rate
The California State Sales Tax is a crucial aspect of the state's revenue system, contributing significantly to the funding of various public services and infrastructure projects. This tax is levied on retail sales, leases, and rentals of goods, as well as on the sales of specific services. As of my last update in January 2023, California has a base state sales and use tax rate of 7.25%, which is applicable across the state. However, when you consider local taxes, the rate can vary from this base, sometimes significantly.
Understanding California State Sales Tax Rates

California's sales tax system is unique due to its two-tier structure. The state sets a base rate, but local governments can add their own tax on top of this, leading to varying rates across the state. This local tax component can include county, city, and district taxes, each with its own rate. As a result, the total sales tax rate can differ greatly from one place to another.
For instance, while the state sales tax rate is 7.25%, a city like San Francisco adds an extra 1.25% in local taxes, resulting in a total sales tax rate of 8.5% for its residents and businesses. Conversely, certain areas, like Los Angeles County, have a total rate that is slightly lower than the state rate due to different local tax rates and special districts.
Tax Rates for Different Counties and Cities
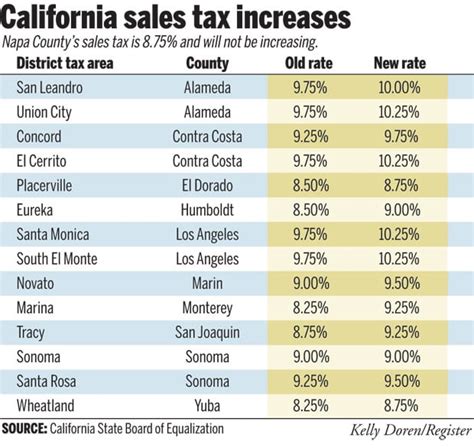
Here's a glimpse at the sales tax rates for some of California's major counties and cities as of my last update:
| Location | State Sales Tax | Local Sales Tax | Total Sales Tax |
|---|---|---|---|
| San Francisco | 7.25% | 1.25% | 8.5% |
| Los Angeles County | 7.25% | 0.25% | 7.5% |
| Sacramento County | 7.25% | 1% | 8.25% |
| Orange County | 7.25% | 0.25% | 7.5% |
| San Diego County | 7.25% | 0.5% | 7.75% |
These rates can change periodically, especially with new legislation or to fund specific projects, so it's crucial to stay updated with the latest rates when planning your purchases or running a business in California.
Sales Tax Exemptions and Special Cases
California's sales tax laws also provide for certain exemptions and special cases. Some goods and services are exempt from sales tax, including most groceries, prescription medications, and select services like medical care. Additionally, some areas have special tax rates or are designated as tax-free zones for specific reasons, such as promoting economic development.
For instance, certain areas in California have been designated as Enterprise Zones, where businesses can enjoy reduced sales and use tax rates as an incentive to operate there. These zones are typically in economically challenged areas and are designed to stimulate economic growth and job creation.
Online Sales and Use Tax
With the rise of e-commerce, California has also implemented a Sales and Use Tax on online sales. This tax applies to retailers that have no physical presence in California but sell to California residents. The rate is based on the destination of the sale, meaning the tax is determined by the location where the item is shipped or delivered.
For example, if an online retailer ships a product to a customer in San Francisco, the retailer must collect the total sales tax rate of 8.5% (7.25% state tax + 1.25% local tax) for that transaction.
The Impact of Sales Tax on the California Economy
California's sales tax plays a significant role in the state's economy, contributing to the funding of various public services and infrastructure projects. The revenue generated from sales tax helps support schools, healthcare, public safety, and transportation systems, among other essential services.
For instance, a substantial portion of the sales tax revenue goes towards funding the state's public education system, ensuring that schools across California have the necessary resources to provide quality education. Similarly, sales tax revenue is used to maintain and improve California's extensive transportation network, including roads, bridges, and public transit systems.
Future Trends and Potential Changes
Looking ahead, there are several factors that could influence the future of California's sales tax rates. One key consideration is the state's ongoing economic growth and the potential impact of new technologies and industries. As the state's economy evolves, the tax structure may need to adapt to ensure it remains fair and effective.
Additionally, with the increasing popularity of online shopping and the challenges it presents for tax collection, there may be further developments in the implementation and enforcement of sales tax on e-commerce transactions. The state will need to find ways to ensure it can collect the necessary taxes from online retailers, especially those without a physical presence in California.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the base California State Sales Tax rate as of 2023?
+The base California State Sales Tax rate as of my last update in 2023 is 7.25%.
How does California’s sales tax system work?
+California has a two-tier sales tax system, with a base state rate and additional local taxes. This means the total sales tax rate can vary significantly depending on the location.
Are there any sales tax exemptions in California?
+Yes, certain goods and services are exempt from sales tax, including most groceries, prescription medications, and select services like medical care.
How does California collect sales tax from online retailers without a physical presence in the state?
+California has implemented a Sales and Use Tax on online sales. This tax is based on the destination of the sale, and the retailer is responsible for collecting and remitting the appropriate tax.
What happens if a business doesn’t collect the correct sales tax in California?
+Businesses that don’t collect the correct sales tax can face penalties and interest charges. It’s important for businesses to understand the sales tax laws and rates to ensure compliance.