What Is Sales Tax In Kentucky

Sales tax in Kentucky is a vital component of the state's revenue generation and plays a significant role in shaping the state's economic landscape. It is a tax imposed on the sale of goods and services within the state, with the revenue collected used to fund various public services and infrastructure projects. Understanding the nuances of Kentucky's sales tax system is essential for both consumers and businesses operating within the state.
Sales Tax Structure in Kentucky
Kentucky’s sales tax system is relatively straightforward. The state levies a 6% sales and use tax on most tangible personal property and certain services. This base rate applies uniformly across the state, ensuring a consistent tax environment for businesses and consumers.
However, it's important to note that local jurisdictions in Kentucky, including cities and counties, have the authority to impose additional sales taxes. These local option sales taxes can vary significantly, resulting in a combined sales tax rate that can exceed the base rate of 6% in certain areas. For instance, the city of Louisville, Kentucky's largest city, has a 2% local option sales tax, bringing the total sales tax rate to 8% within city limits.
Local Sales Tax Variations
The ability of local governments to levy additional sales taxes creates a patchwork of tax rates across the state. This variation can be particularly significant for businesses with multiple locations or for consumers who frequently travel or make purchases in different areas. Here’s a look at some of the key local sales tax rates in Kentucky’s major cities:
| City | Local Sales Tax Rate | Total Sales Tax Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Louisville | 2% | 8% |
| Lexington | 1.5% | 7.5% |
| Bowling Green | 1.5% | 7.5% |
| Owensboro | 1% | 7% |
| Covington | 2% | 8% |
Sales Tax Exemptions and Special Considerations
While Kentucky’s sales tax applies to a broad range of goods and services, there are several notable exemptions and special considerations within the state’s tax code. These exemptions can provide significant savings for businesses and consumers alike.
Food and Grocery Exemptions
One of the most notable sales tax exemptions in Kentucky applies to food and groceries. The state does not impose sales tax on unprepared food items, including most staple grocery items. This exemption is a significant relief for Kentucky’s residents, especially those with lower incomes, as it reduces the tax burden on essential household expenses.
However, it's important to note that this exemption does not apply to all food products. Certain prepared foods, meals, and beverages, including soft drinks and alcohol, are subject to sales tax. Additionally, the exemption does not extend to non-food items typically sold in grocery stores, such as household goods, personal care products, and pet supplies.
Prescription Drugs and Medical Devices
Kentucky also exempts prescription drugs and medical devices from sales tax. This exemption is particularly beneficial for individuals with medical needs, as it reduces the cost of essential medications and medical equipment. It’s a significant advantage for Kentucky’s healthcare system, making necessary medical treatments more accessible and affordable for residents.
Manufacturing and Resale Exemptions
For businesses, Kentucky offers exemptions for manufacturing and resale. Raw materials and components purchased for manufacturing purposes are not subject to sales tax, providing a significant cost savings for Kentucky’s manufacturing sector. Additionally, sales tax is not imposed on goods purchased for resale, ensuring that businesses are not double-taxed on the same inventory.
Other Exemptions
Kentucky’s sales tax code includes a range of other exemptions, including those for certain agricultural products, machinery and equipment used in manufacturing, and certain services such as legal and professional services. These exemptions are designed to support specific industries and encourage economic growth in targeted sectors.
Sales Tax Collection and Remittance
Businesses operating in Kentucky are responsible for collecting and remitting sales tax on behalf of the state and local jurisdictions. The Kentucky Department of Revenue provides resources and guidance to help businesses navigate the sales tax collection process, including registration, filing, and payment procedures.
Businesses are required to collect sales tax at the point of sale, including both in-person and online transactions. This responsibility extends to out-of-state sellers who make sales into Kentucky, a requirement that has gained increased attention with the rise of e-commerce. Kentucky's use tax, which applies to purchases made outside the state for use within Kentucky, helps to ensure that all sales are subject to tax, regardless of where the transaction takes place.
Sales Tax Registration and Filing
To register for sales tax collection in Kentucky, businesses must complete the appropriate forms and provide relevant business information to the Kentucky Department of Revenue. Once registered, businesses are assigned a sales tax account number and are responsible for filing sales tax returns on a regular basis, typically quarterly or monthly depending on their sales volume.
Sales tax returns must include the total taxable sales made during the reporting period, as well as the applicable sales tax rate(s) for each sale. Businesses must remit the collected sales tax to the state and local jurisdictions within the specified timeframe to avoid penalties and interest.
Compliance and Audits
The Kentucky Department of Revenue conducts audits to ensure compliance with sales tax laws. These audits can be complex and time-consuming, so it’s essential for businesses to maintain accurate records and have a clear understanding of their sales tax obligations. Non-compliance can result in significant penalties and interest charges, so staying informed and up-to-date with Kentucky’s sales tax regulations is critical.
Impact of Sales Tax on Businesses and Consumers
Sales tax in Kentucky has a significant impact on both businesses and consumers. For businesses, the sales tax collection process adds administrative overhead and can impact pricing strategies. Businesses must carefully consider the sales tax implications when setting prices to ensure they remain competitive while also meeting their tax obligations.
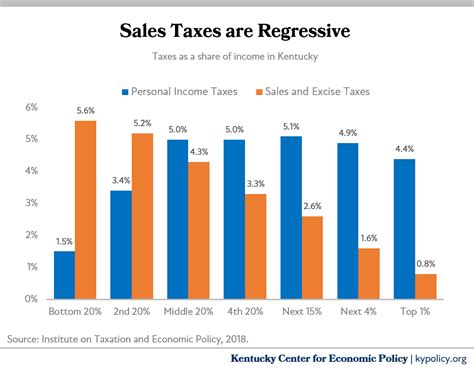
For consumers, sales tax adds to the cost of goods and services. While the base rate of 6% may seem modest, the addition of local option sales taxes can result in a noticeable increase in the total cost of purchases. This can impact consumer spending habits and purchasing decisions, especially for higher-value items or frequent shoppers.
Competitive Pricing and Business Strategy
Businesses operating in Kentucky must carefully consider their pricing strategies to remain competitive within the state’s sales tax environment. While a higher sales tax rate can be a disadvantage, it can also be an opportunity for businesses to differentiate themselves by offering competitive pricing or value-added services that offset the tax burden.
For example, a business may choose to absorb a portion of the sales tax by offering discounted prices, effectively reducing the cost to the consumer. Alternatively, a business could provide additional services or benefits, such as free shipping or extended warranties, to make up for the sales tax cost.
Consumer Spending Patterns
The sales tax rate can also influence consumer spending patterns. In areas with higher sales tax rates, consumers may be more likely to seek out sales or discounts to offset the tax burden. They may also be more inclined to shop online or in neighboring states with lower sales tax rates, a phenomenon known as “border shopping.”
However, for essential purchases or in areas where sales tax rates are more moderate, consumers may be less sensitive to sales tax rates. In these cases, factors such as convenience, product quality, and customer service may take precedence over sales tax considerations.
Sales Tax and Economic Development
Sales tax plays a critical role in Kentucky’s economic development. The revenue generated from sales tax is used to fund a wide range of public services and infrastructure projects, including education, healthcare, transportation, and public safety. This investment in public goods helps to create a robust business environment and enhance the quality of life for Kentucky’s residents.
Additionally, sales tax revenue is a key factor in attracting new businesses to the state. A well-managed sales tax system that is fair, efficient, and transparent can be a significant advantage for Kentucky in the competition for new business investments. By providing a stable and predictable tax environment, Kentucky can encourage economic growth and create new job opportunities for its residents.
Sales Tax Revenue Allocation
The allocation of sales tax revenue in Kentucky is a complex process that involves multiple levels of government. The state government receives the majority of the sales tax revenue, which is used to fund state-level programs and services. Local governments, including cities and counties, also receive a portion of the sales tax revenue to support their operations and provide local services.
The specific allocation of sales tax revenue is determined by state law and can vary depending on the type of tax and the jurisdiction. In general, a portion of the sales tax revenue is distributed to local governments based on a formula that considers factors such as population, sales volume, and other economic indicators. This ensures that local governments have the resources they need to provide essential services to their communities.
Impact on Business Climate
A well-managed sales tax system can have a positive impact on Kentucky’s business climate. By keeping sales tax rates competitive and ensuring a fair and efficient collection process, the state can encourage business growth and investment. This, in turn, leads to job creation and economic prosperity for the state’s residents.
However, it's important for Kentucky to strike a balance between generating sufficient revenue through sales tax and maintaining a business-friendly environment. High sales tax rates can deter businesses from locating in the state and may encourage consumers to shop elsewhere, reducing the overall economic benefits of sales tax revenue.
Future Implications and Potential Reforms
As Kentucky’s economy continues to evolve, the state’s sales tax system will likely face ongoing scrutiny and potential reforms. The rise of e-commerce and the changing nature of consumer behavior present new challenges and opportunities for sales tax collection and administration.
Online Sales and Use Tax
The increase in online sales has made it more challenging for states to collect sales tax from out-of-state sellers. Kentucky, like many other states, has implemented laws to require online retailers to collect and remit sales tax on purchases made by Kentucky residents. This ensures that all sales, whether in-store or online, are subject to the appropriate tax.
However, the enforcement of online sales tax laws can be complex and resource-intensive. Kentucky will need to continue to adapt its sales tax collection processes to keep pace with the evolving nature of e-commerce and ensure compliance with changing tax laws and regulations.
Potential Reforms and Modernization
As Kentucky’s sales tax system evolves, there may be opportunities for reform and modernization. Some potential areas for consideration include:
- Simplification: Kentucky could explore ways to simplify its sales tax system, such as reducing the number of tax rates or providing more consistent exemptions across the state. This would make it easier for businesses to comply with sales tax laws and reduce administrative burdens.
- Enhanced Compliance Measures: The state could invest in technology and resources to improve sales tax compliance and enforcement. This could include implementing real-time sales tax collection systems or expanding audit capabilities to ensure that all businesses are meeting their tax obligations.
- Tax Rate Adjustments: While Kentucky's base sales tax rate is relatively low compared to some other states, there may be opportunities to adjust the rate to better meet the state's revenue needs or to provide competitive advantages to businesses and consumers.
Ultimately, any reforms to Kentucky's sales tax system will need to balance the state's revenue needs with the interests of businesses and consumers. By staying informed and engaged with the state's tax policies, businesses and consumers can ensure that their voices are heard in the sales tax debate and help shape a fair and efficient tax system for the future.
Conclusion
Sales tax in Kentucky is a critical component of the state’s revenue generation and economic development. While the base sales tax rate is relatively low, the addition of local option sales taxes can result in significant variations across the state. These variations, combined with a range of exemptions and special considerations, create a complex but manageable sales tax environment for businesses and consumers.
Understanding Kentucky's sales tax system is essential for businesses to remain compliant and competitive, and for consumers to make informed purchasing decisions. As the state's economy continues to evolve, ongoing dialogue and potential reforms will be necessary to ensure that Kentucky's sales tax system remains fair, efficient, and responsive to the needs of its residents and businesses.
What is the base sales tax rate in Kentucky?
+The base sales tax rate in Kentucky is 6%.
Do local jurisdictions have the authority to impose additional sales taxes in Kentucky?
+Yes, local jurisdictions, including cities and counties, can impose additional sales taxes, known as local option sales taxes, which can vary significantly across the state.
What are some notable sales tax exemptions in Kentucky?
+Kentucky exempts food and groceries, prescription drugs and medical devices, raw materials for manufacturing, and goods purchased for resale from sales tax.
How does Kentucky ensure compliance with sales tax laws for online retailers?
+Kentucky requires online retailers to collect and remit sales tax on purchases made by Kentucky residents to ensure compliance with sales tax laws.
What potential reforms could Kentucky consider for its sales tax system?
+Potential reforms could include simplifying the sales tax system, enhancing compliance measures, and adjusting tax rates to better meet the state’s revenue needs or provide competitive advantages.



