What Is Ifta Tax

In the intricate world of transportation and logistics, understanding the various taxes and fees that apply to commercial vehicles is essential for compliance and efficient operations. Among these, the International Fuel Tax Agreement (IFTA) stands out as a critical regulatory framework for interstate and international transportation. This article delves into the intricacies of IFTA tax, exploring its purpose, mechanics, and implications for trucking companies and owner-operators.
Understanding IFTA Tax: A Regulatory Framework
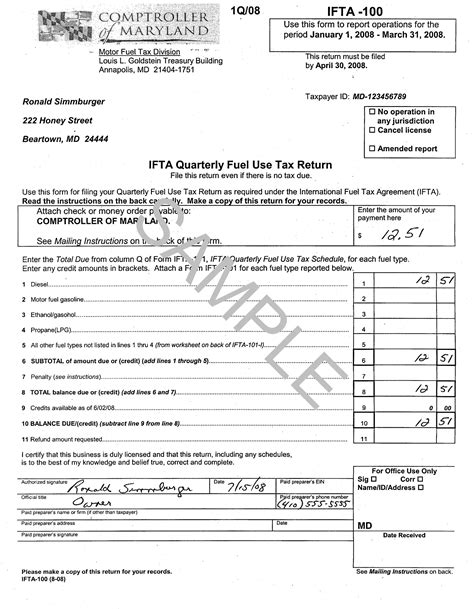
The International Fuel Tax Agreement, commonly known as IFTA, is a legal pact between the United States and Canada. Its primary objective is to streamline the collection and distribution of fuel taxes for commercial vehicles operating across multiple jurisdictions. Established in 1983, IFTA simplifies the tax collection process by providing a unified system for licensed carriers to report and remit fuel taxes to the proper authorities.
The Importance of IFTA for the Transportation Industry
For trucking companies and owner-operators, IFTA is a critical aspect of their operations. It ensures compliance with fuel tax regulations, avoiding penalties and legal issues. By adhering to IFTA, carriers can efficiently manage their tax obligations, maintaining good standing with state and provincial authorities.
How IFTA Works: A Simplified Process
IFTA operates through a registration and reporting system. Licensed carriers must first obtain an IFTA license, which grants them the privilege of purchasing fuel tax-free across all IFTA jurisdictions. This license is typically issued by the base jurisdiction, where the carrier is headquartered or registered.
Once licensed, carriers must maintain accurate records of fuel purchases and mileage traveled in each jurisdiction. These records are then used to calculate the fuel tax liability. The carrier then remits the tax to their base jurisdiction, which, in turn, distributes the funds to the appropriate states and provinces.
Key Components of IFTA Tax

IFTA tax is calculated based on two primary factors: fuel purchases and mileage traveled. The tax rate varies depending on the jurisdiction, with each state or province setting its own rate. The formula for calculating IFTA tax is relatively straightforward:
IFTA Tax = (Fuel Purchases x Tax Rate) / Jurisdiction Miles
Fuel Purchases
Fuel purchases are a critical component of IFTA tax. Carriers must keep meticulous records of all fuel purchases, including the date, location, quantity, and price. These records are essential for accurate tax calculation and audit purposes.
Mileage Traveled
Mileage traveled is the other key factor in IFTA tax calculation. Carriers are required to maintain detailed logs of their trips, including the starting and ending mileage for each jurisdiction. This data is used to determine the proportion of tax owed to each jurisdiction.
| Jurisdiction | Fuel Tax Rate | Mileage Traveled |
|---|---|---|
| State A | 0.25/gallon | 5,000 miles |
| State B | 0.30/gallon | 3,000 miles |
| State C | 0.20/gallon | 2,500 miles |

Benefits and Challenges of IFTA Tax
IFTA tax, while essential for regulatory compliance, presents both benefits and challenges for the transportation industry.
Benefits
- Simplified Tax Compliance: IFTA simplifies the tax collection process, reducing administrative burdens for carriers.
- Uniform Reporting: Carriers need only report to their base jurisdiction, streamlining the tax reporting process.
- Cost Savings: By purchasing fuel tax-free, carriers can reduce their overall fuel tax burden.
Challenges
- Record-Keeping: Maintaining accurate records of fuel purchases and mileage is a significant challenge, especially for large fleets.
- Audit Risks: IFTA audits can be complex and time-consuming, with potential penalties for non-compliance.
- Jurisdictional Differences: Varying tax rates and regulations across jurisdictions can make compliance more challenging.
Staying Compliant: Tips for IFTA Tax Management
To ensure compliance with IFTA tax regulations, carriers should consider the following best practices:
- Accurate Record-Keeping: Implement robust systems for tracking fuel purchases and mileage. Consider digital solutions for real-time data capture and reporting.
- Regular Reconciliation: Reconcile fuel purchases and mileage data regularly to identify any discrepancies or errors.
- Stay Informed: Stay updated on IFTA regulations and changes. Attend industry workshops or webinars to stay ahead of compliance requirements.
- Partner with Experts: Engage the services of tax professionals or consultants specializing in IFTA compliance to ensure accurate reporting and minimize risks.
Conclusion: Navigating the IFTA Landscape
IFTA tax is a critical aspect of the transportation industry, ensuring compliance and efficient tax management for commercial vehicles. By understanding the mechanics of IFTA and implementing best practices, carriers can navigate the regulatory landscape with confidence. Accurate record-keeping, regular reconciliation, and staying informed are key to successful IFTA compliance.
FAQ
What is the purpose of IFTA tax?
+
IFTA tax is a regulatory mechanism designed to streamline the collection and distribution of fuel taxes for commercial vehicles operating across multiple jurisdictions.
How does IFTA benefit trucking companies and owner-operators?
+
IFTA simplifies tax compliance, reduces administrative burdens, and allows carriers to purchase fuel tax-free, leading to cost savings.
What are the key factors in calculating IFTA tax?
+
IFTA tax is calculated based on fuel purchases and mileage traveled. The tax rate varies depending on the jurisdiction.
What are some challenges associated with IFTA tax compliance?
+
Challenges include accurate record-keeping, audit risks, and navigating varying tax rates and regulations across jurisdictions.



