West Virginia State Income Tax

When it comes to state finances, one of the primary sources of revenue for many U.S. states is income tax. Each state has its own unique tax system, and understanding these variations is crucial for individuals and businesses alike. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the world of West Virginia state income tax, exploring its rates, brackets, deductions, and how it compares to other states. Whether you're a resident, a business owner, or simply curious about state finances, this expert analysis will provide you with valuable insights into West Virginia's tax landscape.
Understanding West Virginia’s Income Tax System

West Virginia, nestled in the Appalachian region, has a tax system that plays a significant role in funding public services and infrastructure. The state’s income tax structure is progressive, meaning that as your income increases, so does the tax rate you pay. This progressive nature aims to ensure a fair distribution of tax responsibilities among residents.
Tax Rates and Brackets
West Virginia operates with a straightforward tax rate structure. As of the latest tax year, the state imposes a flat income tax rate of 6.5% on all taxable income. This rate applies uniformly to all residents, regardless of their income level.
While the state’s flat tax rate may seem straightforward, it’s important to note that West Virginia also has adjustments and credits that can impact the final tax liability. These adjustments and credits can either increase or decrease the tax burden, depending on an individual’s specific circumstances.
| Tax Rate | Income Bracket |
|---|---|
| 6.5% | All Taxable Income |
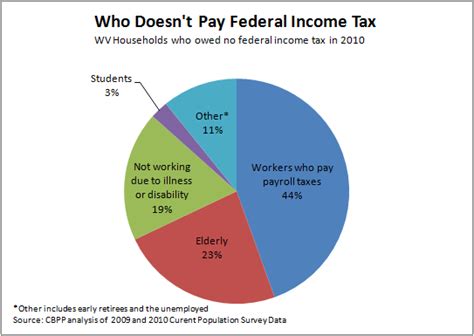
For instance, West Virginia offers a Homestead Exemption for property owners. This exemption reduces the taxable value of a primary residence, providing a credit that can lower the overall tax burden for homeowners. Additionally, the state provides tax credits for various expenses, such as dependent care, education, and certain business-related costs.
Taxable Income and Deductions
West Virginia’s taxable income includes wages, salaries, tips, commissions, bonuses, and other forms of compensation. It also encompasses income from self-employment, partnerships, S-corporations, and trusts. However, certain types of income are exempt from state income tax, such as municipal bond interest and some forms of retirement income.
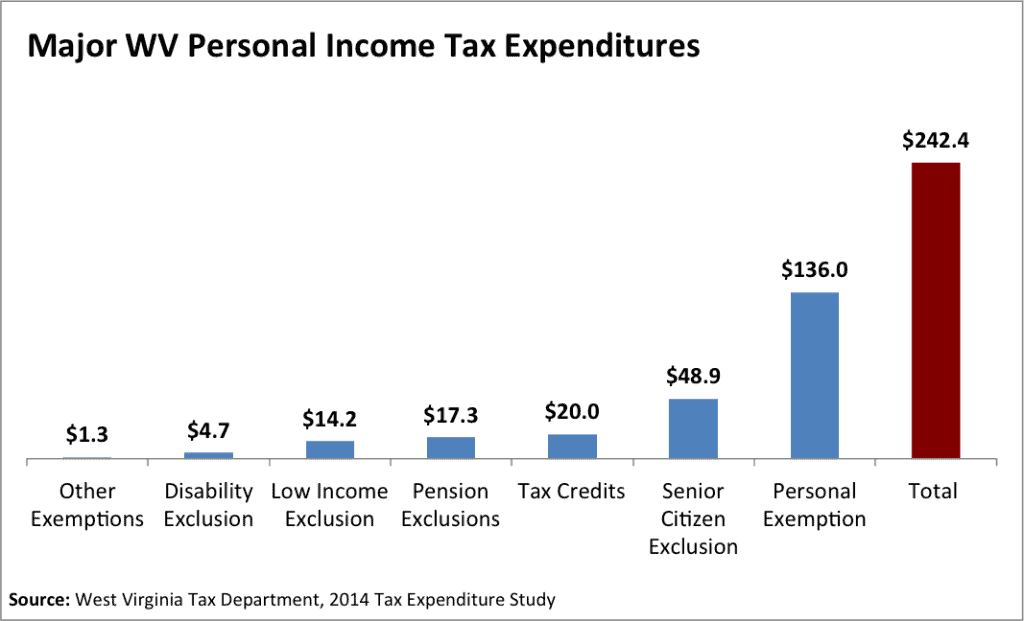
When it comes to deductions, West Virginia allows residents to deduct their federal adjusted gross income (AGI) up to a certain limit. This means that individuals can reduce their taxable income by a portion of their federal AGI, providing a valuable tax relief mechanism. Additionally, the state offers a standard deduction and allows itemized deductions for expenses such as medical costs, charitable contributions, and mortgage interest.
Comparing West Virginia’s Income Tax to Other States
To gain a broader perspective, let’s compare West Virginia’s income tax system to that of its neighboring states and the national average.
| State | Tax Rate | Tax Brackets |
|---|---|---|
| West Virginia | 6.5% | Flat Rate |
| Ohio | 2.8% | 3 Brackets |
| Pennsylvania | 3.07% | Flat Rate |
| Kentucky | 5% | 6 Brackets |
| National Average | 5.35% | Variable |
As seen in the table above, West Virginia's flat tax rate of 6.5% positions it above the national average and slightly higher than neighboring states like Ohio and Pennsylvania. However, it's important to consider the overall tax burden, which includes not only income tax but also sales tax, property tax, and other state-specific taxes.
The Impact of West Virginia’s Income Tax on Residents and Businesses
The income tax system in West Virginia has a significant impact on both individuals and businesses operating within the state. For residents, the flat tax rate provides a level of simplicity and predictability in their tax obligations. However, it’s essential to consider the overall tax burden, as West Virginia’s sales tax and property tax rates are relatively higher than some neighboring states.
Attracting Businesses
When it comes to attracting businesses, West Virginia’s income tax structure can be a double-edged sword. On the one hand, the flat tax rate provides a stable and predictable environment for businesses, which can be appealing for companies looking for tax stability. However, the higher tax rate compared to some neighboring states might deter businesses, especially those with high-income employees or those considering relocation.
Economic Growth and Development
The income tax revenue generated by West Virginia plays a vital role in funding public services and infrastructure projects. This revenue is crucial for economic growth and development, as it supports education, healthcare, transportation, and other essential sectors. By investing in these areas, the state aims to create a favorable environment for businesses and residents alike, fostering long-term economic prosperity.
Tax Policy and Economic Competitiveness
West Virginia’s tax policy, including its income tax structure, is a key factor in determining the state’s economic competitiveness. While a flat tax rate provides simplicity, it may not always align with the needs of a diverse business landscape. Some industries, such as technology and innovation-focused sectors, may prefer more progressive tax structures that offer incentives for high-income earners.
Future Outlook and Potential Reforms
As West Virginia continues to evolve and adapt to changing economic conditions, its tax system is likely to undergo reforms and adjustments. Here are some potential areas of focus for future tax policy considerations:
- Progressive Tax Structure: While West Virginia currently has a flat tax rate, there are discussions about implementing a more progressive tax system. This could involve introducing higher tax brackets for higher income levels, ensuring a fairer distribution of tax responsibilities.
- Tax Incentives for Businesses: To attract and retain businesses, West Virginia might consider offering targeted tax incentives. These could include tax credits for research and development, job creation, or investments in specific industries, fostering economic growth and innovation.
- Revenue Generation Strategies: With the state's reliance on income tax revenue, it's essential to explore additional revenue streams. West Virginia could consider expanding its sales tax base, exploring tourism-related taxes, or implementing innovative strategies to generate revenue while minimizing the impact on residents and businesses.
- Tax Reform for Economic Competitiveness: As the state aims to enhance its economic competitiveness, tax reforms could play a crucial role. This may involve reviewing and adjusting tax rates, brackets, and deductions to create a more attractive environment for businesses and high-income earners.
Conclusion
West Virginia’s income tax system is a vital component of the state’s financial landscape, playing a significant role in funding public services and infrastructure. The state’s flat tax rate of 6.5% provides simplicity and predictability for residents and businesses. However, as West Virginia navigates the complexities of a changing economy, tax policy reforms will likely emerge to ensure the state remains competitive and adaptable.
How does West Virginia’s income tax compare to other states in terms of tax burden?
+West Virginia’s flat tax rate of 6.5% positions it above the national average and slightly higher than some neighboring states. However, the overall tax burden, including sales tax and property tax, should be considered for a comprehensive comparison.
Are there any tax incentives or deductions available for businesses in West Virginia?
+Yes, West Virginia offers tax incentives and deductions for businesses. These include tax credits for research and development, job creation, and investments in specific industries. Additionally, the state provides tax exemptions for certain types of business income.
How does West Virginia’s income tax system impact economic growth and development?
+The income tax revenue generated by West Virginia funds essential public services and infrastructure projects. This investment in education, healthcare, and transportation creates a favorable environment for economic growth and attracts businesses and residents.