Washington State Sales Tax Lookup
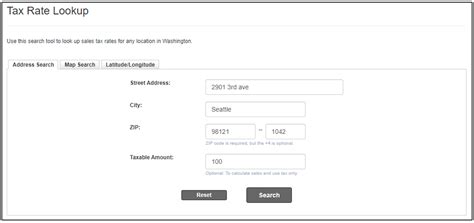
Washington State, nestled in the beautiful Pacific Northwest region of the United States, has a unique sales tax system that impacts both residents and businesses. The sales tax rate in Washington is a critical piece of information for anyone conducting business transactions or planning their finances within the state. This article aims to provide an in-depth analysis of the Washington State sales tax, its rates, exemptions, and the lookup process, ensuring you have all the necessary information at your fingertips.
Understanding Washington’s Sales Tax Landscape
Washington State is one of the few states in the US that operates under a purely retail sales tax system, which means it does not impose a general sales tax on services. This distinction sets Washington apart from many other states and influences the overall tax landscape for businesses and consumers.
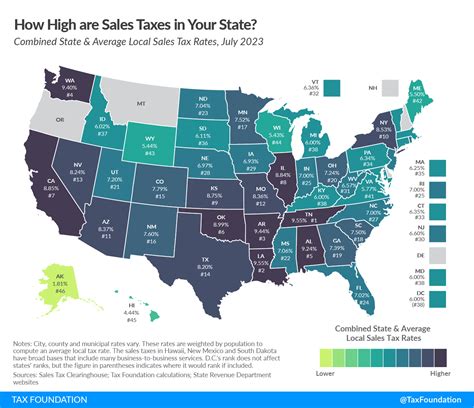
The sales tax in Washington is a statewide tax, meaning that a single tax rate is applied uniformly across the state. However, it's important to note that local jurisdictions can also levy additional taxes, resulting in varying tax rates depending on the specific location of the transaction.
As of [insert most recent data], the statewide sales tax rate in Washington is [current rate]%. This rate is applied to most retail sales of tangible personal property and certain services. However, it's crucial to understand that this base rate can be supplemented by local tax rates, leading to a combined tax rate that may differ from one city or county to another.
Sales Tax Rates by Jurisdiction
Washington State is divided into numerous counties and cities, each with the potential to have its own (Additional Tax Jurisdiction) or ATJ rate. These additional rates are applied on top of the statewide base rate, creating a unique tax environment for each jurisdiction.
County Sales Tax Rates
The following table provides a snapshot of the county-level sales tax rates in Washington State as of [insert most recent data]. These rates are subject to change, so it’s essential to verify the current rates before conducting any significant transactions.
| County | Sales Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Adams County | [Adams County Rate]% |
| Asotin County | [Asotin County Rate]% |
| Benton County | [Benton County Rate]% |
| ... | ... |
| Whatcom County | [Whatcom County Rate]% |
| Yakima County | [Yakima County Rate]% |
Note: This table provides a representative sample of county-level sales tax rates. For a comprehensive list of all county rates, refer to the official Washington State Department of Revenue website.
City Sales Tax Rates
Cities within Washington State also have the authority to impose their own sales tax rates. These city-specific rates can further impact the overall sales tax burden on consumers and businesses.
Below is a table showcasing selected city sales tax rates as of [insert most recent data]. These rates are illustrative and may not represent the complete landscape of city-level sales taxes.
| City | Sales Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Spokane | [Spokane City Rate]% |
| Seattle | [Seattle City Rate]% |
| Tacoma | [Tacoma City Rate]% |
| Vancouver | [Vancouver City Rate]% |
| Bellevue | [Bellevue City Rate]% |
For an exhaustive list of city sales tax rates, consult the Washington State Department of Revenue's website, which provides up-to-date and detailed information on sales tax rates across all jurisdictions.
Sales Tax Exemptions and Special Considerations
Understanding the sales tax landscape in Washington State involves more than just knowing the rates. There are various exemptions and special considerations that can impact the tax liability of certain transactions. These exemptions are designed to support specific industries, promote economic growth, or align with the state’s policy objectives.
Agricultural Sales Tax Exemption
One notable exemption in Washington State’s sales tax system is the agricultural sales tax exemption. This provision exempts the sale of certain agricultural products from the state’s sales tax. The exemption applies to:
- Sales of livestock, including cattle, horses, sheep, and poultry.
- Sales of farm products, such as grains, fruits, vegetables, and nuts.
- Sales of certain farm machinery and equipment used in agricultural production.
This exemption aims to support the state's agricultural sector by reducing the tax burden on farmers and agricultural businesses. It's important for businesses involved in agricultural sales to understand the specific criteria and limitations of this exemption to ensure they are compliant with the law.
Manufacturing and Resale Exemptions
Washington State also offers manufacturing and resale exemptions from sales tax. These exemptions are designed to encourage manufacturing activities and promote the resale of goods within the state.
The manufacturing exemption applies to the sale of tangible personal property that is used or consumed directly in the manufacturing process. This includes raw materials, components, and other items necessary for the manufacturing operation. By exempting these items from sales tax, Washington State aims to support its manufacturing industry and make it more competitive.
The resale exemption, on the other hand, applies to the sale of goods that are purchased for the purpose of resale. In other words, if a business buys goods with the intention of reselling them to customers, these purchases are typically exempt from sales tax. This exemption ensures that the sales tax is collected only at the final point of sale, benefiting both businesses and consumers.
Special Considerations for Online Sales
With the rise of e-commerce, the sales tax landscape has become more complex, especially for online retailers. Washington State, like many other states, has implemented sales tax collection requirements for online sellers.
If an online retailer has a significant presence in Washington State, such as through a physical location, employees, or affiliates, they are generally required to collect and remit sales tax on transactions with Washington residents. This requirement ensures that online retailers contribute to the state's revenue stream and level the playing field with brick-and-mortar businesses.
Online sellers should stay informed about the state's sales tax regulations and consult with tax professionals to ensure they are in compliance with the law. This includes understanding the economic nexus thresholds and the specific requirements for collecting and remitting sales tax in Washington State.
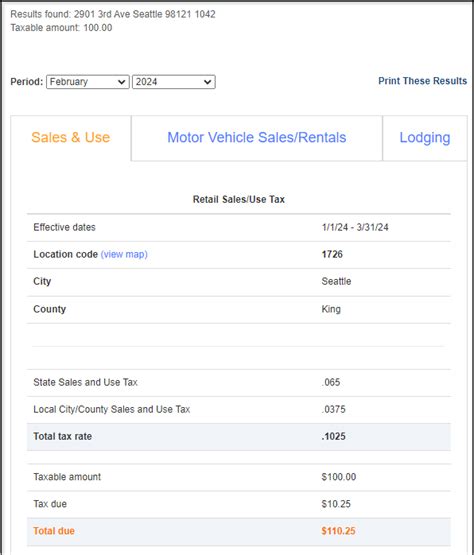
Sales Tax Lookup Tools and Resources
Given the complexity of Washington State’s sales tax system, with varying rates across jurisdictions and a range of exemptions, it’s essential to have access to reliable tools and resources for sales tax lookup.
Washington State Department of Revenue
The Washington State Department of Revenue is the primary source of information for sales tax rates and regulations. Their website offers a wealth of resources, including:
- Sales Tax Rates by Location: A comprehensive database of sales tax rates by city and county, updated regularly.
- Sales Tax Exemptions and Rules: Detailed information on the various exemptions and special considerations in the state’s sales tax system.
- Online Sales Tax Guide: Guidance for online sellers on their sales tax obligations and economic nexus thresholds.
The Department of Revenue's website is a critical resource for businesses and individuals looking to understand and comply with Washington State's sales tax laws.
Third-Party Sales Tax Lookup Tools
In addition to the official government resources, several third-party tools and platforms provide sales tax lookup services for Washington State and other jurisdictions across the US.
These tools often offer real-time rate lookups, allowing users to input an address or ZIP code and instantly retrieve the applicable sales tax rate for that location. Some popular third-party sales tax lookup tools include:
- TaxJar: A comprehensive sales tax management platform that offers rate lookup, tax calculation, and filing services.
- Avalara: Provides a range of sales tax solutions, including rate lookup, tax calculation, and compliance tools.
- TaxCloud: A cloud-based sales tax automation platform that simplifies sales tax management for businesses.
While these third-party tools can be valuable resources, it's essential to verify the accuracy of the rates and ensure they align with the official rates published by the Washington State Department of Revenue.
Sales Tax Registration and Filing
For businesses conducting taxable transactions in Washington State, sales tax registration is a crucial step to ensure compliance with the law. The registration process involves applying for a (Business License) or (Business and Occupation Tax License), depending on the nature of the business.
Business License Application
The Business License Application is typically the first step for businesses looking to operate in Washington State. This application is used to register the business with the state and obtain the necessary licenses and permits.
As part of the application process, businesses are required to provide information about their business activities, ownership structure, and expected sales volume. This information is crucial for determining the appropriate tax obligations and registrations.
Business and Occupation Tax License
The Business and Occupation Tax License is a critical component of sales tax registration in Washington State. This license is required for businesses that engage in specific taxable activities, such as retail sales, manufacturing, or providing services.
The Business and Occupation Tax License application process involves providing detailed information about the business's operations, including the nature of the business, the location(s) of operations, and the types of goods or services sold. This information helps the state determine the applicable tax rates and any additional registrations or permits required.
Sales Tax Filing and Remittance
Once registered, businesses are required to file sales tax returns and remit the collected sales tax to the Washington State Department of Revenue. The filing frequency and due dates depend on the business’s expected sales volume and other factors.
Businesses can typically file sales tax returns monthly, quarterly, or annually, depending on their sales volume and the state's requirements. The returns must include the total taxable sales, any applicable exemptions, and the calculated sales tax due. The Department of Revenue provides online filing options, making the process more efficient and convenient.
It's crucial for businesses to stay informed about their filing obligations and deadlines to avoid penalties and interest charges. The Department of Revenue's website offers detailed guidance and resources for sales tax filing and remittance.
Compliance and Penalties
Compliance with Washington State’s sales tax laws is essential for businesses operating within the state. Non-compliance can result in significant penalties and legal consequences.
Sales Tax Audits
The Washington State Department of Revenue has the authority to conduct sales tax audits to ensure compliance with the state’s tax laws. These audits can be random or triggered by specific indicators, such as suspicious transactions or inconsistent reporting.
During a sales tax audit, the Department of Revenue will examine a business's sales records, tax returns, and other relevant documents to verify the accuracy of the reported sales tax. If discrepancies are found, the business may be required to pay additional tax, penalties, and interest.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
The penalties for non-compliance with Washington State’s sales tax laws can be substantial. The specific penalties depend on the nature and severity of the violation, but they can include:
- Underpayment of Tax: If a business underreports its taxable sales or fails to remit the full amount of sales tax due, it may be subject to penalties and interest on the underpaid amount.
- Late Filing Penalties: Businesses that fail to file their sales tax returns by the due date may be penalized, typically as a percentage of the tax due.
- Failure to Register: Businesses operating in Washington State without the required licenses and registrations may face penalties and fines, as well as potential criminal charges.
It's crucial for businesses to understand their sales tax obligations and maintain accurate records to avoid these penalties. Consulting with tax professionals and staying informed about the state's sales tax regulations can help businesses stay compliant and avoid costly mistakes.
Future of Sales Tax in Washington State
The sales tax landscape in Washington State is subject to ongoing changes and developments. As the state’s economy evolves and new technologies shape the business environment, the sales tax system may also undergo transformations.
Potential Sales Tax Reform
There have been discussions and proposals for sales tax reform in Washington State, aimed at simplifying the tax system and addressing emerging challenges. Some of the potential reforms include:
- Broadening the Tax Base: Proposals to expand the types of goods and services subject to sales tax, potentially reducing the reliance on property taxes and increasing revenue stability.
- Streamlining Sales Tax Rates: Efforts to simplify the sales tax system by reducing the number of jurisdictions with different tax rates or harmonizing rates across the state.
- Addressing E-Commerce Challenges: With the growth of online sales, there may be proposals to revise the sales tax regulations for online sellers to ensure fair competition and adequate tax collection.
While these reforms are still in the discussion phase, they highlight the ongoing efforts to modernize and improve the sales tax system in Washington State.
Impact of Economic Trends
The sales tax system in Washington State is influenced by broader economic trends and shifts in consumer behavior. As the state’s economy evolves, certain industries may experience growth or decline, impacting the sales tax base.
For example, if the e-commerce sector continues to expand, the sales tax collected from online transactions may become a more significant portion of the state's revenue. On the other hand, if certain industries face challenges, such as the decline of brick-and-mortar retail, the sales tax base may be affected, requiring the state to adapt its tax policies.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements, such as the increasing use of automation and digital platforms, can also impact the sales tax system. For instance, the implementation of sales tax software and automated tax calculation tools can streamline the tax filing process for businesses, improving compliance and efficiency.
Additionally, the use of data analytics and artificial intelligence can enhance the state's ability to detect and address tax evasion or non-compliance, ensuring a more fair and equitable tax system.
Conclusion
Understanding the sales tax landscape in Washington State is a critical aspect of doing business in the region. From the statewide base rate to the varying local rates, and from exemptions to compliance requirements, there are numerous factors to consider.
By staying informed about the sales tax rates, exemptions, and regulations, businesses can ensure they are compliant with the law and avoid costly penalties. Additionally, keeping abreast of potential reforms and economic trends can help businesses anticipate and adapt to changes in the sales tax system.
Whether you're a local business or an online seller looking to expand into Washington State, having a comprehensive understanding of the sales tax environment is essential for success and compliance.
How often are sales tax rates updated in Washington State?
+Sales tax rates in Washington State are typically updated annually, usually effective from July 1st of each year. However, local jurisdictions may also adjust their rates, so it’s important



