Washington State Sales Tax
Washington State, known for its diverse landscape and thriving industries, has a unique approach to sales tax that impacts businesses and consumers alike. Understanding the intricacies of Washington's sales tax system is crucial for anyone operating within the state's borders or planning to do business there. This comprehensive guide will delve into the specifics of Washington State sales tax, offering a detailed analysis of its structure, rates, and implications.
Understanding Washington State Sales Tax

Washington State is one of the few states in the US that operates under a purely retail sales tax system, which means it does not impose a general sales tax on all goods and services. Instead, it focuses on taxing retail sales, with some specific exemptions and additional taxes in certain industries.
The state's sales tax system is governed by the Washington State Department of Revenue, which oversees tax administration and ensures compliance with state tax laws. This department provides guidelines, resources, and support for businesses and individuals to understand and meet their tax obligations.
Sales Tax Rates in Washington State
Washington State’s sales tax rates can vary depending on the location and the type of transaction. The state imposes a base sales tax rate of 6.5%, which applies to most retail sales of tangible personal property and certain services. However, this base rate is often augmented by local sales taxes, resulting in a higher effective tax rate for many transactions.
Local sales taxes in Washington are levied by counties, cities, and special purpose districts. These additional taxes can range from a few tenths of a percent to over 2%, depending on the jurisdiction. For example, in Seattle, the combined state and local sales tax rate is approximately 10.1%, one of the highest in the state.
| Location | State Sales Tax Rate | Local Sales Tax Rate | Total Sales Tax Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seattle | 6.5% | 3.6% | 10.1% |
| Spokane | 6.5% | 2.5% | 9% |
| Tacoma | 6.5% | 2.9% | 9.4% |
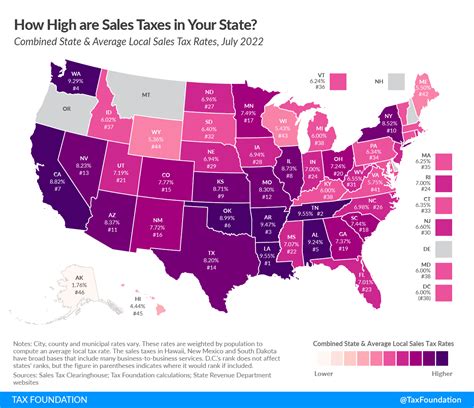
It's important to note that not all locations in Washington have additional local sales taxes. Some areas, particularly in rural parts of the state, operate with the base state sales tax rate of 6.5%.
Sales Tax Exemptions and Special Taxes
Washington State also has a number of sales tax exemptions and special taxes that apply to specific goods and services. These can further complicate the sales tax landscape for businesses and consumers.
Some common sales tax exemptions in Washington include:
- Food products for home consumption
- Prescription and non-prescription drugs
- Most clothing items
- Sales between businesses for resale or manufacturing purposes
Additionally, there are special taxes in certain industries, such as the Real Estate Excise Tax on the sale of real property and the B&O Tax (Business & Occupation Tax) on the gross income of businesses operating in the state.
Sales Tax Registration and Compliance
Any business selling taxable goods or services in Washington State is required to register with the Department of Revenue and obtain a Business License and a Sales Tax Permit. This registration process ensures that businesses are authorized to collect and remit sales tax on behalf of the state.
Businesses are responsible for calculating the correct sales tax rate for each transaction, collecting the tax from customers, and then remitting it to the Department of Revenue on a regular basis. The frequency of these remittances can vary depending on the business's sales volume and tax liability.
Compliance with sales tax regulations is crucial to avoid penalties and legal issues. The Department of Revenue has strict guidelines and procedures for sales tax reporting, and businesses are expected to maintain accurate records and provide detailed reports.
Sales Tax Collection and Remittance
When collecting sales tax, businesses in Washington State must ensure they are charging the correct rate based on the location of the sale and the nature of the transaction. This often involves a careful understanding of the state’s sales tax laws and regulations.
Sales tax collection can be integrated into a business's point-of-sale (POS) system or accounting software to ensure accuracy and ease of reporting. Businesses may also need to consider the impact of online sales and the collection of sales tax for out-of-state customers, especially with the recent changes in sales tax laws due to the Wayfair decision.
Once collected, sales tax must be remitted to the Department of Revenue on a regular basis. The frequency of remittance can vary, with some businesses remitting monthly, quarterly, or annually, depending on their sales volume and tax liability.
| Remittance Frequency | Sales Tax Liability Threshold |
|---|---|
| Monthly | $5,000 or more in taxable sales |
| Quarterly | Less than $5,000 in taxable sales |
| Annually | Limited sales (e.g., farmers' market vendors) |
Businesses are required to file sales tax returns, providing detailed information on taxable sales, exemptions, and the total amount of sales tax collected. Late or incorrect filings can result in penalties and interest charges.
Impact on Businesses and Consumers
Washington State’s sales tax system has a significant impact on both businesses and consumers within the state.
Impact on Businesses
For businesses, the sales tax system in Washington presents both opportunities and challenges. On the one hand, a higher sales tax rate can lead to increased revenue for the business, especially if it is passed on to the consumer. However, it can also make it more challenging to compete with businesses in states with lower tax rates.
Compliance with sales tax regulations can be a complex and time-consuming task, especially for small businesses with limited resources. The need to understand and apply different tax rates based on location, as well as navigate the various exemptions and special taxes, can be a significant burden.
Additionally, businesses selling online or across state lines may face additional challenges in determining their sales tax obligations. The recent changes in sales tax laws due to the Wayfair decision have made it more difficult for out-of-state sellers to avoid collecting sales tax in Washington.
Impact on Consumers
Consumers in Washington State are directly impacted by the sales tax system, as they bear the ultimate responsibility for paying the tax on their purchases. The varying sales tax rates across the state can make it more expensive to shop in certain areas, particularly in cities with higher local sales taxes.
However, the sales tax system also provides some benefits to consumers. For example, the exemption of certain essential items like food and clothing can help alleviate the tax burden on low-income households. Additionally, the absence of a general sales tax on all goods and services can make Washington a more attractive destination for shoppers, especially those from states with higher sales tax rates.
Future Implications and Considerations
Washington State’s sales tax system is subject to ongoing changes and developments, both at the state and federal levels. Understanding these potential changes is crucial for businesses and consumers alike.
Potential Changes in Sales Tax Rates
Sales tax rates in Washington State can be subject to change, often as a result of legislative actions or ballot initiatives. While the base state sales tax rate has remained relatively stable, local sales taxes can fluctuate based on the needs and decisions of local governments.
Businesses and consumers should stay informed about any proposed or enacted changes to sales tax rates to ensure they are compliant and can adapt their strategies accordingly. Monitoring local and state news sources, as well as staying in touch with tax professionals, can help keep stakeholders informed about potential tax changes.
Impact of E-Commerce and Online Sales
The rise of e-commerce and online sales has significantly impacted Washington State’s sales tax system. With more consumers shopping online, the collection of sales tax from out-of-state sellers has become a complex issue.
The Wayfair decision, which allowed states to require out-of-state sellers to collect sales tax even if they don't have a physical presence in the state, has had a significant impact on Washington's sales tax landscape. This decision has made it more challenging for online sellers to avoid collecting sales tax in Washington, potentially increasing revenue for the state and impacting the competitiveness of online businesses.
Comparison with Other States
Washington State’s sales tax system is unique compared to many other states in the US. While some states have higher or lower sales tax rates, the absence of a general sales tax on all goods and services in Washington sets it apart.
This difference can make Washington a more attractive destination for shoppers, especially those from states with higher sales tax rates. However, it can also present challenges for businesses operating in Washington, as they may face increased competition from out-of-state sellers who do not have to collect sales tax.
Sales Tax Simplification Efforts
The complexity of Washington State’s sales tax system, with its varying rates and exemptions, has led to calls for simplification. While simplifying the tax system could reduce compliance burdens for businesses and improve transparency for consumers, it may also require a significant shift in how sales tax is administered and collected.
Efforts to simplify the sales tax system in Washington are ongoing, with proposals and discussions taking place at both the state and federal levels. These efforts aim to create a more streamlined and understandable tax system, which could have significant implications for businesses and consumers alike.
What is the current sales tax rate in Washington State for online purchases?
+As of my last update in January 2023, the sales tax rate for online purchases in Washington State varies depending on the location of the buyer. Generally, online sellers are required to collect the combined state and local sales tax rate applicable to the buyer’s shipping address. This can range from around 6.5% to over 10% depending on the location.
Are there any sales tax holidays in Washington State?
+No, Washington State does not have any official sales tax holidays. However, some local jurisdictions may offer sales tax exemptions or reductions for specific items during certain promotional events or periods.
How does Washington State handle sales tax for remote sellers (sellers without a physical presence in the state)?
+Washington State requires remote sellers to collect and remit sales tax if they meet certain economic thresholds. This is in accordance with the Supreme Court’s ruling in the Wayfair case. Remote sellers are typically required to register with the Department of Revenue and collect the appropriate sales tax based on the buyer’s location.



