Washington Fuel Tax

The state of Washington, known for its lush landscapes and thriving industries, has a complex relationship with fuel taxes. As a crucial source of revenue for transportation infrastructure and environmental initiatives, understanding the intricacies of Washington's fuel tax is essential. This article delves into the details, exploring the historical context, current rates, and future implications of this vital tax.
A Historical Perspective on Washington’s Fuel Tax
Washington’s journey with fuel taxation began in the early 20th century, when the state first imposed a tax on gasoline to fund road construction and maintenance. Over the decades, this tax has evolved to keep pace with the state’s growing transportation needs and changing economic landscapes.
One of the significant milestones in Washington's fuel tax history was the implementation of the Motor Fuel Tax Act in 1937. This act established a dedicated fund, known as the Motor Fuel Tax Account, to support the construction and upkeep of the state's highway system. The act also introduced a flat rate tax on gasoline, which has since been adjusted periodically to account for inflation and evolving transportation demands.
In the late 20th century, Washington witnessed a surge in environmental consciousness, prompting the state to explore ways to integrate ecological considerations into its fuel taxation system. This led to the creation of the Washington State Clean Air Act in 1991, which introduced additional taxes on fuels to fund air quality improvement projects and research.
Furthermore, Washington's commitment to environmental sustainability was evident in the establishment of the Climate Commitment Act in 2021. This act aimed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and set ambitious targets for a carbon-neutral future. As a result, the state implemented a carbon fee on transportation fuels, marking a significant shift in the state's fuel taxation landscape.
Current Fuel Tax Rates and Their Impact

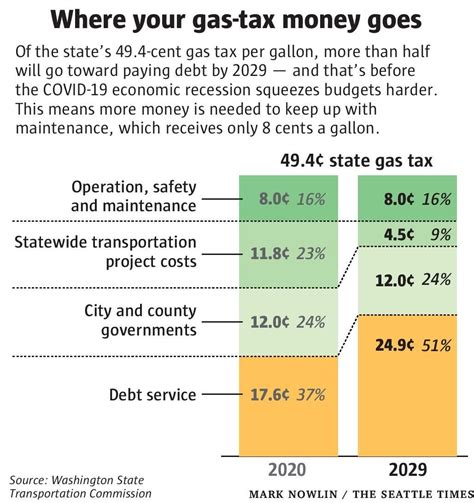
As of 2023, Washington’s fuel tax rates stand at 0.494 per gallon for gasoline and 0.546 per gallon for diesel fuel. These rates are among the highest in the nation and reflect the state’s dedication to maintaining its extensive transportation network and advancing its environmental agenda.
The revenue generated from these fuel taxes is distributed across various state funds, with the majority allocated to the Motor Fuel Tax Account. This fund primarily supports the Washington State Department of Transportation's (WSDOT) activities, including highway construction, maintenance, and safety improvements.
Additionally, a portion of the fuel tax revenue is directed towards the Motor Vehicle Account, which finances the operations of the Washington State Patrol and other law enforcement agencies related to motor vehicle administration and safety. This ensures a seamless flow of resources to maintain public safety on the state's roads.
The impact of Washington's fuel tax extends beyond immediate revenue generation. The tax plays a pivotal role in shaping the state's transportation policy and infrastructure development. By providing a steady stream of funding, the tax enables WSDOT to plan and execute long-term projects, ensuring the state's roads remain efficient, safe, and environmentally friendly.
Fuel Tax Exemptions and Incentives
Washington also offers specific fuel tax exemptions and incentives to promote sustainable practices and support certain industries. For instance, biodiesel producers and distributors are eligible for a tax credit, encouraging the use of cleaner fuels. Similarly, electric vehicle (EV) owners benefit from a reduced fuel tax rate, promoting the adoption of environmentally friendly transportation options.
| Fuel Type | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Gasoline | $0.494 per gallon |
| Diesel | $0.546 per gallon |
| Biodiesel | Eligible for tax credits |
| Electric Vehicles | Reduced fuel tax rate |

These exemptions and incentives are carefully crafted to balance the state's fiscal needs with its environmental goals, creating a delicate equilibrium that fosters sustainable practices and innovation.
The Future of Washington’s Fuel Tax: Navigating Challenges and Opportunities
As Washington navigates the evolving landscape of transportation and energy, the future of its fuel tax system holds both challenges and opportunities. With the rise of electric and alternative fuel vehicles, the state faces the task of adapting its taxation policies to ensure a continued revenue stream while encouraging the adoption of cleaner technologies.
One of the primary challenges is the potential decline in fuel tax revenue as more drivers opt for electric or hybrid vehicles. To address this, Washington is exploring innovative solutions, such as road usage charges or vehicle miles traveled (VMT) fees, which would ensure a sustainable source of funding for transportation infrastructure regardless of the fuel type.
Additionally, the state is investing in research and development to enhance its understanding of emerging technologies and their implications for fuel taxation. This proactive approach allows Washington to stay ahead of the curve, ensuring its fuel tax system remains relevant and effective in the face of technological advancements.
Embracing Sustainability: The Role of Fuel Taxes in Washington’s Green Initiatives
Washington’s fuel tax system is intricately linked to its commitment to sustainability and environmental protection. The revenue generated from these taxes plays a crucial role in funding initiatives that reduce carbon emissions and promote clean energy alternatives.
For instance, a significant portion of the fuel tax revenue is directed towards the state's Clean Energy Fund, which supports projects and research aimed at transitioning Washington towards a carbon-neutral future. This includes investments in renewable energy infrastructure, energy efficiency programs, and the development of sustainable transportation options.
Furthermore, Washington's fuel tax system incentivizes the use of cleaner fuels and electric vehicles, encouraging residents to adopt more sustainable transportation practices. By offering tax credits and reduced fuel tax rates for eco-friendly vehicles, the state promotes a shift towards a greener and more environmentally conscious transportation sector.
In conclusion, Washington's fuel tax system is a complex yet vital component of the state's transportation and environmental policies. By understanding its historical context, current rates, and future implications, we can appreciate the role it plays in shaping the state's infrastructure, sustainability efforts, and overall economic landscape.
How does Washington’s fuel tax revenue compare to other states?
+
Washington’s fuel tax rates are among the highest in the nation, reflecting the state’s commitment to infrastructure development and environmental initiatives. While this may result in higher prices at the pump, it ensures a robust funding source for critical transportation projects and sustainability efforts.
What percentage of Washington’s fuel tax revenue is allocated to environmental projects?
+
A significant portion of Washington’s fuel tax revenue is directed towards environmental projects and initiatives. This includes funding for air quality improvement, renewable energy development, and research into sustainable transportation solutions. The state’s dedication to sustainability ensures that a substantial portion of the tax revenue contributes to a greener future.
How does Washington plan to address the potential decline in fuel tax revenue due to the rise of electric vehicles?
+
Washington is actively exploring alternative funding mechanisms, such as road usage charges or vehicle miles traveled (VMT) fees, to ensure a stable revenue stream for transportation infrastructure. These innovative solutions would ensure that all vehicles, regardless of their fuel type, contribute to the maintenance and development of the state’s roads and highways.
Are there any plans to reduce Washington’s fuel tax rates in the future?
+
While there are no immediate plans to reduce fuel tax rates, Washington is committed to regularly reviewing and adjusting its tax policies to align with the state’s evolving transportation needs and economic realities. Any changes would be carefully considered to ensure a balanced approach that supports both infrastructure development and sustainability initiatives.



