Wa State Sales Tax

In the state of Washington, the sales tax is a crucial aspect of the state's revenue system and a significant consideration for both businesses and consumers. This article aims to provide an in-depth exploration of the Wa State Sales Tax, its intricacies, and its impact on the local economy.
Understanding Wa State Sales Tax
The sales tax in Washington, often referred to as Wa State Sales Tax, is a consumption tax levied on the sale of goods and services within the state. It is an essential revenue generator for the state government, contributing to the funding of various public services and infrastructure projects.
Washington's sales tax operates on a destination-based principle, which means the tax rate is determined by the location where the product is ultimately consumed or the service is rendered. This unique feature sets it apart from many other states and introduces certain complexities for businesses operating across state lines.
The tax is typically added to the purchase price of an item, with the seller responsible for collecting and remitting the tax to the state. It is important to note that the sales tax rate can vary depending on the jurisdiction, with different rates applicable to different counties and municipalities within the state.
Key Features and Characteristics
Wa State Sales Tax is known for its comprehensive coverage, applying to a wide range of goods and services. While certain items are exempt, such as groceries and prescription drugs, most retail transactions are subject to the tax.
One notable aspect of Washington's sales tax is its business and occupation (B&O) tax, which is a gross receipts tax. This tax is imposed on the value of products sold, gross proceeds of sales, or gross income, depending on the business activity. The B&O tax is often considered a complement to the sales tax, as it captures a broader range of economic activities.
Furthermore, Washington has implemented a streamlined sales tax program, which aims to simplify sales tax collection and compliance for businesses operating in multiple jurisdictions. This program has been instrumental in harmonizing tax rates and regulations across the state, making it easier for businesses to navigate the complex sales tax landscape.
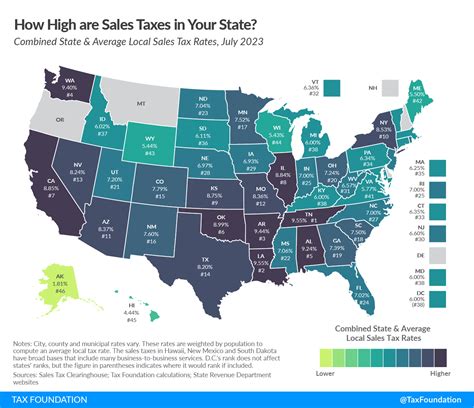
| Sales Tax Rate Type | Rate |
|---|---|
| Statewide Sales Tax Rate | 6.5% |
| Average County and City Rate | 1.46% |
| Total Average Combined Rate | 8.21% |

Sales Tax Exemptions and Special Considerations
While Wa State Sales Tax is applied broadly, there are certain exemptions and special considerations that businesses and consumers should be aware of.
Exempt Items and Services
Some items and services are exempt from sales tax in Washington. These include:
- Groceries: Essential food items purchased from grocery stores are exempt from sales tax.
- Prescription Drugs: Medications prescribed by a licensed healthcare professional are tax-free.
- Educational Materials: Certain educational resources, such as textbooks and school supplies, are exempt.
- Residential Rent: Rent for residential properties is not subject to sales tax.
- Manufacturing Equipment: Machinery and equipment used in manufacturing processes are often exempt.
Special Tax Rates and Areas
Washington also has specific areas and industries with unique tax rates and considerations.
For instance, in the Puget Sound region, there is an additional tax of 0.5% to support the Sound Transit system, which provides public transportation services. This tax is added to the standard sales tax rate for the counties within the region.
Additionally, certain industries, such as the aerospace sector, may benefit from tax incentives and exemptions as part of the state's efforts to promote economic development and attract businesses.
Compliance and Reporting
Ensuring compliance with Wa State Sales Tax regulations is crucial for businesses to avoid penalties and maintain a positive relationship with the state. Here are some key aspects of compliance and reporting.
Registration and Permits
Businesses selling taxable goods or services in Washington must obtain a Business License from the state and register for a Sales and Use Tax Permit. This permit allows businesses to collect and remit sales tax to the state.
The registration process involves providing detailed information about the business, its activities, and its tax obligations. This information is critical for the state to accurately assess the business's tax liability and ensure compliance.
Tax Collection and Remittance
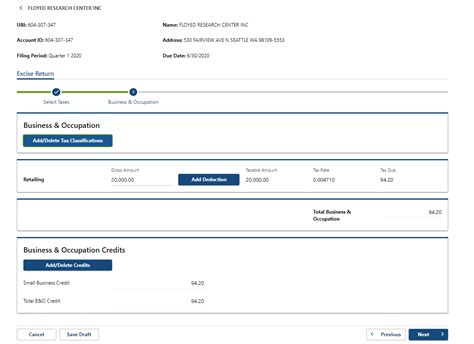
Businesses are responsible for collecting the appropriate sales tax from customers at the point of sale. This tax is then remitted to the state on a regular basis, typically monthly or quarterly, depending on the business’s tax liability and reporting frequency.
The remittance process involves filing tax returns with the Washington State Department of Revenue, providing detailed information about sales, tax collected, and any applicable exemptions or deductions.
Audits and Enforcement
The Washington State Department of Revenue conducts audits to ensure compliance with sales tax regulations. These audits can be random or targeted, and businesses must be prepared to provide accurate records and documentation to support their tax filings.
Failure to comply with sales tax regulations can result in penalties, interest, and even criminal charges in severe cases. It is essential for businesses to maintain accurate records, calculate taxes correctly, and remit payments promptly to avoid legal issues.
Impact on the Economy and Consumers
Wa State Sales Tax has a significant impact on both the state’s economy and consumers. Here’s an exploration of these effects.
Economic Impact
The sales tax is a vital source of revenue for the state, contributing to the funding of essential public services and infrastructure projects. It supports areas such as education, healthcare, transportation, and public safety, which are crucial for the state’s overall economic health and development.
Furthermore, the tax revenue generated helps stimulate economic growth by funding initiatives that create jobs and attract businesses. It also supports the state's efforts to provide a high quality of life for its residents and maintain a competitive business environment.
Consumer Perspective
From a consumer perspective, the sales tax can significantly impact purchasing decisions and overall spending power. The tax adds to the cost of goods and services, potentially influencing consumer behavior and spending patterns.
However, the tax also provides certain benefits to consumers. For instance, the tax revenue is used to fund public services and infrastructure, which indirectly benefits consumers through improved roads, schools, and healthcare facilities. Additionally, the tax system's exemptions for essential items, such as groceries, can help reduce the tax burden on low-income households.
Future Considerations and Potential Changes

As with any tax system, Wa State Sales Tax is subject to potential changes and reforms over time. Here are some future considerations and possible directions for the tax.
Potential Reforms and Simplification
There have been ongoing discussions and proposals for simplifying the sales tax system in Washington. This includes efforts to reduce the complexity of tax rates and regulations, especially for businesses operating across multiple jurisdictions.
One potential reform is the standardization of tax rates across the state, eliminating the variation in rates between counties and municipalities. This could make it easier for businesses to comply with tax regulations and reduce the administrative burden associated with managing multiple tax rates.
Technology and Digital Sales Tax
The rise of e-commerce and digital sales has presented new challenges for sales tax collection and compliance. Washington, like many other states, is exploring ways to effectively tax online sales and ensure that businesses operating solely online are contributing to the state’s revenue.
The state may consider implementing a digital sales tax, which would apply to remote sellers and ensure that online transactions are subject to the appropriate sales tax. This would help level the playing field between traditional brick-and-mortar businesses and online retailers.
Tax Incentives and Economic Development
Washington may continue to utilize tax incentives and exemptions as a tool for economic development and attracting businesses. This could involve offering tax breaks or special tax rates to industries that align with the state’s economic goals, such as technology, clean energy, or healthcare.
By providing these incentives, the state can encourage businesses to invest in Washington, create jobs, and contribute to the overall economic growth of the region.
What is the current statewide sales tax rate in Washington?
+As of my last update in January 2023, the statewide sales tax rate in Washington is 6.5%.
Are there any upcoming changes to the sales tax rates in Washington?
+While I cannot predict future changes, there are ongoing discussions and proposals for tax reforms in Washington. It is advisable to stay updated with the latest news and announcements from the Washington State Department of Revenue for any potential changes to sales tax rates.
How often do businesses need to file sales tax returns in Washington?
+The filing frequency for sales tax returns depends on the business’s tax liability and reporting frequency determined by the Washington State Department of Revenue. Typically, businesses file sales tax returns monthly or quarterly.
Are there any sales tax holidays in Washington?
+Washington does not currently have any sales tax holidays. However, there may be specific tax incentives or programs offered by the state for certain industries or purchases.
Can you provide examples of items that are exempt from sales tax in Washington?
+Yes, some common items exempt from sales tax in Washington include groceries, prescription drugs, educational materials, residential rent, and manufacturing equipment.