Utah Income Tax
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on Utah's income tax system, a vital aspect of the state's financial landscape. Understanding the intricacies of income taxation is crucial for individuals and businesses alike, as it directly impacts their financial planning and overall economic health. In this article, we will delve deep into the specifics of Utah's income tax laws, offering a detailed analysis of the rates, brackets, deductions, and credits that make up this essential component of the state's revenue generation.
Unraveling the Utah Income Tax System
Utah’s income tax system is a fundamental pillar of the state’s financial framework, playing a significant role in funding essential public services and infrastructure projects. The state’s income tax is progressive, meaning that higher incomes are taxed at higher rates, fostering a fair and equitable revenue collection system.
Tax Rates and Brackets
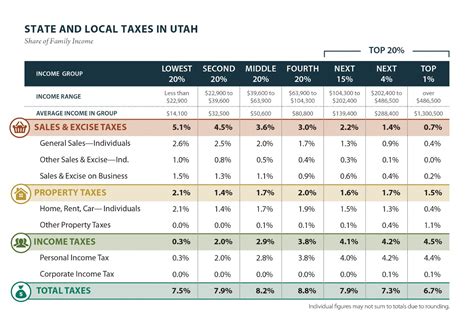
Utah’s income tax rates are divided into several brackets, each with its own tax percentage. These brackets are designed to ensure that individuals and businesses contribute proportionally to the state’s revenue, based on their income levels. The current tax rates for the year 2024 are as follows:
| Tax Bracket | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| First $4,000 of Taxable Income | 4.95% |
| $4,001 - $6,000 | 5.35% |
| $6,001 - $8,000 | 5.40% |
| $8,001 - $10,000 | 5.45% |
| $10,001 - $12,000 | 5.50% |
| Over $12,000 | 5.70% |

These tax rates are applicable to both individuals and businesses, with some variations for specific types of entities. For instance, corporations face a flat tax rate of 5% on their taxable income, while S corporations and limited liability companies (LLCs) are taxed at the individual rate based on the profits allocated to their members.
Deductions and Credits
Utah offers a range of deductions and credits to alleviate the tax burden on individuals and businesses. These provisions allow taxpayers to reduce their taxable income, thereby lowering their overall tax liability. Some of the key deductions and credits include:
- Standard Deduction: Utah residents can claim a standard deduction based on their filing status. For the tax year 2024, the standard deduction amounts are $2,250 for single filers, $4,500 for married filing jointly, and $3,375 for heads of household.
- Itemized Deductions: Taxpayers can choose to itemize their deductions instead of claiming the standard deduction. This involves listing out eligible expenses such as medical costs, charitable contributions, state and local taxes, and mortgage interest. The total of these itemized deductions must exceed the standard deduction amount to provide a tax benefit.
- Personal Exemptions: Utah allows personal exemptions for each taxpayer and dependent. These exemptions reduce the taxable income, providing a direct benefit to individuals with dependents or those who file as single taxpayers.
- Education Credits: Utah offers a variety of education credits to encourage investment in education. These include the Lifetime Learning Credit, the American Opportunity Credit, and the Utah Tuition and Fees Deduction, all of which can significantly reduce the tax liability for students and their families.
- Business Credits: Utah's business tax credits are designed to stimulate economic growth and job creation. These credits include the High-Wage Job Creation Tax Credit, the Angel Investor Tax Credit, and the Rural Economic Development Tax Credit, each targeting specific business activities and sectors.
Tax Filing and Payment
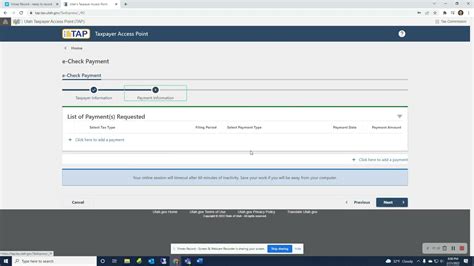
Utah’s tax filing and payment process is streamlined and accessible. Taxpayers can file their income tax returns electronically or by mail, depending on their preference and the complexity of their tax situation. The state offers a user-friendly online filing system, MyTax, which allows individuals and businesses to file their returns and make payments securely.
For those who owe taxes, Utah offers various payment options, including direct bank account debits, credit or debit card payments, and payment by check or money order. Taxpayers can also set up payment plans or apply for extensions if they are unable to pay their taxes in full by the deadline.
Taxable Income and Exemptions
Utah’s income tax applies to various sources of income, including wages, salaries, commissions, bonuses, tips, and self-employment income. It also includes income from investments, such as interest, dividends, capital gains, and rental income. However, not all income is taxable in Utah.
The state exempts certain types of income from taxation. These exemptions include:
- Social Security benefits
- Pensions and annuities
- Military retirement pay
- Worker's compensation benefits
- Veteran's benefits
- Certain government benefits
- Income from certain government-sponsored programs
These exemptions ensure that individuals receiving specific forms of income are not subject to double taxation, maintaining a fair and balanced tax system.
Impact on the State Economy
Utah’s income tax system plays a critical role in shaping the state’s economic landscape. The revenue generated from income taxes funds essential public services, such as education, healthcare, transportation, and public safety. It also supports the state’s infrastructure development, ensuring that Utah remains a desirable place to live, work, and invest.
Furthermore, the income tax system influences business decisions and investment strategies. The state's competitive tax rates and various tax incentives encourage businesses to establish and expand their operations in Utah, contributing to job growth and economic prosperity.
Conclusion

Utah’s income tax system is a vital component of the state’s financial framework, offering a balanced approach to revenue generation. By understanding the intricacies of the tax rates, brackets, deductions, and credits, individuals and businesses can effectively navigate the tax landscape and plan their financial strategies accordingly. As the state continues to evolve and adapt to changing economic conditions, the income tax system will remain a critical tool for fostering economic growth and stability.
When is the deadline for filing Utah income tax returns?
+The deadline for filing Utah income tax returns is typically April 15th each year. However, if this date falls on a weekend or holiday, the deadline is extended to the next business day. It’s important to note that the filing deadline may vary depending on the specific circumstances and the type of tax return being filed.
Can I file my Utah income tax return electronically?
+Yes, Utah offers an electronic filing system called MyTax which allows individuals and businesses to file their income tax returns online securely. Electronic filing is a convenient and efficient way to submit tax returns, and it is highly recommended by the Utah State Tax Commission.
What happens if I miss the filing deadline for my Utah income tax return?
+If you miss the filing deadline for your Utah income tax return, you may be subject to penalties and interest charges. The state imposes a late filing penalty of 5% of the unpaid tax for each month (or part of a month) that the return is late, up to a maximum of 25%. Additionally, interest is charged on any unpaid tax balance at a rate of 0.5% per month (or part of a month) until the balance is paid in full.



