Treasury Bills Taxed

Treasury bills, often referred to as T-bills, are a popular investment option for individuals and institutions seeking a secure and low-risk way to grow their wealth. These short-term debt securities issued by the U.S. government are considered one of the safest investments due to their full backing by the federal government. While the interest earned on T-bills is typically modest, they offer a reliable return and play a crucial role in the nation's financial landscape.
However, it's essential to understand the tax implications of investing in Treasury bills. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) treats the interest earned on T-bills as ordinary income, subject to taxation at the investor's applicable tax rate. This article will delve into the world of Treasury bills, exploring their characteristics, tax treatment, and strategies to navigate the tax landscape effectively.
Understanding Treasury Bills
Treasury bills are short-term debt obligations issued by the U.S. Department of the Treasury to finance the federal government's operations and deficit spending. They are considered highly liquid and safe investments, making them attractive to risk-averse investors and those seeking a stable return.
T-bills are available in various maturities, typically ranging from 4 weeks to 52 weeks. The most common maturities are 4-week, 13-week, and 26-week bills. These securities are sold at a discount from their face value and mature at par, meaning investors receive the full face value upon maturity. For instance, an investor might purchase a $1,000 T-bill for $990 and receive the full $1,000 upon maturity.
The difference between the purchase price and the face value represents the interest earned, known as the discount yield. This yield is determined by the market forces of supply and demand, with the Treasury conducting regular auctions to set the discount rates for each maturity.
Key Characteristics of Treasury Bills:
- Face Value: T-bills have a minimum face value of $100 and are sold in multiples of $100, making them accessible to a wide range of investors.
- Discount Yield: The interest earned on T-bills is the difference between the purchase price and the face value, providing a fixed rate of return.
- Auctions: The Treasury conducts regular auctions, typically on a weekly basis, to determine the discount rates for each maturity.
- Maturity Dates: T-bills have specific maturity dates, and investors receive the full face value upon maturity.
- Liquidity: T-bills are highly liquid and can be easily bought and sold in the secondary market.
Taxation of Treasury Bills

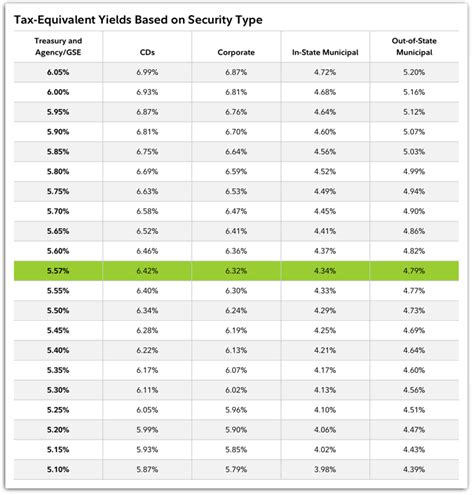
When it comes to taxes, Treasury bills are treated differently from other investment vehicles. The interest earned on T-bills, known as the discount yield, is considered ordinary income and is subject to federal income tax at the investor's applicable tax rate.
This tax treatment applies to all types of T-bills, regardless of the maturity date or the investor's holding period. The IRS requires investors to include the interest earned from T-bills in their gross income for the tax year in which the bills mature.
Tax Reporting and Withholding:
Investors in Treasury bills must report the interest income on their federal income tax returns. The IRS provides specific forms and instructions for reporting income from T-bills and other federal securities.
In some cases, the Treasury may withhold a portion of the interest earned as tax withholding. This withholding is typically applied to non-resident aliens and certain institutions. Investors can claim a credit for the amount withheld on their tax returns.
State and Local Taxes:
While Treasury bills are generally exempt from state and local taxes, this exemption may vary depending on the state and the investor's residency status. It's essential for investors to consult their state's tax regulations to determine if any state or local taxes apply to their T-bill investments.
Strategies for Tax Efficiency
Understanding the tax implications of Treasury bills is crucial for investors to optimize their investment strategies. Here are some strategies to consider when investing in T-bills:
Diversification:
Diversifying your investment portfolio can help manage tax liability. By investing in a mix of T-bills with different maturities, you can spread out the tax impact over multiple tax years. This strategy can be particularly beneficial for investors with high tax brackets, as it allows them to manage their income levels and potentially reduce their overall tax burden.
Strategic Timing:
Timing your T-bill investments can have tax advantages. Consider purchasing T-bills towards the end of the tax year to delay the recognition of interest income until the following year. This strategy can be useful for investors who expect their income or tax bracket to decrease in the subsequent year.
Tax-Advantaged Accounts:
Investing in T-bills within tax-advantaged accounts, such as Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) or 401(k) plans, can provide significant tax benefits. These accounts allow investors to defer taxes on the interest earned until withdrawal, offering a tax-efficient way to grow wealth over the long term.
Tax Loss Harvesting:
If you have realized losses from other investments, you can use those losses to offset the gains from your T-bill investments. This strategy, known as tax loss harvesting, can help reduce your overall tax liability and provide a more tax-efficient portfolio.
Consideration for High-Income Earners:
For high-income earners, investing in T-bills may result in a higher tax rate due to the ordinary income treatment. In such cases, it's essential to explore alternative investment options or consult a tax advisor to find strategies that align with your financial goals and tax situation.
Performance Analysis and Market Impact
The performance of Treasury bills is closely tied to market conditions and economic factors. While T-bills are considered low-risk investments, their yields can be influenced by various economic indicators and policy decisions.
During periods of economic uncertainty or low-interest-rate environments, Treasury bills may offer a relatively higher yield compared to other short-term investments. However, in a rising interest rate environment, the demand for T-bills may decrease, leading to lower yields.
Investors should closely monitor economic indicators such as the federal funds rate, inflation rates, and market sentiment to gauge the potential impact on T-bill yields. Additionally, understanding the role of the Federal Reserve and its monetary policy decisions is crucial for making informed investment choices.
Market Impact on Treasury Bills:
| Economic Indicator | Impact on T-bills |
|---|---|
| Rising Interest Rates | Lower yields and decreased demand |
| Economic Uncertainty | Higher yields as a safe-haven investment |
| Federal Funds Rate Changes | Influence on market interest rates and T-bill yields |
| Inflation Rates | Impact on real returns and purchasing power |

Future Implications and Investment Outlook

The future of Treasury bills is closely tied to the overall economic outlook and monetary policy decisions. As the federal government continues to manage its debt and funding needs, T-bills will remain a crucial component of the nation's financial landscape.
For investors, the appeal of T-bills as a low-risk, secure investment option is expected to persist. However, the ongoing debate around interest rates and the potential for rate hikes may impact the demand and yields associated with T-bills. Investors should stay informed about economic trends and monetary policy shifts to make well-informed investment decisions.
Furthermore, the growing popularity of digital platforms and online brokerage accounts has made it easier for individual investors to access and trade Treasury bills. This increased accessibility may lead to a broader investor base and potentially impact the market dynamics of T-bills.
Conclusion
Treasury bills provide a stable and secure investment opportunity, particularly for risk-averse investors. However, understanding the tax implications and navigating the tax landscape is essential to maximizing the returns from T-bill investments. By employing strategic diversification, timing, and utilizing tax-advantaged accounts, investors can optimize their tax efficiency and overall investment strategy.
As the financial markets continue to evolve, staying informed about economic trends and monetary policy decisions will be crucial for investors to make well-informed choices and adapt their strategies accordingly. Treasury bills remain a vital component of a diversified investment portfolio, offering a reliable and low-risk option for long-term wealth accumulation.
Frequently Asked Questions
How are Treasury Bills taxed differently from other investments?
+
Treasury Bills are taxed as ordinary income, which means the interest earned is subject to federal income tax at the investor’s applicable tax rate. This differs from other investments like stocks or bonds, where capital gains taxes may apply.
Are Treasury Bills exempt from state and local taxes?
+
Generally, Treasury Bills are exempt from state and local taxes. However, this exemption may vary depending on the state and the investor’s residency status. It’s important to consult your state’s tax regulations to determine if any state or local taxes apply.
How can I minimize the tax impact of my Treasury Bill investments?
+
To minimize the tax impact, consider diversifying your investment portfolio with T-bills of different maturities, strategically timing your purchases, and investing in tax-advantaged accounts like IRAs or 401(k) plans. Additionally, tax loss harvesting can help offset gains from T-bills.
What is the role of the Federal Reserve in Treasury Bill yields?
+
The Federal Reserve’s monetary policy decisions, particularly changes in the federal funds rate, can influence market interest rates and, consequently, the yields of Treasury Bills. Investors should monitor Fed announcements and economic indicators to understand their impact on T-bill yields.
Can I invest in Treasury Bills online through brokerage accounts?
+
Yes, many online brokerage platforms offer the ability to buy and sell Treasury Bills. These platforms provide easy access to T-bill auctions and allow investors to manage their holdings conveniently. However, it’s important to research and choose a reputable brokerage platform for your investments.