Texas Sales Tax Permit

Navigating the complex landscape of sales tax compliance is an essential aspect of running a successful business, especially in a state as dynamic as Texas. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the Texas Sales Tax Permit, covering its requirements, registration process, and the implications for businesses operating within the state.
Understanding the Texas Sales Tax Permit

The Texas Sales Tax Permit, officially known as the Texas Seller’s Permit, is a legal authorization granted by the Texas Comptroller of Public Accounts to businesses engaging in taxable sales or leasing activities within the state. It is a critical component of a business’s tax obligations, ensuring compliance with state laws and facilitating the accurate collection and remittance of sales taxes.
Sales tax is a crucial source of revenue for the state, contributing significantly to the funding of public services and infrastructure. As such, the Texas Comptroller's office takes a rigorous approach to tax compliance, making it essential for businesses to understand their sales tax obligations and responsibilities.
The permit is not just a regulatory requirement; it is a tool for businesses to legally operate and thrive in the Texas market. It enables businesses to collect and remit sales tax accurately, ensuring a fair and competitive environment for all businesses and consumers alike. Furthermore, it provides a legal framework for businesses to protect themselves from potential penalties and legal issues that could arise from non-compliance.
The Significance of Sales Tax in Texas
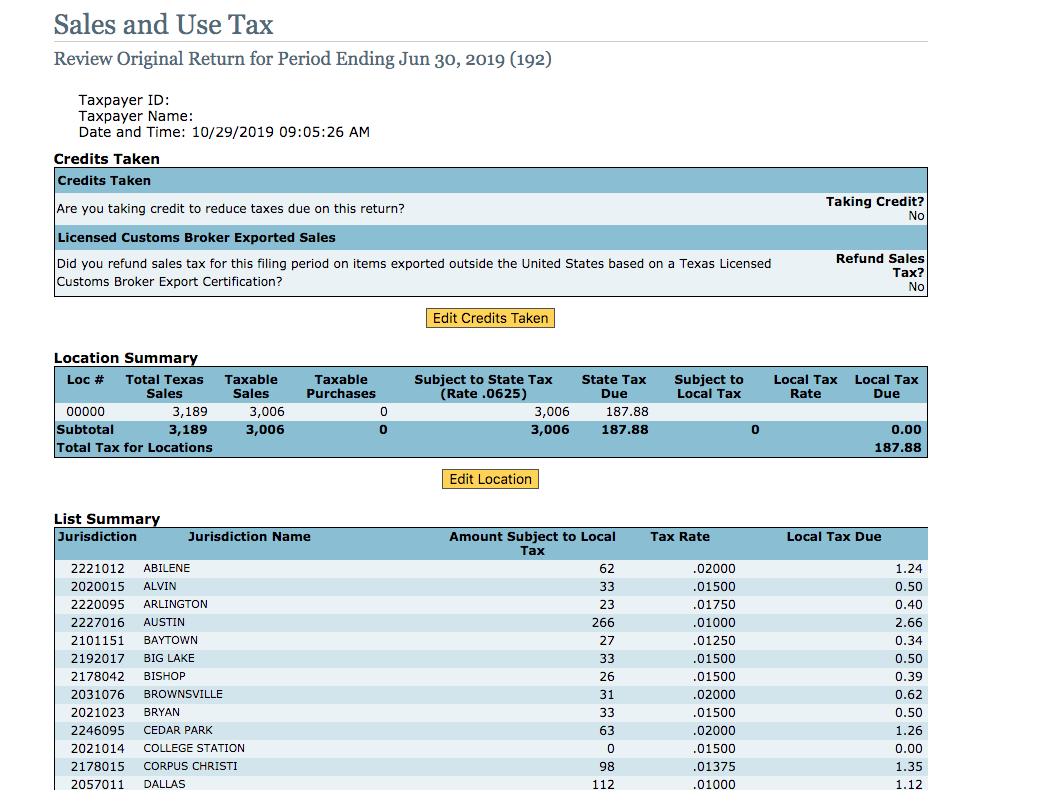
Texas, with its diverse economy and robust growth, has a complex sales tax system that varies across counties and cities. The state’s sales tax rate is currently set at 6.25%, but local municipalities can impose additional taxes, resulting in combined rates that can exceed 8% in some areas.
The state's sales tax is applied to a wide range of goods and services, including retail sales, rentals, and leases. However, there are certain exemptions and special provisions, such as for groceries, prescription drugs, and manufacturing machinery, which are not subject to sales tax. Understanding these nuances is crucial for businesses to ensure accurate tax collection and compliance.
| Taxable Items | Sales Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| General Merchandise | 6.25% |
| Restaurant Meals | 8.25% (including local taxes) |
| Vehicle Sales | 6.25% (state) + local taxes |
| Services (e.g., repairs, installation) | Varies based on local taxes |

The state's sales tax structure is designed to support its vast public infrastructure, from roads and schools to healthcare and social services. It is a critical component of the state's economy, with billions of dollars in revenue collected annually. For businesses, understanding and managing sales tax obligations is not just a legal requirement but a strategic aspect of financial planning and growth.
Eligibility and Requirements
The eligibility criteria for obtaining a Texas Sales Tax Permit are straightforward but rigorous, ensuring that all businesses operating within the state’s borders comply with its tax laws.
Any business involved in the sale of taxable goods or services, or the leasing or rental of tangible personal property, is required to obtain a permit. This includes both in-state and out-of-state sellers who have a physical presence or conduct sufficient business activities within Texas.
The physical presence, or nexus, of a business in Texas can take various forms. It can be an office, warehouse, or retail store. It can also be established through the presence of employees, affiliates, or even through certain digital activities, such as having a substantial number of customers in the state or using digital platforms that have a physical presence in Texas.
Additionally, businesses that facilitate sales through drop shipping or marketplace facilitators are also subject to sales tax obligations and must obtain a permit. Drop shipping, where a business acts as an intermediary between a customer and a third-party seller, and marketplace facilitation, where a platform facilitates sales between buyers and sellers, are increasingly common business models that must comply with Texas' sales tax laws.
Exceptions and Exemptions
While the scope of taxable activities is broad, there are specific exceptions and exemptions to sales tax obligations in Texas. These include:
- Resale Exemption: Businesses that purchase goods for resale are exempt from sales tax on those purchases. This exemption applies to wholesalers, retailers, and other businesses in the distribution chain, provided they hold a valid Texas Sales Tax Permit.
- Exempt Organizations: Certain entities, such as non-profit organizations, religious institutions, and government bodies, are exempt from sales tax. However, they must still register for a permit to ensure compliance and to make any applicable tax-exempt purchases.
- Manufacturing Exemption: Sales of machinery, equipment, and other tangible personal property used directly in manufacturing, processing, or fabrication are exempt from sales tax. This exemption is critical for businesses in the manufacturing sector and is a significant incentive for economic development in Texas.
Understanding these exceptions and exemptions is crucial for businesses to navigate their sales tax obligations accurately and avoid potential penalties. The Texas Comptroller's office provides detailed guidelines and resources to help businesses determine their eligibility and obligations.
Registration Process
Registering for a Texas Sales Tax Permit is a straightforward process that can be completed online through the Texas Comptroller’s website. The registration process is designed to be user-friendly and efficient, ensuring that businesses can quickly obtain their permits and begin operating in compliance with state tax laws.
Online Registration
The online registration process involves several steps, each designed to collect the necessary information to process the permit application. This includes providing basic business information, such as the business name, address, and contact details. Businesses will also need to provide details about their business activities, including the types of goods or services they offer and whether they have any physical presence in Texas.
The online system guides applicants through the process, providing clear instructions and prompts to ensure all necessary information is provided. It also allows applicants to save their progress and return to complete the registration at a later time, making it convenient for businesses to manage their tax obligations alongside their daily operations.
Upon completion of the online registration, businesses will receive an immediate acknowledgment, confirming that their application has been received. This acknowledgment serves as a temporary permit, allowing businesses to begin collecting and remitting sales tax while their application is being processed.
Documentation and Supporting Materials
In addition to the basic business information, applicants may need to provide additional documentation to support their application. This can include articles of incorporation, partnership agreements, or other legal documents that establish the business’s structure and ownership.
For out-of-state businesses, the documentation requirements may be more extensive. They may need to provide proof of their out-of-state registration and tax obligations, as well as information about their activities within Texas that establish their nexus in the state. This ensures that all businesses operating in Texas, regardless of their location, comply with the state's tax laws.
The Texas Comptroller's office provides a comprehensive checklist of required documentation on its website, ensuring that businesses have a clear understanding of what is needed to complete their application. This transparency and clarity are key aspects of the registration process, helping businesses navigate the requirements efficiently and effectively.
Permitting Process and Timeline
Once the application is submitted, the Texas Comptroller’s office undertakes a thorough review process to ensure compliance with state tax laws. This process involves verifying the information provided, assessing the business’s activities and nexus in the state, and ensuring that all required documentation is in order.
The permitting process typically takes 2-3 weeks from the date of application. However, this timeline can vary depending on the complexity of the business's operations and the completeness of the application. For example, if a business has a complex structure or operates in multiple states, the review process may take longer.
During the review process, the Comptroller's office may reach out to the applicant for additional information or clarifications. It is crucial for businesses to respond promptly to these requests to ensure a smooth and timely permitting process. The office provides regular updates and notifications to applicants, keeping them informed about the status of their application.
Upon successful completion of the review process, businesses will receive their official Texas Sales Tax Permit. This permit authorizes the business to collect and remit sales tax in compliance with state laws. It is a critical document for businesses to maintain and display, as it serves as proof of their tax compliance and legal standing in the state.
Renewal and Updates
Texas Sales Tax Permits are valid for a period of three years from the date of issuance. Businesses must renew their permits before the expiration date to continue operating in compliance with state tax laws. The renewal process is similar to the initial registration, involving an online application and the provision of updated business information and documentation.
During the renewal process, businesses should review their activities and ensure that the information provided is accurate and up-to-date. Any changes to the business, such as a change in ownership, location, or activities, should be reflected in the renewal application. This ensures that the permit remains valid and that the business continues to comply with its tax obligations.
The Texas Comptroller's office provides reminders and notifications to businesses approaching the renewal deadline, helping them stay compliant and avoid any lapses in their tax obligations. This proactive approach ensures that businesses can focus on their core operations while maintaining their legal and tax compliance.
Compliance and Reporting Requirements
Obtaining a Texas Sales Tax Permit is just the first step towards compliance. Businesses must also understand and adhere to the state’s sales tax reporting requirements to ensure they are collecting and remitting taxes accurately and on time.
Taxable Sales and Reporting
Businesses are required to collect sales tax on all taxable sales, rentals, or leases of tangible personal property. This includes sales made in person, online, or through other remote channels. The tax is calculated based on the total sale price, including any shipping, handling, or other charges, and is typically collected at the point of sale.
The frequency of sales tax reporting and payment depends on the business's sales volume and activity. The Texas Comptroller's office offers several filing frequencies, including monthly, quarterly, or annually. Businesses must choose the frequency that best suits their operations and ensure they meet the corresponding deadlines for filing and payment.
The sales tax reporting process involves providing detailed information about the business's taxable sales, including the total sales amount, the tax collected, and any exemptions or deductions claimed. The Comptroller's office provides user-friendly online tools and resources to help businesses calculate and report their sales tax obligations accurately.
Recordkeeping and Audits
Proper recordkeeping is a critical aspect of sales tax compliance. Businesses must maintain accurate and detailed records of their sales, including the date, amount, and type of sale, as well as any applicable taxes collected. These records must be retained for a minimum of three years to facilitate accurate reporting and to respond to any audit requests.
The Texas Comptroller's office has the authority to conduct audits to ensure compliance with sales tax laws. Audits can be triggered by various factors, such as random selection, a history of non-compliance, or specific indicators of potential tax evasion. During an audit, the Comptroller's office will review the business's records, sales data, and tax returns to verify the accuracy of the reported sales and tax payments.
Businesses should be prepared for audits by maintaining organized and complete records. They should also be familiar with their rights and responsibilities during an audit, including the right to representation and the obligation to provide accurate and timely responses to audit requests. The Comptroller's office provides guidance and resources to help businesses understand the audit process and their obligations.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Sales tax compliance is not just a legal requirement; it is a critical aspect of maintaining a business’s reputation and financial health. Non-compliance with sales tax obligations can result in severe consequences, including financial penalties, legal actions, and damage to the business’s reputation.
Penalties and Interest
The Texas Comptroller’s office imposes penalties for late or non-payment of sales tax, as well as for late filing of tax returns. The penalty amount can range from 5% to 15% of the tax due, depending on the severity and frequency of the non-compliance. In addition, interest is charged on the outstanding tax amount, accruing at a rate of 1% per month or fraction thereof.
For example, if a business owes $10,000 in sales tax and fails to pay on time, they would be subject to a penalty of $500 to $1,500, depending on the circumstances. Additionally, interest would accrue on the outstanding amount at a rate of 12% per year, adding a significant financial burden to the business.
| Penalty Type | Penalty Rate |
|---|---|
| Late Payment | 5% to 15% of tax due |
| Late Filing | 5% to 15% of tax due |
| Interest on Outstanding Tax | 1% per month (12% per year) |
These penalties and interest charges can quickly add up, especially for businesses with significant sales tax obligations. It is therefore crucial for businesses to prioritize timely payment and filing to avoid these financial consequences.
Legal Actions and Collection Efforts
In cases of severe or repeated non-compliance, the Texas Comptroller’s office has the authority to take legal action against the business. This can include the filing of a lawsuit to collect outstanding taxes, penalties, and interest, as well as the imposition of liens on the business’s assets.
The Comptroller's office may also refer cases of non-compliance to the Texas Attorney General's office for criminal prosecution. Sales tax evasion is a serious offense, and individuals found guilty can face fines, imprisonment, or both. For businesses, this can result in severe reputational damage, loss of business opportunities, and even the potential for bankruptcy.
To avoid these severe consequences, businesses should prioritize sales tax compliance and seek professional advice or assistance if they have any doubts or concerns about their obligations. The Comptroller's office provides resources and support to help businesses understand and meet their tax obligations, ensuring a fair and compliant business environment.
Conclusion: A Commitment to Compliance
Obtaining and maintaining a Texas Sales Tax Permit is a critical aspect of doing business in the state. It ensures that businesses comply with state tax laws, contributing to the funding of essential public services while also protecting their own legal and financial interests.
The process of obtaining a permit, while thorough, is designed to be efficient and user-friendly. The Texas Comptroller's office provides clear guidelines, user-friendly online tools, and comprehensive resources to support businesses through the registration, compliance, and reporting processes.
By understanding their sales tax obligations and committing to compliance, businesses can operate with confidence in the dynamic and thriving Texas market. This commitment to compliance not only ensures legal and financial stability but also contributes to the state's robust economy and vibrant business landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take to receive a Texas Sales Tax Permit after applying online?
+
The Texas Comptroller’s office aims to process permit applications within 2-3 weeks from the date of submission. However, this timeline can vary depending on the complexity of the business’s operations and the completeness of the application. Businesses can track the status of their application online through the Comptroller’s website.
Are there any exceptions to the requirement to obtain a Texas Sales Tax Permit?
+
Yes, there are certain exceptions and exemptions to the sales tax permit requirement. For example, businesses engaged solely in the sale of exempt goods or services, such as groceries or prescription drugs, may not need a permit. Additionally, certain exempt organizations, such as non-profit entities, may be exempt from the requirement. However, it is always advisable to consult the Texas Comptroller’s office or a tax professional to confirm eligibility.



