Taxes Payable
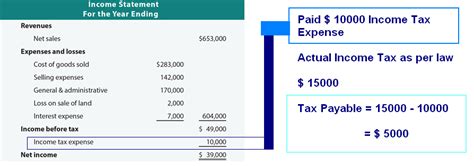
Taxes payable is a crucial concept in the realm of finance and accounting, playing a pivotal role in both personal and business financial management. This article aims to provide an in-depth exploration of taxes payable, shedding light on its definition, importance, and various aspects that make it a significant financial consideration. From understanding the legal obligations to strategic tax planning, this comprehensive guide will navigate through the complexities of taxes payable, offering valuable insights and practical tips.
Understanding Taxes Payable

Taxes payable, often referred to as tax liabilities, represent the amount of tax that an individual or entity is legally obligated to pay to the government. It is a financial obligation that arises from various transactions, activities, and income sources, and failure to meet these obligations can result in severe legal consequences.
The concept of taxes payable is broad and encompasses a wide range of tax types, including income tax, sales tax, property tax, payroll tax, and more. Each type of tax has its own rules, regulations, and calculation methods, making tax management a complex but essential task.
Key Aspects of Taxes Payable
Taxes payable are not just about compliance; they also have a significant impact on financial planning and strategy. Here are some key aspects to consider:
- Tax Rates and Brackets: Understanding the tax rates and brackets applicable to your income or business activities is crucial. Tax rates can vary based on income levels, business structures, and even geographical locations. Staying updated on these rates is essential for accurate tax planning.
- Tax Deductions and Credits: Tax deductions and credits can significantly reduce the amount of tax payable. These incentives are offered by governments to encourage specific behaviors, such as investing in certain industries or supporting social causes. Familiarizing yourself with available deductions and credits can lead to substantial tax savings.
- Tax Compliance and Filing: Ensuring timely and accurate tax compliance is vital. This involves maintaining proper records, calculating taxes correctly, and filing tax returns within the stipulated deadlines. Non-compliance can lead to penalties, interest charges, and even legal action.
- Tax Planning and Strategy: Proactive tax planning can help minimize tax liabilities and maximize financial benefits. This involves analyzing income sources, business activities, and investment opportunities to optimize tax efficiency. Seeking professional advice from tax experts can be beneficial in developing effective tax strategies.
Taxes Payable for Individuals

For individuals, taxes payable primarily revolve around income tax. This includes tax obligations on salaries, wages, investments, and other sources of income. The tax liability is calculated based on the individual’s income level and applicable tax rates.
Key considerations for individuals include:
- Personal Tax Allowance: Most countries offer a personal tax allowance, which is a certain amount of income that is tax-free. Understanding this allowance and ensuring you optimize your income to fall within this limit can help reduce tax liabilities.
- Tax-Efficient Savings and Investments: Exploring tax-efficient savings and investment options, such as pension contributions or ISAs (Individual Savings Accounts), can help reduce the overall tax burden. These schemes often offer tax relief or defer tax liability, making them attractive financial planning tools.
- Tax Returns and Self-Assessment: In many countries, individuals are required to file tax returns annually. This process involves declaring income, claiming deductions, and calculating the tax payable. Accurate and timely self-assessment is crucial to avoid penalties and ensure compliance.
Case Study: Maximizing Tax Benefits for Individuals
Consider the case of Sarah, a freelance graphic designer. She earns a significant portion of her income from client projects but also has a small rental property. By carefully managing her income sources and understanding the tax implications, Sarah can maximize her tax benefits.
She ensures that her freelance income stays within the personal tax allowance by strategically timing her invoices and payments. Additionally, she takes advantage of tax-efficient savings schemes, such as contributing to a pension plan, to further reduce her tax liability. By keeping meticulous records and seeking professional advice, Sarah optimizes her tax position and ensures compliance.
Taxes Payable for Businesses
Businesses face a more complex tax landscape, with obligations extending beyond income tax. They must navigate various tax types, including corporate income tax, sales tax, payroll tax, and property tax.
Key considerations for businesses include:
- Corporate Tax Rates: Corporate tax rates vary across countries and can significantly impact a business's profitability. Understanding these rates and their applicability to your business is crucial for financial planning.
- Sales and Value-Added Tax (VAT): Sales tax or VAT is applicable to most business transactions. Proper management of sales tax, including accurate record-keeping and timely remittances, is essential to avoid penalties and maintain compliance.
- Payroll Tax and Employee Benefits: Businesses must also consider payroll tax, which includes income tax withholding, social security contributions, and other employee-related taxes. Offering tax-efficient employee benefits, such as pension contributions or healthcare plans, can help attract and retain talent while reducing the overall tax burden.
- Tax Planning and Strategy: Business tax planning involves a strategic approach to minimize tax liabilities and optimize cash flow. This may include exploring tax-efficient business structures, investment opportunities, or taking advantage of tax incentives offered by governments.
Example: Strategic Tax Planning for a Small Business
Imagine a small e-commerce business owned by John. He operates an online store selling handcrafted jewelry. By understanding the tax landscape, John can implement strategic tax planning measures to optimize his business’s financial health.
John explores tax-efficient business structures, such as incorporating his business, which offers limited liability protection and potential tax benefits. He also considers the impact of sales tax on his online sales and ensures he has proper systems in place to manage and remit these taxes accurately. Additionally, he offers tax-efficient employee benefits to his small team, fostering a positive work environment while reducing his tax obligations.
The Impact of Taxes Payable on Financial Health
Taxes payable have a direct and significant impact on an individual’s or business’s financial health. They influence cash flow, profitability, and overall financial planning.
For individuals, managing taxes effectively can lead to increased disposable income, allowing for better financial management and the pursuit of financial goals. For businesses, optimal tax management can enhance profitability, improve cash flow, and create opportunities for growth and expansion.
Strategies for Effective Tax Management
To ensure effective tax management, consider the following strategies:
- Stay Informed: Keep yourself updated on tax laws, regulations, and changes. Governments often introduce new tax policies or modify existing ones, so staying informed is crucial for compliance and strategic planning.
- Seek Professional Advice: Tax laws can be complex, and seeking guidance from tax professionals or accountants can provide valuable insights. They can help navigate the intricacies of tax obligations and identify opportunities for tax optimization.
- Implement Robust Record-Keeping: Accurate and organized record-keeping is essential for tax management. Maintain proper documentation for all income sources, expenses, and transactions to ensure compliance and facilitate tax planning.
- Plan Ahead: Tax planning is a proactive process. Start early and review your financial situation regularly to identify potential tax liabilities and opportunities for optimization. This proactive approach can help minimize surprises and ensure a more stable financial position.
Future Implications and Trends

The landscape of taxes payable is continually evolving, with governments introducing new initiatives and policies to meet economic and social objectives. Staying abreast of these developments is crucial for effective tax management.
Some emerging trends and implications include:
- Digital Taxation: With the rise of digital economies, governments are exploring ways to tax digital transactions and services. This includes initiatives like the proposed Digital Services Tax and Value-Added Tax (VAT) on digital services, which could significantly impact businesses operating in the digital space.
- Sustainability and Green Taxation: Governments are increasingly focusing on sustainability and environmental concerns. This has led to the introduction of green taxes, incentives for sustainable practices, and penalties for environmentally harmful activities. Businesses and individuals should consider the impact of these initiatives on their tax obligations.
- International Tax Reforms: Global tax reforms, such as the Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS) project, aim to address tax avoidance and ensure a fair distribution of tax obligations. These reforms can have implications for multinational corporations and individuals with international income sources.
| Tax Type | Key Consideration |
|---|---|
| Income Tax | Personal tax allowance, tax-efficient savings |
| Sales Tax/VAT | Accurate record-keeping, timely remittances |
| Payroll Tax | Employee benefits, tax withholding |
| Property Tax | Assessment and payment deadlines |

What is the difference between taxes payable and tax refunds?
+Taxes payable refer to the amount of tax owed to the government, while tax refunds are the amounts that individuals or businesses receive from the government when they have overpaid their taxes. Tax refunds occur when the tax payable is less than the taxes withheld or paid during the year.
How often should I review my tax obligations and planning strategies?
+It is recommended to review your tax obligations and planning strategies at least annually, especially when there are significant changes in your income, business activities, or personal circumstances. Additionally, staying updated on tax law changes throughout the year is beneficial for proactive tax management.
Can I reduce my tax liabilities through charitable donations or investments?
+Yes, charitable donations and certain types of investments can provide tax benefits. These activities often qualify for tax deductions or credits, reducing the overall tax liability. However, it is important to consult with tax professionals to understand the specific rules and requirements for claiming these benefits.