Tax Treatment Of Annuities

Annuities have become increasingly popular financial instruments, offering individuals a steady income stream during their retirement years. However, understanding the tax implications of these investments is crucial for maximizing their benefits. This comprehensive guide delves into the tax treatment of annuities, exploring the various aspects that impact their financial performance and providing valuable insights for investors.
The Tax Landscape for Annuities

Annuities are financial contracts that provide a guaranteed income stream over a specified period or for the rest of an individual’s life. They are often used as a means to secure a steady income during retirement, offering peace of mind and financial stability. However, the tax treatment of annuities can vary depending on several factors, including the type of annuity, the timing of contributions, and the distribution method.
Types of Annuities and Their Tax Implications
There are two primary types of annuities: qualified annuities and non-qualified annuities. Qualified annuities, also known as tax-deferred annuities, are typically funded with pre-tax dollars, such as contributions from an employer-sponsored retirement plan. These annuities grow tax-free until the funds are withdrawn, at which point the entire distribution, including earnings, is subject to ordinary income tax rates.
On the other hand, non-qualified annuities are funded with after-tax dollars, and the growth on these investments is also tax-free. However, the tax treatment of distributions from non-qualified annuities can be more complex. Earnings are taxed as ordinary income, while the original investment amount, known as the cost basis, is returned tax-free. This means that only the earnings portion of each distribution is taxable.
Taxation of Annuity Contributions and Growth
The tax treatment of annuity contributions and growth varies based on the type of annuity and the source of funding. For qualified annuities, contributions are typically made with pre-tax dollars, which means they are not taxed immediately. The earnings on these contributions grow tax-deferred until the annuity is distributed.
In contrast, contributions to non-qualified annuities are made with after-tax dollars, so there is no immediate tax benefit. However, the growth on these investments is tax-free, allowing the funds to accumulate without being eroded by taxes.
| Annuity Type | Tax Treatment of Contributions | Tax Treatment of Growth |
|---|---|---|
| Qualified Annuity | Pre-tax, not immediately taxed | Tax-deferred |
| Non-Qualified Annuity | After-tax, no immediate tax benefit | Tax-free growth |

Taxation of Annuity Distributions
The taxation of annuity distributions is a critical aspect of understanding the financial impact of these investments. When it comes to qualified annuities, distributions are subject to ordinary income tax rates. The entire distribution, including both the earnings and the original contribution, is taxable. This means that individuals must pay taxes on the growth of their investment, which can significantly impact their overall returns.
For non-qualified annuities, the taxation of distributions is more nuanced. As mentioned earlier, the cost basis, or the original investment amount, is returned tax-free. Only the earnings portion of each distribution is taxable as ordinary income. This tax treatment allows individuals to recoup their initial investment without paying taxes, making non-qualified annuities an attractive option for those seeking tax-efficient retirement income.
Annuity Tax Advantages and Considerations
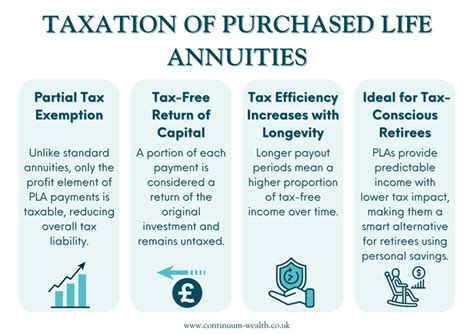
Annuities offer several tax advantages that can make them a valuable component of a comprehensive retirement plan. One of the key benefits is the potential for tax-deferred growth, particularly with qualified annuities. By deferring taxes on contributions and earnings, individuals can allow their investments to grow more rapidly, taking advantage of the power of compounding.
Additionally, annuities can provide a guaranteed income stream for life, which can be particularly valuable for those seeking financial security during retirement. This income is often taxable, but the tax treatment of annuity distributions can be more favorable than other types of investments, as mentioned earlier.
However, it's important to consider the potential downsides as well. Annuities may have high fees and surrender charges, which can eat into an investor's returns. Additionally, the tax treatment of distributions can be complex, and individuals may need to consult with a tax professional to fully understand the implications.
Maximizing the Tax Benefits of Annuities
To make the most of the tax advantages offered by annuities, investors should consider several strategies. One approach is to carefully time their annuity purchases and distributions to optimize tax efficiency. For instance, individuals may want to consider purchasing an annuity when their income is lower, as this can result in a lower tax rate on distributions.
Another strategy is to utilize multiple annuities with different distribution methods. This allows investors to customize their income streams and potentially reduce their overall tax liability. For example, combining an immediate annuity with a deferred annuity can provide a steady income stream while also allowing for tax-deferred growth on a portion of the investment.
Tax-Efficient Withdrawal Strategies
When it comes to annuity distributions, there are several strategies to consider for maximizing tax efficiency. One approach is to structure distributions to minimize the tax burden on each withdrawal. This can be achieved by carefully planning the timing and amount of distributions, taking into account an individual’s tax bracket and other income sources.
Additionally, individuals may want to consider using annuities as part of a comprehensive tax planning strategy. By coordinating annuity distributions with other income sources, such as Social Security benefits or pension payments, individuals can potentially reduce their overall tax liability. This requires careful planning and an understanding of the tax implications of each income stream.
The Role of Annuities in Retirement Planning
Annuities play a crucial role in retirement planning, offering a reliable income stream and potential tax advantages. When incorporated into a well-rounded retirement strategy, annuities can provide a valuable source of guaranteed income, ensuring financial stability during the retirement years.
However, it's important to remember that annuities are not a one-size-fits-all solution. The tax treatment of annuities can vary significantly, and individuals should carefully consider their financial goals, risk tolerance, and overall retirement plan when deciding whether and how to incorporate annuities into their investment portfolio.
Conclusion: Navigating the Tax Landscape
Understanding the tax treatment of annuities is essential for making informed investment decisions. By navigating the complexities of annuity taxation, individuals can maximize the benefits of these financial instruments and ensure a secure financial future. Whether it’s optimizing tax efficiency, minimizing fees, or coordinating distributions with other income sources, a comprehensive understanding of the tax landscape is key to successful retirement planning.
As with any financial decision, seeking the advice of a qualified financial advisor is crucial. They can provide personalized guidance based on an individual's unique circumstances, helping them navigate the tax implications of annuities and make the most of their retirement investments.
Are all annuities treated the same way for tax purposes?
+No, the tax treatment of annuities can vary based on factors such as the type of annuity, the timing of contributions, and the distribution method. Qualified annuities and non-qualified annuities are taxed differently.
How are qualified annuity distributions taxed?
+Distributions from qualified annuities are subject to ordinary income tax rates. The entire distribution, including both earnings and contributions, is taxable.
What is the tax treatment of non-qualified annuity distributions?
+Non-qualified annuity distributions are more complex. The cost basis, or original investment amount, is returned tax-free, while only the earnings portion is taxable as ordinary income.
Can annuities be a part of a tax-efficient retirement strategy?
+Yes, annuities can be a valuable component of a tax-efficient retirement plan. By carefully timing purchases and distributions and coordinating income streams, individuals can potentially reduce their overall tax liability.