Tax Id Vs Ein

In the realm of business and financial management, understanding the nuances of different identification systems is crucial. Two terms that often come up in discussions about business entities are "Tax ID" and "EIN." While these terms are sometimes used interchangeably, they refer to distinct identification mechanisms with specific purposes. Let's delve into the intricacies of these concepts and explore their unique roles in the world of finance and business administration.
Tax ID: The Universal Identifier

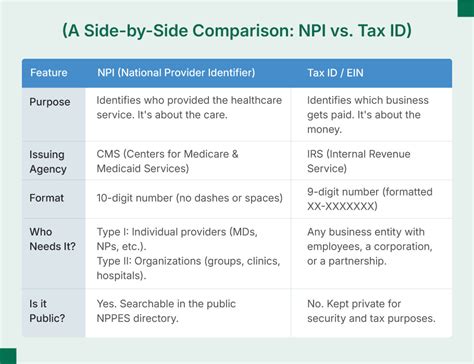
A Tax ID, formally known as a Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN), serves as a unique identifier for individuals, businesses, and organizations in the context of tax and financial transactions. This number is akin to a social security number for businesses, facilitating the tracking of tax obligations and payments.
Types of Tax IDs
There are several types of Tax IDs, each catering to different categories of entities:
- Social Security Number (SSN): This is the Tax ID assigned to individuals, used for personal tax filings and various other identification purposes.
- Employer Identification Number (EIN): While this term is often used synonymously with Tax ID, it specifically refers to the identification number for businesses. We'll explore EINs in more detail below.
- Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN): ITINs are issued to individuals who are required to have a U.S. taxpayer number but are not eligible for an SSN. This could include foreign nationals or their dependents.
- Prepared Filer Identification Number (PFIN): This number is assigned to tax return preparers who are required to include it on returns they prepare.
Each of these Tax IDs serves a distinct purpose, but they all contribute to the comprehensive identification system used by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) to manage tax obligations.
Applications of Tax IDs
Tax IDs are utilized in a multitude of financial and administrative scenarios, including:
- Tax Filing: Individuals and businesses use their respective Tax IDs when filing tax returns, ensuring accurate identification and proper tax assessment.
- Opening Bank Accounts: Financial institutions often require a Tax ID to open a business or personal account, helping to verify the identity of the account holder.
- Payroll Management: Employers use EINs to manage payroll taxes and report employee earnings to the IRS.
- Government Benefits: Certain government benefits, such as Social Security benefits or Medicare, are linked to specific Tax IDs, ensuring proper distribution.
EIN: The Business-Specific Identifier

An Employer Identification Number (EIN), often referred to as a Tax ID, is a unique nine-digit number assigned to businesses by the IRS. It serves as the business equivalent of a social security number, facilitating the identification of businesses for tax purposes and various other administrative functions.
When is an EIN Required?
Businesses may need an EIN for various reasons, including:
- Tax Purposes: An EIN is necessary for businesses to file their taxes, report payroll, and comply with other tax-related obligations.
- Opening a Business Bank Account: Many financial institutions require an EIN to open a business account, ensuring proper identification and compliance.
- Hiring Employees: When a business plans to hire employees, an EIN is essential for managing payroll taxes and employee-related tax obligations.
- Certain Legal Requirements: Some business structures, such as corporations or partnerships, may be required to obtain an EIN to comply with legal and tax regulations.
Obtaining an EIN
Businesses can obtain an EIN by completing the IRS Form SS-4, either online or through traditional mail. The online application process is generally faster, with an immediate response in most cases. However, businesses should ensure they have the necessary information, such as the business owner's SSN or ITIN, business address, and the nature of the business, before beginning the application process.
EIN vs. FEIN
It's worth noting the distinction between an EIN and a Federal Employer Identification Number (FEIN). While the terms are often used interchangeably, an FEIN specifically refers to an EIN issued to an entity that has employees. This clarifies that the EIN is not only for tax purposes but also for managing employee-related obligations.
Applications of an EIN
An EIN is utilized in various business contexts, including:
- Tax Filing: Businesses use their EIN to file their tax returns, ensuring proper identification and tax compliance.
- Payroll Management: With an EIN, businesses can manage payroll taxes, report employee earnings, and comply with employment tax regulations.
- Opening Business Accounts: An EIN is often required to open a business bank account, providing a secure and identifiable financial entity.
- Business Licensing and Permits: Some business licenses and permits may require an EIN as part of the application process, especially for businesses with employees.
| Tax ID Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Social Security Number (SSN) | Personal Tax ID for individuals |
| Employer Identification Number (EIN) | Unique number for businesses |
| Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN) | For individuals not eligible for SSN |
| Prepared Filer Identification Number (PFIN) | For tax return preparers |
Conclusion: Navigating the Identification Landscape
Understanding the differences between Tax IDs and EINs is essential for individuals and businesses alike. Whether it's for tax filing, opening a bank account, or managing payroll, the appropriate identification number ensures compliance with legal and financial regulations. By recognizing the unique roles of these identifiers, individuals and businesses can navigate the financial landscape with confidence and precision.
Can an individual use their SSN as a Tax ID for business purposes?
+In certain circumstances, an individual may use their Social Security Number (SSN) as a Tax ID for business purposes. This is often the case for sole proprietors or single-member LLCs, where the business and the individual are considered the same entity for tax purposes. However, it’s important to consult with a tax professional to ensure compliance with specific regulations.
Are there any costs associated with obtaining an EIN?
+Obtaining an EIN is a free service provided by the IRS. There are no fees or costs involved in the application process, whether it’s done online or through traditional mail.
Can a business have multiple EINs?
+Yes, a business can have multiple EINs, especially if it operates in different states or has distinct business entities. For example, a corporation that also operates as a partnership or has multiple locations may require separate EINs for each entity or location.