Tax Evasion Minimum Sentence
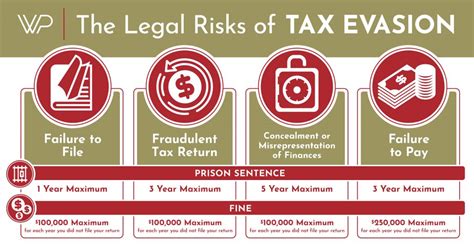
The criminal justice system in many countries, including the United States, treats tax evasion as a serious offense, carrying potential consequences that can significantly impact an individual's freedom and financial well-being. Understanding the minimum sentences for tax evasion is crucial for both taxpayers and legal professionals alike.
Understanding Tax Evasion

Tax evasion refers to the illegal practice of intentionally failing to pay taxes owed to the government. It involves a deliberate attempt to conceal income, overstate deductions, or engage in other fraudulent activities to reduce one’s tax liability. This is distinct from tax avoidance, which is the legal practice of minimizing tax obligations through legitimate means.
The severity of tax evasion lies in its potential to undermine the financial stability of nations and the fairness of the tax system. It can lead to reduced government revenue, impacting public services and infrastructure, and create an unfair advantage for those who evade taxes over those who pay their fair share.
Minimum Sentences for Tax Evasion
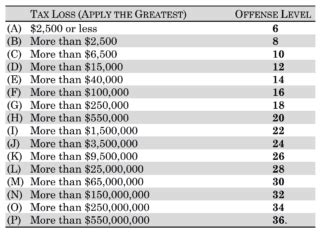
The penalties for tax evasion vary significantly based on jurisdiction and the specific circumstances of the case. In the United States, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) and the Department of Justice (DOJ) work together to investigate and prosecute tax crimes. The penalties can include both criminal and civil consequences.
Criminal Penalties
Criminal tax evasion, as defined by 26 U.S.C. § 7201, is a felony offense. It occurs when an individual willfully attempts to evade or defeat any tax imposed by the Internal Revenue Code. The key element of willfulness distinguishes criminal tax evasion from mere errors or negligence in tax reporting.
The minimum sentence for criminal tax evasion in the United States is typically characterized by the following:
- Imprisonment: A conviction for criminal tax evasion can result in a prison sentence. The length of the sentence depends on various factors, including the amount of tax evaded and the individual's criminal history. For first-time offenders, the minimum prison sentence can range from a few months to several years.
- Fines: In addition to imprisonment, individuals convicted of tax evasion may be subject to substantial fines. These fines are often calculated based on the amount of tax evaded and can amount to thousands or even millions of dollars.
- Restitution: The court may order the individual to pay restitution, which involves reimbursing the government for the taxes evaded, plus interest and penalties. This can be a significant financial burden, especially for those who have substantial tax liabilities.
| Factor | Minimum Sentence |
|---|---|
| Tax Evaded (in $) | Varies; higher amounts result in longer sentences |
| Criminal History | First-time offenders may receive shorter sentences |
| Cooperation with Authorities | Cooperating defendants may receive reduced sentences |
It's important to note that the minimum sentence serves as a starting point, and the actual sentence can be influenced by various mitigating and aggravating factors. Judges have discretion to impose sentences that deviate from the minimum based on the specifics of each case.
Civil Penalties
In addition to criminal penalties, tax evasion can also result in civil penalties imposed by the IRS. These penalties are administrative in nature and do not involve imprisonment. However, they can still be significant and financially burdensome.
- Failure to File Penalty: Individuals who intentionally fail to file tax returns may face a penalty of up to $250,000 for individuals and $500,000 for corporations.
- Failure to Pay Penalty: Those who intentionally fail to pay taxes owed can be subject to a penalty of up to 25% of the unpaid tax amount.
- Fraud Penalty: In cases of fraudulent tax evasion, the IRS can impose a penalty of up to 75% of the underpayment of tax attributed to fraud.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Examining real-world tax evasion cases can provide valuable insights into the potential consequences individuals face. Here are a few notable examples:
The Case of Wesley Snipes
In one of the most high-profile tax evasion cases, actor Wesley Snipes was charged with multiple counts of tax evasion. He was accused of failing to file tax returns and attempting to evade taxes by claiming false refunds. Snipes was ultimately convicted and sentenced to three years in prison, in addition to facing significant fines.
Enron Corporation Scandal
The Enron scandal, which involved complex financial manipulations and tax evasion, resulted in severe consequences for the company and its executives. Several executives were convicted of tax evasion and other charges, leading to prison sentences ranging from five to 24 years.
Famous Athletes and Tax Evasion
Tax evasion is not limited to the entertainment industry. Several high-profile athletes have faced tax evasion charges. For instance, boxer Floyd Mayweather Jr. was sentenced to serve two months in prison and pay a fine of $5 million for tax evasion related to his earnings from a boxing match.
Prevention and Compliance
Tax evasion is a serious offense that carries significant legal and financial consequences. To avoid these penalties, it is crucial for individuals and businesses to maintain proper tax compliance.
- Seek Professional Advice: Engaging the services of a qualified tax professional or accountant can help ensure accurate and compliant tax reporting. These experts can provide guidance on tax laws and strategies to minimize tax liabilities within legal boundaries.
- Keep Detailed Records: Maintaining thorough financial records is essential for accurate tax reporting. This includes keeping track of income, expenses, and deductions to support the figures reported on tax returns.
- Understand Tax Laws: Tax laws can be complex, and it is important to stay informed about changes and updates. Keeping abreast of tax regulations can help individuals and businesses avoid unintentional violations.
Conclusion

Tax evasion is a criminal offense that can lead to severe consequences, including imprisonment and substantial financial penalties. The minimum sentences for tax evasion serve as a deterrent and reflect the seriousness with which the legal system treats such offenses. By understanding the potential penalties and maintaining tax compliance, individuals and businesses can avoid the pitfalls of tax evasion and the resulting legal and financial repercussions.
What are the common signs of tax evasion?
+Signs of tax evasion may include consistently failing to file tax returns, underreporting income, overstating deductions, and using offshore accounts to conceal assets.
Can tax evasion charges be reduced or dismissed?
+In some cases, charges may be reduced or dismissed if the taxpayer cooperates with authorities, pays the outstanding taxes, and demonstrates genuine remorse. However, this is not guaranteed and depends on the specific circumstances.
What is the statute of limitations for tax evasion charges?
+The statute of limitations for tax evasion charges in the United States is typically six years from the date the tax return was due. However, this can be extended if the taxpayer commits certain acts, such as filing a fraudulent return.



