State Of Virginia Sales Tax

The State of Virginia has a unique sales tax system that impacts both residents and businesses. This article delves into the specifics of Virginia's sales tax, exploring its rates, applicability, and the potential impact on businesses and consumers alike. With a comprehensive understanding of Virginia's sales tax, businesses can make informed decisions to ensure compliance and manage their tax obligations effectively.
Understanding Virginia’s Sales Tax Structure

Virginia imposes a sales and use tax on the retail sale, lease, or rental of tangible personal property as well as certain services. The tax is administered by the Virginia Department of Taxation and is a significant source of revenue for the state, contributing to various public services and infrastructure development.
The sales tax rate in Virginia is composed of two main components: the state sales tax and any applicable local sales tax rates. This dual structure allows for a flexible and localized tax system, catering to the diverse needs of different regions within the state.
As of [current date], the state sales tax rate in Virginia stands at 4.3%, a rate that has been consistent for several years. This rate applies uniformly across the state, providing a stable foundation for businesses and consumers to plan their financial strategies.
Local Sales Tax Variations
In addition to the state sales tax, localities in Virginia have the authority to levy additional local sales and use taxes. These local sales tax rates can vary significantly, with some regions imposing higher taxes to fund specific projects or initiatives.
For instance, in Arlington County, the local sales tax rate is 1%, bringing the total sales tax to 5.3%. On the other hand, Fairfax County has a local sales tax rate of 0.75%, resulting in a combined sales tax of 5.05%. These variations highlight the localized nature of sales tax in Virginia.
| Locality | Local Sales Tax Rate | Total Sales Tax |
|---|---|---|
| Arlington County | 1% | 5.3% |
| Fairfax County | 0.75% | 5.05% |
| City of Richmond | 0.5% | 4.8% |
| Loudoun County | 0.25% | 4.55% |
| City of Virginia Beach | 1.5% | 5.8% |
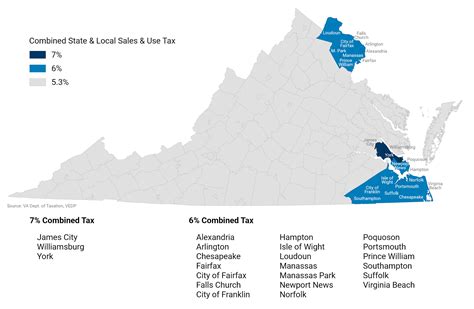
It's important for businesses with a physical presence in multiple localities to be aware of these variations to accurately calculate and remit sales tax. The Virginia Department of Taxation provides resources to assist businesses in understanding the complex web of sales tax rates across the state.
Sales Tax Exemptions and Special Considerations
Virginia’s sales tax system also includes a range of exemptions and special considerations that businesses and consumers should be aware of. These provisions can significantly impact the tax liability of certain transactions, making it crucial to understand the nuances of the sales tax code.
Sales Tax Exemptions
Virginia offers a number of sales tax exemptions for specific goods and services. These exemptions are designed to promote certain industries, support community development, and provide relief to specific consumer groups.
- Groceries: Many staple food items, including bread, milk, and eggs, are exempt from sales tax in Virginia.
- Prescription Drugs: Sales tax is not applicable to prescription drugs, ensuring that essential healthcare items are more affordable for residents.
- Certain Manufacturing Equipment: Sales tax exemptions are provided for the purchase of certain manufacturing machinery, encouraging industrial growth in the state.
- Military Sales: Sales to active-duty military personnel stationed in Virginia are exempt from sales tax, honoring the service of our armed forces.
Businesses operating in these sectors or catering to these specific customer groups should be well-versed in the applicable exemptions to ensure accurate tax calculations and compliance.
Special Sales Tax Considerations
In addition to exemptions, Virginia’s sales tax code includes several special considerations that can impact the taxability of certain transactions.
- Remote Sales Tax: Virginia has implemented a remote seller nexus, which means that out-of-state sellers who meet certain sales thresholds must collect and remit sales tax to the state. This provision ensures that online retailers are held accountable for their sales in Virginia.
- Sales Tax Holidays: To provide relief to consumers, Virginia occasionally holds sales tax holidays, during which specific items, such as school supplies or energy-efficient appliances, are exempt from sales tax for a limited time.
- Use Tax: In addition to sales tax, Virginia imposes a use tax on tangible personal property or services purchased from out-of-state sources and used, stored, or consumed in Virginia. This tax ensures that consumers pay their fair share, even if they purchase items online or out-of-state.
Sales Tax Registration and Compliance
Businesses operating in Virginia, whether online or with a physical presence, are required to register for a sales tax permit with the Virginia Department of Taxation. This permit authorizes the business to collect and remit sales tax on behalf of the state.
The sales tax registration process involves completing an application, providing business details, and determining the applicable tax rates and filing frequencies. The Department of Taxation provides a Registration Guide to assist businesses in navigating this process.
Once registered, businesses are responsible for collecting sales tax from customers at the point of sale and remitting these funds to the state on a regular basis. The frequency of these remittances depends on the business's sales volume and can range from monthly to annually.
To ensure compliance, businesses should maintain accurate records of sales, including the applicable tax rates and any exemptions applied. The Virginia Department of Taxation offers forms and publications to assist businesses in managing their sales tax obligations effectively.
Impact on Businesses and Consumers
Virginia’s sales tax system has a significant impact on both businesses and consumers within the state. Understanding these impacts can help businesses make strategic decisions and consumers plan their purchases effectively.
Impact on Businesses
For businesses, Virginia’s sales tax structure presents both opportunities and challenges.
- Revenue Generation: Sales tax is a significant source of revenue for businesses, especially those with high-volume sales. This revenue can be reinvested into the business for growth and development.
- Compliance Complexity: The dual state-local sales tax structure and the presence of exemptions can make compliance complex. Businesses must ensure they are aware of the applicable rates and regulations to avoid penalties.
- Competitive Advantage: Businesses can leverage sales tax exemptions or lower tax rates to offer competitive pricing, attracting customers and boosting sales.
- Remote Seller Considerations: Out-of-state businesses selling to Virginia residents must navigate the remote seller nexus and ensure they are collecting and remitting sales tax correctly.
Impact on Consumers
Consumers in Virginia also feel the impact of the state’s sales tax system.
- Price Transparency: Sales tax adds to the final cost of a product or service, impacting consumers' purchasing decisions. Understanding the sales tax rate in their locality helps consumers budget effectively.
- Exemptions and Relief: Sales tax exemptions on essential items like groceries and prescription drugs provide financial relief to consumers, especially those with limited incomes.
- Sales Tax Holidays: Consumers benefit from sales tax holidays, which allow them to save on specific purchases during designated periods.
- Online Shopping Considerations: Consumers should be aware that online purchases from out-of-state retailers may be subject to use tax, which they are responsible for paying.
Sales Tax in Virginia: A Comprehensive Guide

Virginia’s sales tax system is a dynamic and ever-evolving aspect of the state’s tax landscape. Businesses and consumers alike must stay informed about the latest regulations and changes to ensure compliance and make informed financial decisions.
For businesses, understanding the intricacies of Virginia's sales tax is crucial for strategic planning, tax compliance, and maintaining a competitive edge. Consumers, on the other hand, can benefit from a clear understanding of sales tax rates and exemptions to make informed purchases and manage their finances effectively.
As Virginia's economy continues to grow and evolve, so too will its sales tax system. By staying engaged with the latest developments and resources provided by the Virginia Department of Taxation, businesses and consumers can navigate this complex tax landscape with confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the current state sales tax rate in Virginia?
+
As of [current date], the state sales tax rate in Virginia is 4.3%.
Do I need to pay sales tax on online purchases in Virginia?
+
Yes, if you make an online purchase from a remote seller that meets the sales threshold, you may be subject to sales tax. The remote seller is responsible for collecting and remitting this tax.
Are there any sales tax holidays in Virginia?
+
Yes, Virginia occasionally holds sales tax holidays for specific items like school supplies or energy-efficient appliances. During these holidays, these items are exempt from sales tax.
How often do businesses need to remit sales tax in Virginia?
+
The frequency of sales tax remittances depends on the business’s sales volume. Businesses with higher sales may need to remit monthly, while others may remit quarterly or annually.
What happens if I don’t register for a sales tax permit in Virginia?
+
Failing to register for a sales tax permit can result in penalties and interest charges. It’s important to register with the Virginia Department of Taxation to avoid these consequences.



