State Of Ohio Tax Brackets
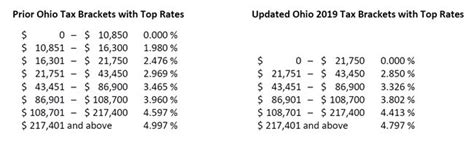
The State of Ohio's tax system, like many other states in the US, operates on a progressive income tax structure, meaning that taxpayers are subjected to different tax rates based on their income levels. Understanding the tax brackets is crucial for individuals and businesses operating within Ohio, as it directly impacts their financial obligations and planning.
Overview of Ohio’s Tax Brackets

Ohio’s income tax system is relatively straightforward, with a flat state tax rate applied to most types of income, including wages, salaries, and business profits. However, it’s important to note that there are certain exemptions and deductions that can reduce the taxable income, which we will explore later in this article.
The current income tax rate in Ohio is set at 2.85% for the 2023 tax year, a decrease from the previous rate of 2.98%. This flat rate applies to all income levels, making it a simpler system compared to states with multiple tax brackets. Despite the simplicity, the rate is subject to change, and it's crucial for taxpayers to stay updated with any modifications made by the Ohio Department of Taxation.
While Ohio has a flat tax rate, it's essential to consider the federal income tax brackets, as they can significantly impact the overall tax liability. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) determines these brackets, and they are adjusted annually to account for inflation. For the 2023 tax year, the federal income tax brackets for Ohio residents are as follows:
| Tax Rate | Single Filers | Married Filing Jointly |
|---|---|---|
| 10% | $0 - $10,275 | $0 - $20,550 |
| 12% | $10,276 - $41,775 | $20,551 - $83,550 |
| 22% | $41,776 - $89,075 | $83,551 - $178,150 |
| 24% | $89,076 - $170,050 | $178,151 - $340,100 |
| 32% | $170,051 - $215,950 | $340,101 - $431,900 |
| 35% | $215,951 - $539,900 | $431,901 - $647,850 |
| 37% | $539,901 and above | $647,851 and above |
It's important to note that these federal tax brackets are applicable to taxable income after deductions and exemptions. The interaction between Ohio's flat state tax rate and these federal brackets can result in varying effective tax rates for individuals and businesses.
Understanding Ohio’s Taxable Income
In Ohio, the concept of taxable income is key to determining an individual’s or business’s tax liability. Taxable income is calculated by subtracting any applicable deductions and exemptions from the total income. Ohio offers a standard deduction, which is a set amount that taxpayers can subtract from their income to reduce their taxable income. For the 2023 tax year, the standard deduction for single filers is 4,700</strong>, while married couples filing jointly receive a deduction of <strong>9,400. Additionally, taxpayers can claim personal exemptions, which further reduce their taxable income.
For example, let's consider a single taxpayer with an annual income of $50,000. After subtracting the standard deduction of $4,700 and a personal exemption of $4,500, their taxable income would be $40,800. This amount is then subjected to the flat state tax rate of 2.85%, resulting in a state tax liability of $1,160.40.
It's important to consult with tax professionals or utilize tax calculation tools to accurately determine taxable income and the corresponding tax liability.
Exemptions and Deductions in Ohio
Ohio offers several exemptions and deductions that can reduce taxable income, providing taxpayers with opportunities to minimize their tax burden. Here are some key exemptions and deductions to consider:
- Standard Deduction: As mentioned earlier, Ohio provides a standard deduction that reduces taxable income. The amount varies based on filing status, with higher deductions for married couples filing jointly.
- Personal Exemptions: Taxpayers can claim personal exemptions for themselves and their dependents. Each exemption reduces taxable income by a set amount, which is subject to annual adjustments.
- Itemized Deductions: Taxpayers have the option to itemize their deductions instead of claiming the standard deduction. This allows them to list specific expenses that qualify for tax deductions, such as medical expenses, state and local taxes, charitable contributions, and mortgage interest.
- Retirement Plan Contributions: Contributions to certain retirement plans, such as 401(k)s and IRAs, can be deducted from taxable income. These deductions encourage savings for retirement and provide tax benefits.
- Education Expenses: Ohio taxpayers can deduct qualified education expenses, including tuition and fees, for themselves, their spouses, or their dependents. This deduction promotes access to education and can significantly reduce taxable income.
It's crucial to review the eligibility criteria and guidelines for each exemption and deduction to ensure compliance with Ohio's tax laws.
Tax Rates and Brackets for Different Income Sources

Ohio’s tax system applies different tax rates to various sources of income. While the state tax rate is flat, certain income types are subject to specific rules and rates. Here’s an overview of the tax rates for different income sources:
Wages and Salaries
Wages and salaries earned by Ohio residents are subjected to the state’s flat tax rate of 2.85% for the 2023 tax year. This rate applies to all levels of income, making it a straightforward calculation. Employers are responsible for withholding the appropriate amount of tax from employees’ wages, ensuring compliance with the state’s tax obligations.
Business Income
Ohio imposes a flat tax rate of 2.85% on business income, including sole proprietorships, partnerships, and S corporations. This rate applies to the net income generated by the business after accounting for all allowable deductions and expenses. Business owners should carefully track their income and expenses to accurately determine their tax liability.
Rental Income
Rental income generated from properties located in Ohio is subject to the state’s flat tax rate. However, it’s important to note that rental income is often considered passive income and may be taxed at a different rate than earned income. Additionally, rental expenses, such as maintenance, repairs, and property taxes, can be deducted to reduce the taxable income.
Investment Income
Investment income, including dividends, capital gains, and interest, is taxed at the federal level. The tax rate applied to investment income depends on the type of investment and the taxpayer’s overall income level. For example, qualified dividends and long-term capital gains are generally taxed at more favorable rates compared to ordinary income.
Retirement Income
Retirement income, such as pensions, annuities, and retirement account distributions, is subject to taxation in Ohio. However, certain retirement plans, like Roth IRAs and 401(k) plans, offer tax-free distributions if specific conditions are met. It’s crucial for retirees to understand the tax implications of their retirement income sources and plan accordingly.
Impact of Ohio’s Tax Brackets on Taxpayers
Ohio’s tax brackets and rates have a significant impact on the financial obligations of individuals and businesses within the state. The flat state tax rate simplifies the calculation process, providing a clear understanding of the tax liability. However, the interaction with federal tax brackets can result in varying effective tax rates, especially for high-income earners.
For individuals with lower incomes, the combination of Ohio's flat tax rate and the federal tax brackets can lead to a relatively low overall tax burden. On the other hand, high-income earners may face a higher effective tax rate due to the progressive nature of the federal tax system. It's important for taxpayers to carefully plan their finances and explore opportunities to reduce their taxable income through deductions and exemptions.
Businesses operating in Ohio also need to consider the impact of the state's tax system on their bottom line. The flat tax rate provides consistency and simplicity, making it easier to estimate tax liabilities. However, businesses with multiple income streams should be aware of the different tax rates applied to each source of income.
Tax Planning Strategies
Understanding Ohio’s tax brackets and rates allows taxpayers to employ effective tax planning strategies. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Maximizing Deductions: Taxpayers can reduce their taxable income by maximizing deductions. This includes claiming the standard deduction, itemizing deductions, and contributing to tax-advantaged retirement plans.
- Strategic Timing of Income: Individuals and businesses can benefit from strategic timing of income to fall within a lower tax bracket. For instance, delaying bonuses or income recognition until a new tax year can reduce the overall tax liability.
- Exploring Tax Credits: Ohio offers various tax credits, such as the Research and Development Tax Credit and the Motion Picture Tax Credit, which can provide significant tax savings for eligible taxpayers.
- Utilizing Tax Preparation Services: Engaging the services of tax professionals or utilizing reputable tax preparation software can ensure accurate tax calculations and help identify opportunities to minimize tax liabilities.
It's important to note that tax laws and regulations can change frequently, so staying updated with the latest information is crucial for effective tax planning.
Future Outlook and Potential Changes
The tax landscape in Ohio, like any other state, is subject to potential changes and reforms. While the current flat tax rate of 2.85% provides simplicity and consistency, there have been discussions and proposals for tax reform in recent years.
Some proposed changes include modifying the flat tax rate to a graduated system, similar to the federal tax brackets. This could result in higher tax rates for higher income levels, aiming to provide more revenue for state programs and services. However, such reforms face political and economic considerations and may take time to implement.
Additionally, there have been discussions about expanding the types of income subject to taxation, such as capital gains and investment income, to increase revenue. These changes could impact taxpayers' financial planning and require adjustments to their tax strategies.
It's crucial for taxpayers and businesses to stay informed about any proposed changes to Ohio's tax system and consider the potential implications on their financial obligations.
Staying Informed and Seeking Professional Advice
As tax laws and regulations can be complex and subject to frequent changes, it’s essential for taxpayers to stay updated with the latest information. The Ohio Department of Taxation provides official guidance and resources on its website, offering valuable insights into tax obligations and any upcoming changes.
For complex tax situations or specific concerns, seeking professional advice from certified public accountants (CPAs) or tax attorneys is highly recommended. These professionals can provide tailored guidance based on individual circumstances and ensure compliance with Ohio's tax laws.
By staying informed and seeking expert advice, taxpayers can navigate Ohio's tax brackets and rates effectively, minimizing their tax liabilities and maximizing their financial well-being.
How often are Ohio’s tax brackets updated or modified?
+Ohio’s tax brackets are typically updated annually to account for inflation and economic changes. The Ohio Department of Taxation announces any modifications to the tax rates and brackets, and taxpayers should stay informed to ensure compliance with the latest regulations.
Are there any plans to change Ohio’s flat tax rate to a graduated system?
+There have been discussions and proposals to modify Ohio’s flat tax rate to a graduated system, similar to the federal tax brackets. However, as of the 2023 tax year, Ohio maintains its flat tax rate of 2.85%. Any future changes will depend on political and economic considerations.
What are some common tax deductions available in Ohio?
+Ohio offers various tax deductions, including the standard deduction, personal exemptions, itemized deductions for medical expenses, state and local taxes, charitable contributions, and mortgage interest. Additionally, taxpayers can deduct qualified education expenses and retirement plan contributions.
How can taxpayers stay updated with Ohio’s tax laws and regulations?
+Taxpayers can stay informed by regularly visiting the Ohio Department of Taxation’s website, which provides official guidance and updates on tax laws. Additionally, subscribing to tax-related newsletters or following reputable tax publications can ensure access to the latest information.
What should taxpayers do if they have specific tax-related concerns or questions?
+For complex tax situations or specific concerns, taxpayers should consult with certified public accountants (CPAs) or tax attorneys. These professionals can provide expert advice tailored to individual circumstances and ensure compliance with Ohio’s tax laws.



