State Of Ohio Income Tax
The State of Ohio's income tax system is a crucial component of its revenue stream, contributing significantly to the state's financial stability and the provision of essential public services. With a diverse economy and a population of over 11 million, Ohio's income tax plays a vital role in supporting infrastructure, education, healthcare, and other vital sectors. This article delves into the intricacies of Ohio's income tax, exploring its history, structure, rates, deductions, and its impact on the state's economy and residents.
A Historical Perspective on Ohio’s Income Tax

Ohio’s journey with income taxation began relatively late compared to many other states. The Buckeye State introduced its first income tax system in 1919, following a period of economic growth and industrialization. This initial income tax system was a response to the increasing demand for public services and the need to diversify the state’s revenue sources.
However, Ohio's income tax underwent significant changes over the decades. In the 1970s, the state experienced a period of fiscal challenges, prompting reforms to make the tax system more progressive and equitable. These reforms included the introduction of tax brackets and the adjustment of rates to align with the cost of living and economic growth.
The Current Income Tax Structure in Ohio

Today, Ohio’s income tax system operates on a graduated, progressive scale, meaning that as income increases, so does the tax rate. This approach ensures that those with higher earnings contribute a larger proportion of their income to the state’s revenue, promoting fairness and social equity.
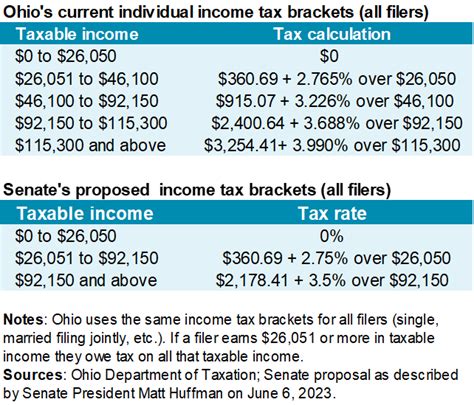
The current tax structure consists of five tax brackets, each with its own rate. These brackets are designed to capture various income levels, ensuring that individuals and families of different financial standings contribute appropriately. The rates range from 0.479% to 4.799%, with the highest rate applicable to incomes exceeding $231,000 for single filers and $410,000 for joint filers.
| Tax Bracket | Income Range | Tax Rate |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Up to $10,000 | 0.479% |
| 2 | $10,001 to $50,000 | 1.549% |
| 3 | $50,001 to $100,000 | 2.549% |
| 4 | $100,001 to $231,000 | 3.549% |
| 5 | Over $231,000 (single) or $410,000 (joint) | 4.799% |
Key Features of Ohio’s Income Tax System
Ohio’s income tax system offers several notable features and benefits for taxpayers:
- Tax Credits and Deductions: Ohio provides various tax credits and deductions to ease the tax burden on specific groups. These include credits for low-income families, seniors, and individuals with disabilities, as well as deductions for medical expenses, charitable contributions, and certain business-related expenses.
- Net Operating Loss (NOL) Carryover: Businesses in Ohio can benefit from NOL carryover provisions, allowing them to offset current-year losses against past or future profits. This provision promotes financial stability and encourages investment.
- E-Filing and Payment Options: Ohio offers convenient electronic filing and payment options, streamlining the tax process for individuals and businesses. This digital approach reduces administrative burdens and enhances efficiency.
The Economic Impact of Ohio’s Income Tax
Ohio’s income tax system has a profound impact on the state’s economy and its residents. By generating significant revenue, the tax supports vital public services and infrastructure projects. This, in turn, creates a positive feedback loop, contributing to economic growth and development.
Moreover, the progressive nature of Ohio's income tax system ensures that the state's wealthiest residents contribute a substantial portion of their income, fostering a sense of social responsibility and fairness. This approach also helps reduce income inequality, promoting a more equitable distribution of wealth.
Income Tax and Ohio’s Business Climate
Ohio’s income tax system has been designed to attract and support businesses. The state offers a competitive tax environment, with a top income tax rate lower than many other states. This, combined with Ohio’s central location, skilled workforce, and robust infrastructure, makes it an attractive destination for businesses seeking to expand or relocate.
Additionally, Ohio provides various tax incentives and credits to businesses, especially those investing in research and development, job creation, and community development. These incentives not only encourage economic growth but also promote social and environmental responsibility.
Comparative Analysis: Ohio’s Income Tax vs. Other States
When compared to other states, Ohio’s income tax system stands out for its fairness, simplicity, and competitiveness. While the top income tax rate is relatively moderate, the progressive structure ensures that higher-income earners contribute significantly to the state’s revenue.
In contrast to some states with flat tax rates, Ohio's graduated system promotes social equity. It recognizes that individuals with higher incomes have a greater ability to pay, thus ensuring a more balanced tax burden. This approach has contributed to Ohio's reputation as a state with a fair and efficient tax system.
Income Tax and Resident Well-being
The income tax system in Ohio is not only about revenue generation but also about supporting the well-being of its residents. The tax revenue funds essential services like education, healthcare, and social programs, which directly impact the quality of life for Ohioans.
For instance, Ohio's income tax supports its public education system, ensuring that schools have the resources to provide quality education. This investment in education not only benefits current students but also contributes to the state's future economic prosperity by nurturing a skilled workforce.
The Future of Ohio’s Income Tax: Trends and Projections

Looking ahead, Ohio’s income tax system is expected to continue evolving to meet the changing needs of its residents and the state’s economy. As the state’s population grows and diversifies, the tax system will need to adapt to ensure it remains fair, efficient, and capable of supporting public services.
One trend to watch is the increasing focus on tax simplification and transparency. Ohio, like many other states, is exploring ways to streamline its tax system, making it easier for taxpayers to understand and comply with. This includes potential reforms to tax brackets, deductions, and credits, as well as enhanced digital platforms for filing and payment.
Furthermore, as the state continues to prioritize economic growth and job creation, Ohio's income tax system may see adjustments to encourage investment and business expansion. This could involve targeted tax incentives, credits, or even adjustments to tax rates to make Ohio an even more attractive destination for businesses.
What are the key differences between Ohio’s income tax system and that of its neighboring states?
+
Ohio’s income tax system differs from its neighboring states in several ways. While some states, like Indiana and Kentucky, have flat tax rates, Ohio’s graduated system ensures a more progressive approach. Additionally, Ohio offers a range of tax credits and deductions that are unique to the state, providing relief to specific groups like low-income families and seniors.
How does Ohio’s income tax impact the state’s business environment and economic growth?
+
Ohio’s income tax system, with its competitive rates and various tax incentives, plays a crucial role in attracting and retaining businesses. This, in turn, drives economic growth, job creation, and investment in the state. The tax revenue generated also supports vital infrastructure and public services, further enhancing Ohio’s business climate.
Are there any plans to reform or simplify Ohio’s income tax system in the near future?
+
Yes, there is an ongoing discussion about simplifying and modernizing Ohio’s tax system. This includes potential reforms to tax brackets, deductions, and credits to make the system more transparent and user-friendly. The aim is to ensure that Ohio’s tax system remains fair, efficient, and capable of supporting the state’s economic growth and resident well-being.