State Of Indiana Sales Tax Rate
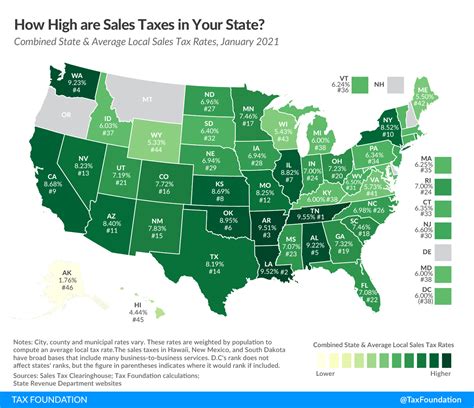
The State of Indiana has a robust sales tax system that contributes significantly to its revenue generation. Sales tax rates in Indiana are subject to both state and local regulations, resulting in varying tax rates across different counties and municipalities. Understanding the intricacies of Indiana's sales tax landscape is essential for businesses and consumers alike.
The Indiana Sales Tax Structure
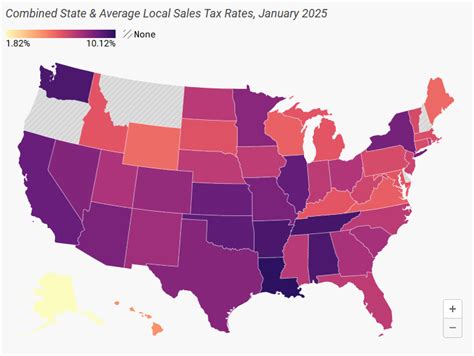
Indiana imposes a state sales tax rate of 7%, which applies uniformly across the state. However, the tax system also allows for the addition of local sales taxes, leading to variations in the overall tax burden experienced by residents and businesses.
Local Sales Tax Rates
In addition to the state sales tax, Indiana counties and municipalities have the authority to levy their own sales taxes. These local taxes can range from 0% to 4%, depending on the specific jurisdiction. As a result, the total sales tax rate can vary significantly from one region to another.
| County | Local Sales Tax Rate | Total Sales Tax Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Marion County | 2% | 9% |
| Lake County | 4% | 11% |
| Allen County | 3% | 10% |
| Vanderburgh County | 2% | 9% |
| Tippecanoe County | 3% | 10% |

The table above provides a glimpse into the varying local sales tax rates across some of Indiana's counties. It's important to note that these rates are subject to change and may not reflect the most recent updates. For the most accurate information, it is advisable to consult the Indiana Department of Revenue or local government websites.
Sales Tax Exemptions in Indiana
While Indiana’s sales tax applies to a wide range of goods and services, there are certain categories that are exempt from this tax. Understanding these exemptions is crucial for businesses and individuals to ensure compliance and avoid unnecessary tax liabilities.
Food and Grocery Items
One notable exemption in Indiana’s sales tax system is for certain food and grocery items. While the specifics can vary, in general, unprepared foods and beverages, as well as ingredients used for home cooking, are exempt from sales tax. This exemption provides a significant relief for consumers, especially those with lower incomes, by reducing the tax burden on essential food items.
Prescription Drugs and Medical Devices
Indiana also exempts prescription drugs and certain medical devices from sales tax. This exemption aims to make essential healthcare more accessible and affordable for residents. It includes items like prescription medications, medical supplies, and certain durable medical equipment.
Manufacturing and Industrial Equipment
The state encourages economic growth and development by exempting manufacturing and industrial equipment from sales tax. This exemption applies to machinery, tools, and other equipment used in the manufacturing process. By reducing the tax burden on businesses, Indiana aims to foster innovation and job creation in the industrial sector.
Educational and Charitable Organizations
Sales tax exemptions are also extended to educational and charitable organizations in Indiana. This includes items purchased by or for these organizations, as well as services provided by them. By reducing the tax burden on these entities, the state supports their crucial work in the community and encourages further investment in education and charitable causes.
Sales Tax Filing and Compliance
For businesses operating in Indiana, understanding the sales tax filing requirements is essential for compliance. The Indiana Department of Revenue provides detailed guidelines and resources to assist businesses in navigating the sales tax system.
Registration and Permits
Businesses must register with the Indiana Department of Revenue to obtain a Sales and Use Tax Permit. This permit authorizes the business to collect and remit sales tax on behalf of the state and local governments. The registration process involves providing detailed information about the business, its activities, and its tax obligations.
Sales Tax Collection and Remittance
Once registered, businesses are responsible for collecting sales tax from customers at the point of sale. The tax rate applied depends on the location of the sale and the nature of the goods or services provided. Businesses must then remit the collected sales tax to the appropriate tax authorities, typically on a monthly or quarterly basis, depending on their revenue and sales volume.
Sales Tax Returns and Filing
In addition to remitting the collected sales tax, businesses must also file sales tax returns. These returns provide a detailed account of the sales tax collected and remitted during a specific period. The Indiana Department of Revenue provides online filing options, making the process more efficient and convenient for businesses. Late filings or non-compliance can result in penalties and interest charges.
The Impact of Sales Tax on Indiana’s Economy
Indiana’s sales tax system plays a significant role in shaping the state’s economy. It generates substantial revenue for state and local governments, which is then invested back into critical areas such as education, infrastructure, and social services.
Revenue Generation and Allocation
The sales tax is a key source of revenue for Indiana, contributing billions of dollars to the state’s budget each year. This revenue is allocated to various government programs and initiatives, ensuring the smooth functioning of state and local services. The sales tax also supports essential infrastructure projects, such as road construction and maintenance, which are vital for the state’s economic development.
Economic Development and Job Creation
By exempting certain sectors and industries from sales tax, Indiana’s tax system encourages economic growth and job creation. The exemptions for manufacturing and industrial equipment, for instance, make Indiana an attractive destination for businesses looking to expand or relocate. This, in turn, leads to increased investment, job opportunities, and a thriving business environment.
Consumer Spending and Economic Stimulus
Sales tax also has an impact on consumer spending habits. While it adds to the cost of goods and services, it also provides a form of economic stimulus. Consumers are incentivized to spend within the state, supporting local businesses and contributing to the overall economic health of Indiana. Additionally, the varying sales tax rates across regions can encourage tourism and leisure spending, further boosting the state’s economy.
Future Implications and Considerations
As Indiana’s economy continues to evolve, the sales tax system is likely to undergo changes and adjustments. Here are some key considerations for the future:
Sales Tax Harmonization
With varying local sales tax rates, there is a growing need for harmonization to simplify the tax system and reduce administrative burdens. Harmonization would involve standardizing the sales tax rate across the state, potentially eliminating the complexity of local taxes. This could make it easier for businesses to comply with tax regulations and provide a more consistent experience for consumers.
Online Sales and E-Commerce
The rise of e-commerce and online sales presents unique challenges for sales tax collection. Indiana, like many other states, is working to adapt its tax system to ensure that online retailers and marketplaces collect and remit sales tax appropriately. This includes implementing laws and regulations that require online sellers to collect and remit sales tax, even for remote sales.
Tax Policy and Economic Equity
As Indiana considers its tax policies, there is an ongoing debate about the balance between revenue generation and economic equity. Sales tax, being a consumption tax, places a heavier burden on lower-income individuals who spend a larger proportion of their income on taxable goods and services. As such, policymakers must carefully consider the impact of sales tax on different income groups and ensure that the tax system remains fair and equitable.
Technological Innovations in Tax Administration
The advancement of technology offers new opportunities for tax administration. Indiana can leverage technology to streamline the sales tax collection and remittance process, making it more efficient and accurate. This could involve implementing digital platforms and tools for tax filing, payment, and compliance, reducing the administrative burden on both businesses and tax authorities.
Conclusion
Indiana’s sales tax system is a complex yet vital component of the state’s economy. It generates revenue, supports essential services, and encourages economic growth. While there are challenges and considerations for the future, the state’s tax system continues to evolve, adapting to the changing economic landscape and technological advancements. Understanding Indiana’s sales tax rates and exemptions is crucial for businesses and consumers to navigate the tax landscape effectively and ensure compliance.
What is the current state sales tax rate in Indiana?
+The current state sales tax rate in Indiana is 7%.
Are there any sales tax exemptions in Indiana?
+Yes, Indiana has several sales tax exemptions. These include food and grocery items, prescription drugs and medical devices, manufacturing and industrial equipment, and purchases by educational and charitable organizations.
How often do businesses need to file sales tax returns in Indiana?
+The frequency of filing sales tax returns in Indiana depends on the business’s revenue and sales volume. Typically, businesses file sales tax returns on a monthly or quarterly basis.
What is the impact of varying local sales tax rates in Indiana?
+Varying local sales tax rates in Indiana can lead to differences in the overall tax burden experienced by residents and businesses across different regions. It can also impact consumer spending patterns and the competitiveness of local economies.
How does Indiana address online sales and e-commerce in its sales tax system?
+Indiana has implemented laws and regulations to ensure that online retailers and marketplaces collect and remit sales tax for remote sales. This is part of the state’s efforts to adapt its tax system to the evolving e-commerce landscape.



