Mastering the Schedule D Tax Form: A Step-by-Step Guide to Simplify Your Taxes
Within the intricate tapestry of personal finance and taxation, the Schedule D form emerges as more than just a bureaucratic requirement; it embodies a fundamental intersection of numerical precision, strategic planning, and individual financial storytelling. While often perceived as a mere appendix to the primary tax return, Schedule D encapsulates the nuanced art of documenting capital gains and losses, serving as a bridge between complex investment activities and their fiscal implications. Mastering this form is akin to attuning oneself to a symphony of financial signals—each line and entry offering insights into past transactions, current standings, and future strategies. Its mastery reflects a broader philosophical principle: that effective financial stewardship hinges not solely on the accumulation of assets but on the deliberate, informed management of their transaction histories, which this form meticulously records.
The Significance of the Schedule D in the Broader Tax Ecosystem

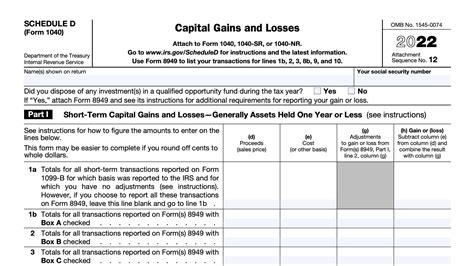
The Schedule D, titled “Capital Gains and Losses,” functions within the larger framework of the IRS tax code as a crucial component for taxpayers engaging in investment activities. Its foundation rests on a fundamental principle: that capital assets—such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and other investment instruments—are not just financial tools but are also subjects of taxable events. This form captures the essence of these events, translating the abstract realm of asset transactions into quantifiable, reportable figures that directly influence tax liability. Understanding its role provides a philosophical perspective: that every financial decision, including buying or selling an asset, leaves an indelible mark on one’s fiscal identity, and Schedule D serves as the ledger recording these marks. In the context of personal economic history, it transforms individual investment journeys into tangible, analyzable data points, allowing for reflective assessment and strategic planning.
Historical Evolution and Regulatory Framework
Fundamentally, the Schedule D’s origins trace back to the codification of capital gains taxation, which gained prominence in the early 20th century alongside the development of modern securities markets. Over decades, it has evolved considerably, shaped by regulatory changes aimed at closing loopholes and increasing transparency. For instance, the Tax Reform Act of 1986 introduced more detailed reporting requirements, emphasizing the importance of accurate record-keeping for investors. Its current form embodies complex legal principles, including holding period distinctions (short-term versus long-term), wash sale rules, and basis calculations. From a philosophical standpoint, these developments highlight society’s ongoing negotiation with the balance between encouraging investment and ensuring equitable taxation—a conversation that Schedule D continually mediates through its detailed reporting requirements.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Number of capital transactions reported annually | Approximately 150 million entries in Schedule D forms processed each year in the US |
| Percentage of taxpayers using Schedule D | Over 30% of individual taxpayers report capital gains or losses |
Key Points
- Precise record-keeping: The cornerstone of accurate Schedule D filing; entails maintaining detailed transaction records including purchase dates, costs, sale prices, and holding periods.
- Understanding holding periods: Differentiating short-term from long-term gains influences tax rates; mastery involves strategic planning to optimize tax outcomes.
- Tax-loss harvesting: A tactical approach to offset gains with losses, reducing overall taxable income while adhering to IRS rules.
- Regulatory awareness: Staying updated on IRS regulations, wash sale rules, and basis adjustments ensures compliant and advantageous filings.
- Strategic planning: Using Schedule D insights to inform investment decisions, asset reallocation, and future transaction timing for tax efficiency.
Step-by-Step Process to Complete Schedule D Effectively
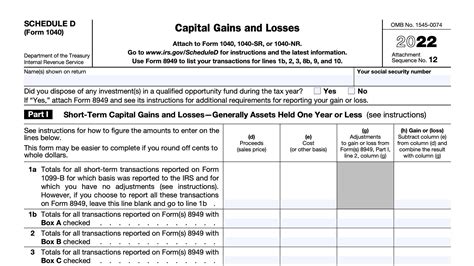
Approaching the Schedule D with a strategic lens begins not with a blank form but with a structured methodology rooted in comprehensive record-keeping and analytical foresight. The process encompasses meticulous compilation of transaction data, classification of gains or losses, and careful calculation of net amounts—each step reflecting a deliberate attempt to portray an accurate financial and fiscal narrative.
Gathering and Organizing Transaction Data
Fundamental to successful Schedule D completion is the systematic collection of all relevant transaction data. This includes brokerage statements, trade confirmations, cost basis reports, and any relevant documentation of property sales. Given the potential volume—particularly for active investors—employing digital record-keeping tools such as specialized tax software or personalized spreadsheets can streamline data management. The key is ensuring that each transaction, whether a single stock trade or complex property sale, has a clear, traceable record that facilitates subsequent classification and calculation. From a philosophical perspective, this diligent documentation reflects respect for the legal process and acknowledgment of the integral role that transparency plays in individual financial sovereignty.
Classifying Gains and Losses: Short-term vs. Long-term
Once the data is compiled, the next step involves categorizing each transaction based on the holding period—short-term if held for one year or less, long-term if for more than one year. This classification bears significant legal and financial weight, given the differential tax rates that can range from 0% to 20% for long-term capital gains. Proper classification requires not only accurate date tracking but also an understanding of how specific events—like partial sales or exchanges—may affect this status. Technical accuracy here embodies a critical philosophical principle: that careful segmentation of one’s financial activities underpins informed decision-making and effective tax planning.
| Impact of Classification | Implication |
|---|---|
| Tax rates differentiation | Long-term gains taxed at preferential rates, incentivizing holding investments longer |
| Loss offsetting | Facilitates strategic mitigation of gains through realized losses |
Calculating Gains and Losses Accurately
The core of Schedule D lies in the precise calculation of gains or losses for each transaction, which entails understanding the basis of each asset, adjustments for commissions and fees, and applicable holding periods. The IRS permits several methods for determining basis, including FIFO (First-In, First-Out), Specific Identification, and sometimes average cost, each suited to different circumstances and investment types. Accurate calculation demands a rigorous application of these methods, supported by records that substantiate each figure. This precision transforms raw transactional data into meaningful fiscal narratives, reinforcing the interconnectedness between meticulous record-keeping and effective tax management.
| Common Basis Determination Method | Suitability |
|---|---|
| FIFO | Most common; simple when assets are homogeneous |
| Specific Identification | Allows strategic selection of lots to optimize tax outcome |
| Average Cost | Applicable to mutual funds and certain pooled investments |
Finalizing and Filing Schedule D: Best Practices
Completing Schedule D is the culmination of a disciplined process—requiring diligence in cross-verifying figures, understanding complex rules, and ensuring adherence to IRS guidelines. Utilizing IRS-approved tax software or consulting with tax professionals enhances accuracy and compliance. Double-checking entries, confirming classification, and ensuring supportive documentation is in order reinforce the integrity of the filing. In a broader sense, this meticulous effort echoes the philosophical recognition that individual financial responsibility is not just a legal duty but a moral act of stewarding one’s wealth with integrity and foresight.
Addressing Common Challenges and Pitfalls
One of the most frequent issues is misclassification or basis miscalculation, which can lead to audits or penalties. To mitigate this, continuous education, utilizing reliable documentation, and leveraging advanced tax tools are advantageous strategies. Understanding IRS notices related to Schedule D, such as those pertaining to wash sale disallowance, enhances preparedness. Ultimately, a proactive stance rooted in ongoing learning and disciplined record-keeping affirms a strategic mindset aligned with fiscal responsibility.
Enhancing Tax Efficiency with Schedule D Insights
Beyond mere compliance, fully mastering Schedule D enables the savvy taxpayer to harness opportunities for tax optimization. Strategies such as tax-loss harvesting—selling investments at a loss to offset gains—are facilitated by clear, accurate Schedule D data. Moreover, strategic asset reallocation based on this reporting can lead to long-term tax benefits, especially when synchronized with broader investment plans and anticipated market shifts. This level of mastery exemplifies a holistic viewpoint: viewing taxes not as a burden but as an integral component of wealth management, where each transaction record informs smarter, more sustainable financial decisions.
What are the key differences between short-term and long-term capital gains?
+Short-term gains are realized on assets held for one year or less and are taxed at ordinary income rates. Long-term gains, from assets held over one year, benefit from reduced tax rates, often ranging from 0% to 20%, depending on taxable income. Understanding these distinctions influences investment timing and strategic planning to optimize after-tax returns.
How does wash sale rules impact Schedule D transactions?
+The wash sale rule disallows claiming a loss if the same or a substantially identical security is purchased within 30 days before or after a sale at a loss. This regulation requires careful transaction tracking and potentially adjusting basis calculations. Proper understanding ensures compliance while maximizing tax benefit realization.
What tools can assist in accurately completing Schedule D?
+Tax software with integrated investment tracking features, professional tax preparation services, and detailed brokerage reports can streamline Schedule D completion. These tools help automate calculations, ensure proper classifications, and reduce errors—enhancing both accuracy and confidence in filing.



