Sales Tax Rate For New York City

The sales tax rate in New York City is an essential aspect of doing business and understanding the financial landscape for both consumers and entrepreneurs. This comprehensive guide aims to provide an in-depth analysis of the sales tax rate, its structure, and its implications for New York City's vibrant economy.
Understanding the Sales Tax Rate in New York City

Sales tax is a crucial revenue source for local and state governments in the United States, and New York City is no exception. With its diverse economy and bustling business environment, the city has a unique sales tax structure that affects millions of residents and visitors alike.
The sales tax rate in New York City is composed of several components, each serving a specific purpose. The tax rate varies depending on the type of transaction and the location within the city. Understanding these variations is essential for businesses to ensure compliance and for consumers to make informed financial decisions.
The Components of New York City’s Sales Tax
New York City’s sales tax rate consists of the following key components:
- State Sales Tax: A state-wide tax applied to most retail sales, including goods and certain services. The state sales tax rate is set by the New York State Department of Taxation and Finance and is uniform across the state.
- City Sales Tax: In addition to the state tax, New York City imposes its own sales tax to fund local initiatives and infrastructure. This tax rate is set by the city government and can vary based on the type of goods or services being sold.
- Additional Local Taxes: Certain boroughs or neighborhoods within New York City may have their own additional sales taxes. These taxes are typically levied to support specific community projects or initiatives and can further increase the overall sales tax burden.
The interplay between these components results in a dynamic sales tax structure that can vary greatly depending on the transaction and the location within the city. It is crucial for businesses to stay informed about these variations to ensure accurate tax collection and reporting.
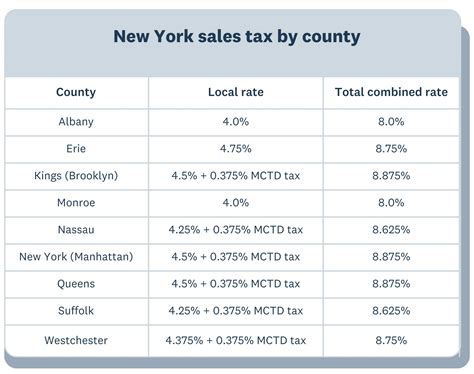
Sales Tax Rates by Borough
New York City is divided into five boroughs: Manhattan, Brooklyn, Queens, the Bronx, and Staten Island. Each borough has its own unique sales tax rate, as shown in the table below:
| Borough | Sales Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Manhattan | 8.875% |
| Brooklyn | 8.875% |
| Queens | 8.875% |
| The Bronx | 8.875% |
| Staten Island | 8.875% |

It's important to note that while the sales tax rate is uniform across the boroughs, there may be additional local taxes or exemptions that apply to specific industries or types of transactions. Businesses operating in multiple boroughs should be aware of these variations to ensure compliance.
Impact on Consumers and Businesses
The sales tax rate in New York City has a significant impact on both consumers and businesses. For consumers, it directly affects their purchasing power and the overall cost of living. A higher sales tax rate can make certain goods and services more expensive, impacting their ability to afford essential items.
For businesses, the sales tax rate influences pricing strategies, operational costs, and profitability. Companies must carefully consider the sales tax burden when setting prices and managing their financial operations. Additionally, the complexity of the sales tax structure can present challenges in tax compliance and reporting, requiring businesses to stay updated on tax regulations and seek professional guidance when necessary.
Sales Tax Exemptions and Special Considerations
While the standard sales tax rate applies to most transactions, New York City also offers certain exemptions and special considerations that can reduce the tax burden for specific goods or services. These exemptions are designed to support specific industries, promote economic growth, or provide relief to certain consumer groups.
Tax Exemptions for Essential Goods
New York City, like many other jurisdictions, recognizes the importance of certain essential goods and provides sales tax exemptions for these items. This is done to ensure that basic necessities remain affordable for all residents. Some of the commonly exempted essential goods include:
- Prescription medications
- Certain medical devices and equipment
- Food items for home consumption (excluding prepared meals and restaurant food)
- Clothing and footwear (up to a certain price threshold)
- School supplies and textbooks
By exempting these essential items from sales tax, the city aims to reduce the financial burden on residents, especially those with lower incomes, and ensure access to necessary goods and services.
Sales Tax Exemptions for Businesses
New York City also offers sales tax exemptions for businesses operating within specific industries or meeting certain criteria. These exemptions are designed to promote economic growth, support innovation, and encourage business development. Some of the notable business-related sales tax exemptions include:
- Manufacturing: Certain manufacturing processes and equipment are exempt from sales tax, encouraging the growth of the manufacturing sector in the city.
- Research and Development: Businesses engaged in research and development activities may qualify for sales tax exemptions on certain purchases, fostering innovation and technological advancement.
- Export Sales: Sales of goods that are exported outside the United States are typically exempt from sales tax, supporting international trade and business expansion.
- Wholesale Transactions: Sales between businesses (wholesale transactions) are often exempt from sales tax, facilitating smooth operations within the supply chain.
These exemptions not only reduce the tax burden for eligible businesses but also encourage investment and job creation within the city. It is crucial for businesses to stay informed about these exemptions and consult with tax professionals to ensure they are taking full advantage of the available benefits.
Special Sales Tax Considerations for Tourism
New York City is a global tourism hub, attracting millions of visitors each year. To support the tourism industry and promote visitor spending, the city offers special sales tax considerations for certain tourism-related transactions. These considerations aim to make the city more competitive as a destination and enhance the overall visitor experience.
One notable special consideration is the exemption of sales tax on hotel accommodations for stays of 30 consecutive days or more. This exemption encourages longer-term stays and promotes the development of extended-stay accommodations. Additionally, certain tourism-related services, such as guided tours and entertainment events, may also be eligible for reduced or exempted sales tax rates, depending on the specific circumstances.
These special considerations not only benefit tourists but also support the local tourism industry, including hotels, tour operators, and entertainment venues. By providing tax incentives, the city aims to create a vibrant and attractive tourism ecosystem that contributes significantly to the local economy.
Compliance and Reporting: A Guide for Businesses
For businesses operating in New York City, understanding the sales tax rate and its intricacies is only the first step. Ensuring compliance with tax regulations and accurately reporting sales tax liabilities is equally crucial to avoid penalties and maintain a positive relationship with tax authorities.
Sales Tax Registration and Permits
Before collecting and remitting sales tax, businesses must obtain the necessary permits and registrations. In New York City, this typically involves registering with the New York State Department of Taxation and Finance and obtaining a Certificate of Authority for Sales Tax. The process may vary depending on the business’s legal structure and the nature of its operations.
Businesses should carefully review the registration requirements and ensure they have all the necessary documentation in place. Failure to register properly can result in penalties and complications in the future.
Sales Tax Collection and Remittance
Once registered, businesses are responsible for collecting sales tax from customers at the point of sale. This involves accurately calculating the tax based on the applicable rate and the transaction value. It is crucial to maintain accurate records of all sales transactions, including the tax amount collected, to facilitate proper reporting.
The frequency of sales tax remittance to the tax authorities depends on the business's sales volume and the tax jurisdiction. Some businesses may need to remit sales tax monthly, while others may do so quarterly or annually. Staying informed about the remittance schedule and ensuring timely payments is essential to avoid penalties and maintain compliance.
Sales Tax Reporting and Filing
Accurate sales tax reporting is a critical aspect of compliance. Businesses must file sales tax returns with the tax authorities, providing detailed information about their sales transactions, the tax collected, and any exemptions or deductions claimed. The filing process typically involves submitting the required forms and supporting documentation electronically or through traditional mail.
It is important to maintain meticulous records and supporting documentation to substantiate the sales tax reported. This includes invoices, receipts, and any relevant records that demonstrate compliance with tax regulations. Inaccurate reporting can lead to audits, penalties, and legal consequences, so businesses should prioritize accurate and transparent sales tax reporting.
Tips for Accurate Sales Tax Compliance
- Stay Informed: Tax regulations and rates can change periodically. Businesses should stay updated on any amendments to sales tax laws and ensure they are applying the correct rates and exemptions.
- Seek Professional Advice: Tax compliance can be complex, especially for businesses with diverse operations or those operating in multiple jurisdictions. Consulting with tax professionals or accounting firms can provide valuable guidance and ensure accurate compliance.
- Use Reliable Software: Utilizing sales tax software or accounting systems can streamline the tax compliance process. These tools can automate tax calculations, reporting, and filing, reducing the risk of errors and saving time and resources.
- Keep Records Organized: Maintaining organized records is crucial for audit purposes and for supporting sales tax reporting. Businesses should establish efficient record-keeping systems and ensure all relevant documentation is easily accessible.
By following these tips and maintaining a proactive approach to sales tax compliance, businesses can operate with confidence, minimize the risk of penalties, and contribute to the economic vitality of New York City.
The Future of Sales Tax in New York City
As New York City continues to evolve and adapt to changing economic landscapes, the sales tax rate and its structure are likely to undergo further modifications. The city’s tax policies are shaped by a dynamic interplay of economic factors, political considerations, and the needs of its diverse population.
Potential Changes and Their Implications
Here are some potential changes and their potential impacts on the sales tax rate in New York City:
- Economic Growth and Revenue Needs: As the city experiences economic growth and faces increasing demands for public services, there may be considerations to adjust the sales tax rate to meet revenue goals. A higher sales tax rate could generate additional revenue for infrastructure development, social programs, and essential services.
- Equity and Social Justice: Discussions around tax equity and social justice may lead to changes in the sales tax structure. For example, implementing a progressive sales tax system could alleviate the tax burden on lower-income individuals while ensuring adequate revenue for essential services.
- Technology and E-Commerce: The rise of e-commerce and digital platforms has transformed the way businesses operate and consumers shop. As a result, there may be considerations to adjust sales tax regulations to accommodate online transactions and ensure fair taxation for both brick-and-mortar and online businesses.
- Regional Competition: New York City operates within a competitive regional market. Changes in sales tax rates in neighboring jurisdictions could prompt the city to adjust its own rates to maintain competitiveness and attract businesses and investments.
These potential changes highlight the dynamic nature of tax policies and the need for ongoing adaptation. It is crucial for businesses, consumers, and policymakers to stay informed about these discussions and their potential implications.
Preparing for Future Sales Tax Changes
To navigate potential future changes in the sales tax rate, businesses and consumers can take proactive steps:
- Stay Informed: Follow tax policy discussions and stay updated on any proposed changes. This allows businesses and consumers to plan and adapt their strategies accordingly.
- Engage with Policymakers: Businesses and community leaders can actively engage with policymakers to provide input and advocate for tax policies that support economic growth, equity, and the well-being of residents.
- Adapt Pricing Strategies: Businesses should consider the potential impact of sales tax changes on their pricing strategies. This may involve reviewing pricing models, exploring alternative revenue streams, and ensuring financial flexibility to adapt to changing tax landscapes.
- Build Tax Compliance Expertise: Investing in tax compliance expertise, either through in-house resources or external consultants, can help businesses navigate changing tax regulations and ensure ongoing compliance.
By staying engaged and proactive, businesses and consumers can contribute to a healthy and adaptive tax environment that supports the long-term prosperity of New York City.
Conclusion

The sales tax rate in New York City is a complex yet essential component of the city’s economic landscape. From understanding the structure of the sales tax to navigating exemptions and compliance, this comprehensive guide has provided an in-depth analysis of the key aspects impacting businesses and consumers.
As New York City continues to thrive and adapt to changing circumstances, the sales tax rate will undoubtedly evolve to meet the needs of its dynamic economy. By staying informed, engaging with tax authorities, and adopting best practices, businesses can ensure compliance, optimize their financial strategies, and contribute to the city's economic success.
For consumers, understanding the sales tax rate and its variations empowers them to make informed purchasing decisions and advocate for tax policies that support their interests. Together, businesses and consumers can shape a tax environment that fosters growth, equity, and prosperity for all New Yorkers.
How often are sales tax rates updated in New York City?
+Sales tax rates in New York City are subject to periodic updates and amendments. While the frequency of changes can vary, it is generally recommended for businesses and consumers to stay informed about any potential changes, especially during budget seasons or when significant economic shifts occur.
Are there any online resources to stay updated on sales tax rates and regulations in New York City?
+Yes, the New York State Department of Taxation and Finance provides an online resource called the “Taxpayer Guidance Center” (https://www.tax.ny.gov/guidance-center). This website offers comprehensive information on tax rates, regulations, and updates. Additionally, businesses can subscribe to tax alerts and newsletters to receive timely notifications about any changes.
What happens if a business fails to collect or remit sales tax in New York City?
+Failure to collect and remit sales tax in New York City can result in significant penalties and legal consequences. The tax authorities may impose fines, interest charges, and even criminal penalties for non-compliance. It is crucial for businesses to understand their sales tax obligations and seek professional guidance if needed to ensure compliance.
Are there any sales tax holidays in New York City?
+Unlike some other states, New York City does not currently have designated sales tax holidays



