Sales Tax Rate Florida
In the state of Florida, sales tax is a crucial component of the revenue system, impacting both residents and businesses alike. This article aims to delve into the intricacies of Florida's sales tax rate, exploring its structure, applicability, and implications for various sectors of the economy.
Understanding Florida’s Sales Tax Rate
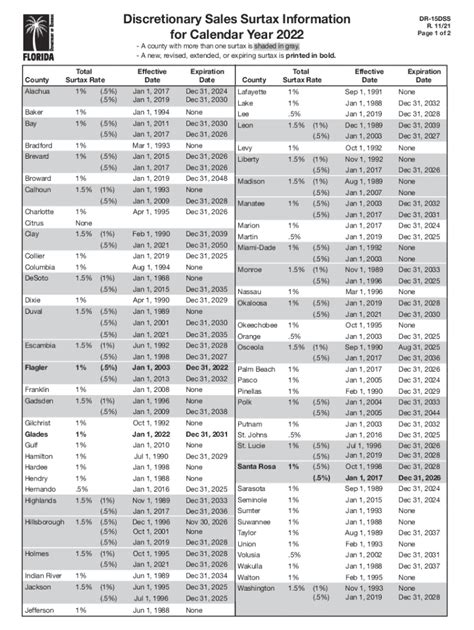
Florida, known for its sunny beaches and vibrant tourism industry, boasts a unique sales tax structure. The state sales tax rate in Florida is currently set at 6%, making it one of the lower rates among U.S. states. However, it’s important to note that this is just the base rate, and local governments can add their own sales taxes on top of this, creating a complex landscape of varying tax rates across the state.
The Florida Department of Revenue is responsible for administering and enforcing the sales tax regulations. They ensure compliance and provide guidance to businesses and consumers alike. The state's sales tax system is designed to generate revenue for essential public services, infrastructure development, and other government initiatives.
Sales Tax on Specific Goods and Services
While the base sales tax rate of 6% applies to most tangible personal property and select services, there are exceptions and additional taxes to consider. For instance, certain goods like groceries, prescription drugs, and non-prescription drugs are exempt from sales tax, providing some relief to consumers.
Additionally, specific industries and sectors have unique sales tax considerations. For example, the tourism industry, a significant contributor to Florida's economy, often faces additional taxes on accommodations and rental cars. These taxes can vary depending on the location and type of accommodation, with rates ranging from 5% to 13.5% in certain areas.
| Industry | Sales Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| General Merchandise | 6% |
| Accommodations | 5% - 13.5% |
| Rental Cars | Variable, often 11% |
| Alcoholic Beverages | 6% + Local Option Tax |
| Restaurant Meals | 6% |

Impact on Businesses and Consumers
The sales tax rate in Florida can have a substantial impact on both businesses and consumers. For businesses, especially those in the retail and hospitality sectors, managing and accounting for various sales tax rates can be a complex task. It requires meticulous record-keeping and compliance with state and local regulations to avoid penalties.
From a consumer perspective, the sales tax rate directly influences purchasing power and spending habits. While a lower sales tax rate can encourage spending, the variability in rates across the state can lead to confusion and potential surprises at the checkout counter. It's crucial for consumers to be aware of the applicable sales tax rates in their area to make informed purchasing decisions.
Florida’s Sales Tax: A Local Perspective

Florida’s diverse landscape and vibrant local communities result in a patchwork of sales tax rates across the state. Let’s explore some specific examples to understand the local variations:
Miami: A Tourist Hub with Higher Taxes
Miami, known for its vibrant nightlife and cultural attractions, has a sales tax rate of 7%, which is 1% higher than the state’s base rate. This additional tax, often referred to as the “Local Option Tax,” is implemented to support local infrastructure and tourism-related initiatives. For businesses in Miami, this means navigating a higher sales tax rate, while consumers should be prepared for slightly higher prices compared to other parts of the state.
Orlando: Balancing Tourism and Local Needs
Orlando, a popular tourist destination, has a sales tax rate of 6.5%, which includes the base state rate and a local option tax. This rate strikes a balance between supporting local communities and maintaining competitiveness in the tourism industry. Businesses in Orlando must adapt their pricing strategies to accommodate this rate, ensuring they remain attractive to both tourists and locals.
Tallahassee: A Capital City with Standard Rates
Tallahassee, Florida’s capital city, operates with the standard state sales tax rate of 6%. This rate is applicable to most goods and services, providing a straightforward tax environment for businesses and consumers alike. However, it’s essential to note that specific industries, such as accommodations and rental cars, may have additional taxes, similar to other parts of the state.
Future Implications and Considerations
Florida’s sales tax system is dynamic and subject to change, influenced by various economic and political factors. Here are some key considerations for the future:
- Economic Impact: Changes in the sales tax rate can have a significant economic impact, affecting consumer spending, business profitability, and overall economic growth. Policymakers must carefully consider these implications when proposing any alterations.
- Revenue Generation: Sales tax revenue is a critical component of Florida's budget. The state and local governments rely on this revenue to fund essential services and infrastructure projects. Any adjustments to the sales tax rate must ensure adequate revenue generation without placing an undue burden on businesses or consumers.
- Competitiveness: Florida's sales tax rate, especially in tourist destinations, can influence the state's competitiveness in the global tourism market. Balancing revenue generation with maintaining a competitive edge is a delicate task for policymakers.
How often does Florida revise its sales tax rate?
+Florida's sales tax rate is relatively stable, with revisions occurring infrequently. However, local governments can propose changes to their local option taxes, which can result in varying rates across the state.
Are there any sales tax holidays in Florida?
+Yes, Florida has designated sales tax holidays, typically around back-to-school season. During these periods, specific items like school supplies and clothing are exempt from sales tax, providing relief to consumers.
How do online sales impact Florida's sales tax revenue?
+Online sales have presented challenges for sales tax collection, but Florida has implemented measures to ensure online retailers collect and remit sales tax. This helps maintain a level playing field for brick-and-mortar businesses and ensures a fair tax system.
In conclusion, Florida’s sales tax rate, while seemingly straightforward at the state level, becomes a complex landscape when considering local variations. Businesses and consumers must navigate these nuances to ensure compliance and make informed financial decisions. As Florida continues to evolve, its sales tax system will remain a crucial aspect of the state’s economic framework.



