Sales Tax Ga

Understanding the intricacies of sales tax regulations is essential for businesses operating in the state of Georgia. With a unique tax structure and specific rules, navigating the sales tax landscape in Georgia requires a comprehensive understanding of the state's laws and guidelines. This article aims to provide an in-depth analysis of Sales Tax Ga, offering a thorough guide to help businesses and individuals make sense of this complex topic.
A Comprehensive Guide to Sales Tax in Georgia

Georgia, often referred to as the Peach State, boasts a vibrant economy and a diverse business landscape. As such, it is imperative for businesses, especially those new to the state, to grasp the nuances of sales tax regulations to ensure compliance and avoid penalties. This guide will delve into the specifics of sales tax laws, rates, collection, and remittance, offering a comprehensive resource for anyone seeking clarity on this important topic.
Sales Tax Rates and Exemptions
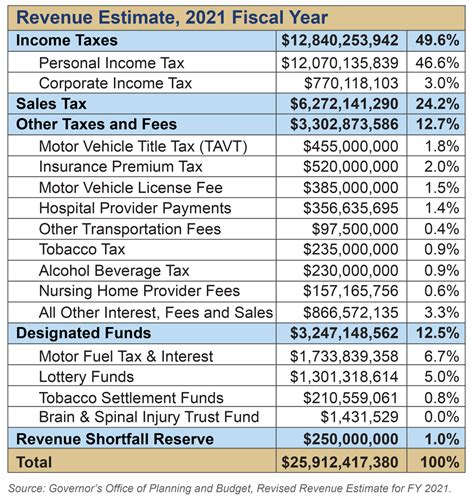
Georgia's sales tax structure is composed of a state-level tax rate and an additional local tax rate, which varies depending on the county. The sales tax rate in Georgia is divided into two components: the state sales and use tax and the local option sales tax. The state sales and use tax rate is a flat 4%, while the local option sales tax rate varies from 0% to 4%, bringing the total sales tax rate in the state to a maximum of 8%.
| Tax Component | Rate |
|---|---|
| State Sales and Use Tax | 4% |
| Local Option Sales Tax | 0% - 4% |
| Maximum Total Sales Tax | 8% |
It's important to note that certain goods and services are exempt from sales tax in Georgia. These exemptions can vary based on the type of item or the purpose for which it is purchased. For instance, prescription drugs, most non-prepared foods, and manufacturing equipment are typically exempt from sales tax. Additionally, Georgia offers various tax incentives and credits, such as the Sales and Use Tax Exemption for Manufacturers and the Research and Development Tax Credit, which can significantly reduce a business's sales tax liability.
Sales Tax Collection and Remittance
Businesses in Georgia that are required to collect sales tax must register with the Georgia Department of Revenue and obtain a Sales and Use Tax Permit. The Permit authorizes the business to collect sales tax from customers and remit it to the state. The frequency of sales tax remittance depends on the business's estimated sales tax liability and can range from monthly to annually.
Georgia operates a Self-Assessment system, where businesses are responsible for calculating and reporting their sales tax liability. This involves regularly reviewing sales records, determining the applicable tax rate for each transaction, and accurately reporting the sales tax collected. Late or incorrect remittance of sales tax can result in penalties and interest charges.
To facilitate the sales tax collection and remittance process, the Georgia Department of Revenue provides an online Taxpayer Portal that allows businesses to manage their tax accounts, file returns, and make payments electronically. This platform offers a user-friendly interface, making it easier for businesses to stay compliant with sales tax regulations.
Special Considerations for Online Sales
With the rise of e-commerce, it's crucial for online businesses to understand their sales tax obligations in Georgia. The state has adopted the Wayfair Nexus standard, which broadens the criteria for determining whether a business has a Nexus (a physical presence) in the state, thereby triggering sales tax collection responsibilities.
Under the Wayfair Nexus standard, businesses that meet certain economic thresholds, such as making a certain number of sales or exceeding a specific revenue amount in Georgia, are considered to have a Nexus in the state and must collect sales tax from Georgia customers. This includes online retailers, drop shippers, and other remote sellers.
Future Implications and Potential Changes
While Georgia's sales tax structure is relatively stable, it's important for businesses to stay informed about potential changes and updates to the regulations. The state regularly reviews and adjusts its tax laws to align with economic trends and to ensure fairness and simplicity in the tax system.
One area of potential change is the state's approach to remote sellers and sales tax collection. As e-commerce continues to grow, states are exploring ways to ensure that out-of-state businesses with substantial economic presence in the state contribute to the state's tax revenue. This could lead to further refinements to the Wayfair Nexus standard or the introduction of new legislation.
Additionally, with the ongoing debate around sales tax fairness and the potential for federal sales tax legislation, businesses in Georgia should monitor national developments that could have a significant impact on their sales tax obligations.
Conclusion
Understanding and complying with sales tax regulations is a critical aspect of doing business in Georgia. By familiarizing themselves with the state's sales tax rates, exemptions, collection processes, and potential future changes, businesses can ensure they meet their sales tax obligations and avoid penalties. This guide provides a comprehensive resource for businesses to navigate the complex world of sales tax in Georgia, offering a solid foundation for tax compliance and strategic planning.
What is the current sales tax rate in Georgia for 2023?
+The current sales tax rate in Georgia for 2023 remains at 4% for the state sales and use tax, with local option sales tax rates varying from 0% to 4%. This means the total sales tax rate can range from 4% to 8%, depending on the county.
Are there any sales tax holidays in Georgia, and what are the eligible items?
+Yes, Georgia offers sales tax holidays throughout the year. These are specific periods when certain items are exempt from sales tax. Common sales tax holidays include back-to-school sales tax holidays, energy efficiency sales tax holidays, and other special event sales tax holidays. The eligible items vary depending on the holiday.
How often do sales tax rates change in Georgia, and what is the process for updates?
+Sales tax rates in Georgia can change periodically, typically based on legislative decisions. When changes occur, the Georgia Department of Revenue announces the updates, providing information on the new rates and the effective dates. Businesses are expected to comply with the new rates from the specified effective date onwards.