Sale Tax In Texas

Welcome to an in-depth exploration of the Sales Tax system in the state of Texas, a crucial aspect of financial management and compliance for businesses and consumers alike. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of Texas sales tax, covering its history, structure, rates, and its impact on the state's economy. Whether you're a business owner, accountant, or just an interested individual, this article aims to provide a thorough understanding of this essential revenue mechanism.
A Historical Perspective on Texas Sales Tax
The story of sales tax in Texas began in the early 20th century, with the state’s first sales tax legislation being enacted in 1931. The initial sales tax rate was set at 2%, a far cry from the varying rates we see today. This move was a response to the financial strains of the Great Depression, providing a new revenue stream for the state.
Over the decades, the sales tax has played a pivotal role in Texas' fiscal policies, contributing significantly to state revenue. It has undergone several amendments and adjustments, with the last major revision occurring in 2006. This reform brought about a new era of sales tax administration, introducing streamlined processes and clarifying exemptions.
Understanding the Texas Sales Tax Structure
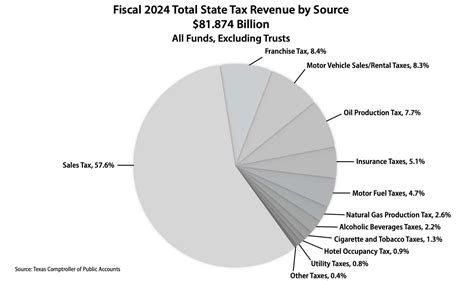
The sales tax system in Texas is a complex web of rates and regulations. At its core, it operates as a destinational tax, meaning the tax rate applied to a sale is determined by the location where the goods are delivered or services are performed, not the seller’s location.
Texas employs a state-local sales tax system, where the state sets a base sales tax rate, and local governments (cities, counties, and special purpose districts) are authorized to levy additional taxes on top of this base rate. This system creates a diverse landscape of sales tax rates across the state.
| State Sales Tax Rate | 6.25% |
|---|---|
| Average Local Sales Tax Rate | 2.00% |
| Highest Combined Rate | 8.25% (Alamogordo) |
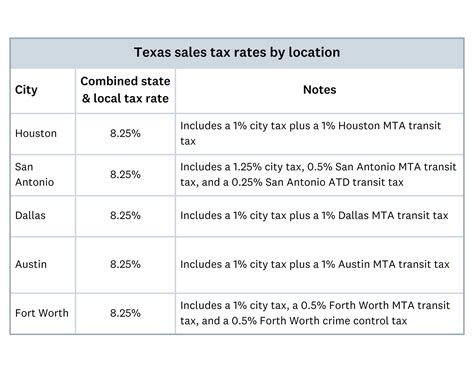
This table offers a snapshot of the Texas sales tax rates. The state sales tax rate is set by the Texas Comptroller of Public Accounts, while local governments determine their own rates, leading to a wide range of combined rates across the state.
Key Components of the Texas Sales Tax System
The Texas sales tax system encompasses a wide range of transactions, including sales of tangible personal property, certain services, and rentals. It is a consumption tax, meaning it is levied on the end consumer, not the producer or seller. This system is designed to be neutral, ensuring that producers and sellers are not taxed on their production or sales activities.
One unique aspect of Texas sales tax is its destination-based nature. This means that sales tax is collected based on the location where the product is delivered or the service is provided, not the location of the seller. For instance, if a product is sold online and shipped to a different city or county within Texas, the tax is calculated based on the shipping destination, not the seller's location.
Additionally, Texas has a use tax system in place, which is designed to complement the sales tax. The use tax is levied on tangible personal property or taxable services purchased from out-of-state vendors, ensuring that Texas residents pay taxes on goods and services they purchase, regardless of where the seller is located.
Texas Sales Tax Rates: A County-by-County Breakdown
The sales tax rates in Texas vary significantly across its 254 counties. This diversity is a result of the state’s decentralized tax system, where local governments have the autonomy to set their own tax rates, often based on local needs and revenue requirements.
| County | State Sales Tax Rate | Local Sales Tax Rate | Combined Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Andrews County | 6.25% | 2.00% | 8.25% |
| Angelina County | 6.25% | 1.75% | 8.00% |
| Aransas County | 6.25% | 1.50% | 7.75% |
This table provides a glimpse into the diverse sales tax rates across Texas. The combined rates range from a low of 6.25% in some counties to a high of 8.25% in others. These rates can significantly impact the prices consumers pay for goods and services, making them a crucial consideration for both businesses and consumers.
Sales Tax Rates in Major Texas Cities
Major cities in Texas also have their own unique sales tax rates, often higher than the state average due to the additional taxes levied by city governments. Here’s a look at some of the major cities and their sales tax rates:
- Austin: 8.25% (State: 6.25%, Local: 2%)
- Dallas: 8.25% (State: 6.25%, Local: 2%)
- Houston: 8.25% (State: 6.25%, Local: 1.75%)
- San Antonio: 8.125% (State: 6.25%, Local: 1.875%)
- Fort Worth: 8.25% (State: 6.25%, Local: 1.75%)
These cities' higher sales tax rates can have a significant impact on the cost of living and doing business, making them an important consideration for residents and businesses alike.
Sales Tax Exemptions and Special Considerations in Texas
Texas, like many other states, has a range of sales tax exemptions and special considerations in place. These exemptions are designed to alleviate the tax burden on certain goods and services, often for social or economic reasons.
Common Sales Tax Exemptions in Texas
- Groceries: Most food items purchased at grocery stores are exempt from sales tax in Texas.
- Prescription Drugs: Sales of prescription medications are not subject to sales tax.
- Resale Items: Items purchased for resale are exempt, as the tax is typically collected from the final consumer.
- Manufacturing Equipment: Machinery and equipment used directly in manufacturing or fabrication processes are often exempt.
- Educational Resources: Sales of certain educational resources, like textbooks and school supplies, are tax-free.
Special Considerations for Online Sales and Remote Sellers
With the rise of e-commerce, Texas has implemented laws to ensure sales tax collection from online sales. This includes the requirement for out-of-state sellers to collect and remit Texas sales tax if they have a certain level of sales or economic presence in the state.
Texas also has a sales tax holiday each year, typically in August, where certain items, often back-to-school supplies, are exempt from sales tax for a designated period. This holiday provides a significant savings opportunity for consumers and is a popular event for both retailers and shoppers.
The Economic Impact of Sales Tax in Texas

Sales tax is a significant revenue source for the state of Texas, contributing billions of dollars annually to the state’s budget. This revenue is crucial for funding essential services and infrastructure, from education and healthcare to transportation and public safety.
The sales tax also plays a key role in local economies, providing a stable revenue stream for counties and cities. This funding is vital for local services, including police and fire departments, schools, and community development projects.
Sales Tax and Business Operations in Texas
For businesses, understanding and managing sales tax is a critical aspect of financial operations. Texas has a sales and use tax permit system in place, requiring businesses to obtain a permit and remit sales tax to the state. This process can be complex, with varying rates and regulations across the state, making it essential for businesses to stay informed and compliant.
Businesses in Texas also benefit from the state's robust economic environment, which is often cited as a reason for its thriving business climate. The state's low tax burden, including its lack of a state income tax, makes it an attractive location for businesses, further boosting its economy.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions about Texas Sales Tax
What is the current state sales tax rate in Texas?
+The current state sales tax rate in Texas is 6.25%.
Are there any cities in Texas with a sales tax rate above 8%?
+Yes, there are several cities in Texas with a combined sales tax rate above 8%, including Austin, Dallas, and Houston, where the rate is 8.25%.
What is the use tax, and when is it applicable in Texas?
+The use tax is a tax on tangible personal property or taxable services purchased from out-of-state vendors. It is applicable in Texas when sales tax is not paid at the time of purchase.
Are there any sales tax holidays in Texas, and what items are typically exempt during these periods?
+Yes, Texas has an annual sales tax holiday, usually in August, where certain items, often back-to-school supplies, are exempt from sales tax for a designated period.
How does Texas handle sales tax for online sales and remote sellers?
+Texas requires out-of-state sellers to collect and remit Texas sales tax if they have a certain level of sales or economic presence in the state. This ensures that online sales are subject to the same tax requirements as in-state sales.



