Property Taxes In Virginia
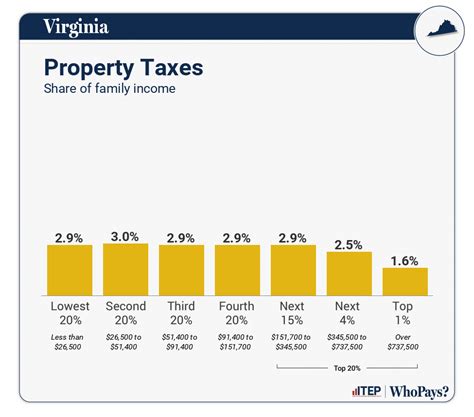
Understanding property taxes is crucial for homeowners and prospective buyers, as these taxes significantly impact one's financial obligations and overall cost of living. In the state of Virginia, property taxes play a vital role in funding various public services and infrastructure, making it essential for residents to have a comprehensive understanding of how these taxes work.
Property Tax Fundamentals in Virginia

Virginia operates on an ad valorem tax system for real estate, meaning that property taxes are calculated based on the assessed value of the property. This value is determined by local assessors who consider various factors, including the property’s size, location, and market conditions. The assessed value, along with the applicable tax rate, determines the annual property tax bill for each homeowner.
Tax Rates and Assessment
The tax rate, often referred to as the tax levy, is established by local governments, including cities, counties, and towns. These entities use property taxes to finance essential services such as schools, police and fire departments, road maintenance, and more. As a result, tax rates can vary significantly across different jurisdictions within the state.
| County/City | Tax Rate (per $100 of Assessed Value) |
|---|---|
| Arlington County | $1.391 |
| Fairfax County | $1.155 |
| Loudoun County | $1.238 |
| Prince William County | $1.320 |
| City of Alexandria | $1.305 |

It's important to note that these rates are subject to change annually and may differ based on the property's location and type (residential, commercial, or agricultural). Property owners receive a notice of their assessed value and the corresponding tax rate from their local government, typically before the tax payment deadline.
Exemptions and Relief Programs
Virginia offers various property tax exemptions to eligible homeowners. These exemptions aim to provide relief to specific groups, such as disabled veterans, senior citizens, and individuals with low incomes. For instance, the Homestead Exemption reduces the assessed value of a primary residence by up to $2,000, resulting in lower property taxes for qualifying homeowners.
Additionally, the state provides a Land Conservation Tax Credit for landowners who preserve their land for agricultural or forest use. This credit effectively reduces the assessed value of the land, leading to lower property taxes for these landowners.
Property Tax Calculation and Payment

Calculating property taxes in Virginia involves multiplying the assessed value of the property by the applicable tax rate. For example, a homeowner with a property assessed at 300,000 in an area with a tax rate of 1.2 per 100 of assessed value would have an annual property tax bill of 3,600.
Property tax payments are typically due in two installments, with specific due dates set by each locality. Late payments may incur penalties and interest, so it's crucial for homeowners to stay informed about their payment schedules.
Online Payment Options
Virginia offers convenient online payment platforms for property taxes, allowing homeowners to make payments securely and efficiently. These platforms often provide real-time updates on tax balances and payment history, making it easier for homeowners to manage their financial obligations.
Property Tax Appeals
If a homeowner believes their property’s assessed value is inaccurate, they have the right to appeal. The Virginia Department of Taxation provides guidelines and resources for filing an appeal, which can result in a reduced assessed value and, consequently, lower property taxes.
Impact of Property Taxes on Homeownership
Property taxes are a significant consideration for anyone planning to buy or own a home in Virginia. These taxes contribute to the overall cost of homeownership and should be factored into financial planning. Understanding the local tax rates and potential exemptions can help prospective buyers make informed decisions about their future homes.
Property Tax Trends
Over the years, property tax rates in Virginia have generally trended upward, primarily due to increasing demand for public services and infrastructure improvements. However, the rate of increase can vary from year to year and between different localities.
Monitoring these trends is essential for homeowners and buyers alike. While tax rates may rise, property values can also appreciate, potentially offsetting the impact of higher taxes. Understanding the local real estate market and tax trends is crucial for long-term financial planning.
Comparative Analysis: Virginia vs. Other States
Virginia’s property tax rates are relatively moderate compared to some other states. For instance, Virginia’s average effective property tax rate of 0.85% is lower than the national average of 1.08%. This makes Virginia an attractive option for homeowners seeking a balanced approach to property taxes.
| State | Effective Tax Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| Virginia | 0.85 |
| New York | 1.69 |
| Texas | 1.78 |
| Illinois | 2.17 |
| New Jersey | 2.21 |
When comparing Virginia to other states, it's essential to consider the overall cost of living and the services provided by local governments. While Virginia's property taxes may be lower, the quality of public services and infrastructure can vary, impacting the overall value proposition for homeowners.
Conclusion
Property taxes in Virginia are an integral part of the state’s financial landscape, impacting homeowners and the overall economy. Understanding the assessment process, tax rates, and available exemptions is crucial for individuals to manage their financial obligations effectively. By staying informed and utilizing available resources, homeowners can navigate the property tax system with confidence and ensure their financial well-being.
What is the average property tax rate in Virginia?
+The average effective property tax rate in Virginia is 0.85%, which is lower than the national average of 1.08%.
How often do property tax rates change in Virginia?
+Property tax rates can change annually, as they are set by local governments. These changes often reflect the financial needs and priorities of the locality.
Are there any property tax exemptions available in Virginia?
+Yes, Virginia offers various property tax exemptions, including the Homestead Exemption and Land Conservation Tax Credit, which provide relief to eligible homeowners.
How can I appeal my property’s assessed value in Virginia?
+To appeal your property’s assessed value, you can follow the guidelines provided by the Virginia Department of Taxation. This process typically involves submitting an appeal form and supporting documentation to your local assessor’s office.
What are the consequences of late property tax payments in Virginia?
+Late property tax payments in Virginia may result in penalties and interest charges. It’s important to stay informed about your payment due dates to avoid these additional fees.



