Property Tax Indiana
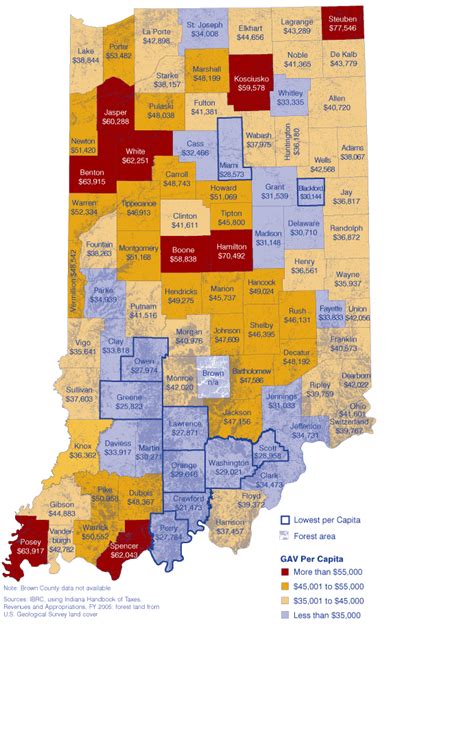
In Indiana, property taxes play a significant role in funding various local services and infrastructure. These taxes are levied on real estate properties, including land and buildings, and contribute to the financial stability of communities across the state. The property tax system in Indiana is unique and often a topic of interest for homeowners, investors, and policymakers alike. This comprehensive guide aims to delve into the intricacies of property taxes in Indiana, providing a detailed understanding of the assessment process, tax rates, and the factors influencing these rates.
Understanding Indiana’s Property Tax Assessment Process

The property tax assessment process in Indiana is a critical aspect of the state’s fiscal system. It involves a series of steps to determine the value of a property, which forms the basis for calculating the tax liability. Here’s a breakdown of the assessment process:
1. Property Appraisal
The first step in the assessment process is the appraisal of a property. Assessors, who are typically appointed by the county government, are responsible for this task. They visit properties, evaluate their characteristics, and assign a value based on factors such as size, location, and recent sales data. This initial appraisal sets the foundation for the subsequent steps.
2. Assessment Ratio Calculation
Once the appraised value is determined, assessors apply an assessment ratio to calculate the assessed value of the property. This ratio is set by the Indiana Department of Local Government Finance (DLGF) and varies depending on the type of property. For residential properties, the assessment ratio is generally 100%, meaning the assessed value is equal to the appraised value. However, for commercial and industrial properties, the ratio can be lower, resulting in a lower assessed value.
3. Tax Rate Determination
After the assessed value is calculated, the property’s tax rate is applied to determine the final tax liability. Tax rates in Indiana are established by local governing bodies, such as city councils or county commissioners. These rates are expressed as a percentage and can vary significantly across different jurisdictions within the state. Factors influencing tax rates include the cost of providing local services, debt obligations, and the overall financial needs of the community.
4. Property Tax Deductions and Exemptions
Indiana offers several deductions and exemptions that can reduce a property owner’s tax liability. These include homestead deductions, which provide a reduction in taxes for primary residences, and various exemptions for elderly homeowners, disabled veterans, and agricultural land. Additionally, certain properties, such as churches and government-owned lands, are exempt from property taxes altogether.
5. Property Tax Bills and Payment
Once the assessment process is complete and the tax liability is determined, property owners receive a tax bill. This bill outlines the assessed value of the property, the applicable tax rate, and the total amount due. In Indiana, property taxes are typically due in two installments, with payment deadlines set by the local tax office. Failure to pay property taxes can result in penalties, interest charges, and, in extreme cases, a tax sale of the property.
| Assessment Ratio | Tax Rate (%) | Tax Deductions |
|---|---|---|
| Residential: 100% | Varies by County (e.g., 1.5% - 3.0%) | Homestead Deduction |
| Commercial: 25% | Similar to Residential | Agricultural Land Exemption |
| Industrial: 10% | Varies | Elderly/Disabled Exemptions |
Factors Influencing Property Tax Rates in Indiana

Property tax rates in Indiana are influenced by a multitude of factors, each playing a unique role in determining the final tax liability. Understanding these factors is crucial for property owners and investors to make informed decisions about their real estate holdings.
1. Local Government Budgets and Services
One of the primary drivers of property tax rates is the budgetary needs of local governments. Counties, cities, and townships rely on property taxes to fund essential services such as education, public safety, infrastructure maintenance, and social programs. As these expenses rise, local governing bodies may adjust tax rates to meet their financial obligations.
2. Debt Service and Capital Projects
Indiana’s local governments often incur debt to finance large-scale projects or infrastructure improvements. Property taxes are a significant source of revenue to service this debt. Additionally, when communities undertake capital projects like building new schools, renovating public spaces, or expanding transportation networks, the associated costs are often financed through increased property taxes.
3. Economic Conditions and Property Values
The economic health of a region directly impacts property tax rates. During economic booms, property values tend to rise, leading to higher assessments and potentially higher tax liabilities. Conversely, during economic downturns, property values may decline, resulting in lower assessments and a decrease in tax revenue for local governments.
4. Local Tax Base and Equity Considerations
The composition of the local tax base is another crucial factor. Areas with a diverse tax base, including a mix of residential, commercial, and industrial properties, may experience more stability in tax rates. On the other hand, communities heavily reliant on a single sector may face challenges if that sector experiences economic fluctuations.
5. Policy Decisions and Tax Reform
Indiana’s policy landscape plays a significant role in property tax rates. Changes in tax laws, reform initiatives, and political decisions can directly impact tax structures. For instance, the introduction of tax caps or circuit breakers, which limit the amount of tax increase a property can face in a given year, can provide relief to taxpayers.
6. Special Assessments and Levies
Special assessments are charges levied on specific properties to fund local improvements that directly benefit those properties. This could include street lighting, sidewalk construction, or drainage projects. While these assessments are separate from regular property taxes, they can significantly impact a property owner’s overall tax burden.
| Factor | Impact on Tax Rates |
|---|---|
| Local Government Budgets | Higher budgets lead to increased tax rates to cover expenses. |
| Debt Service | Tax rates may rise to service debt obligations. |
| Economic Conditions | Economic booms can lead to higher property values and tax rates. |
| Local Tax Base | A diverse tax base provides stability, while a single-sector base may be more volatile. |
| Policy Decisions | Tax reform initiatives can lead to changes in tax structures and rates. |
Performance Analysis and Future Implications
Understanding the performance of Indiana’s property tax system and its future implications is crucial for both policymakers and property owners. Let’s delve into some key aspects of this analysis.
1. Revenue Generation and Budgetary Impact
Property taxes are a significant source of revenue for local governments in Indiana. The tax revenue generated funds essential services and infrastructure projects, shaping the quality of life in communities across the state. A thorough analysis of revenue generation patterns can help identify trends and potential areas for improvement.
2. Tax Burden Distribution
Examining the distribution of tax burdens is essential for ensuring fairness and equity. This involves studying how tax liabilities are distributed among different types of properties and ownership categories. An uneven distribution could indicate a need for adjustments to maintain a balanced and equitable tax system.
3. Impact on Property Values and Market Dynamics
Property tax rates can significantly influence property values and market dynamics. Higher tax rates may deter potential buyers, especially in areas with a large number of investors or second-home owners. Conversely, lower tax rates could stimulate market activity and attract new residents or businesses.
4. Policy and Regulatory Changes
Indiana’s property tax system is subject to ongoing policy reviews and regulatory changes. These changes can have far-reaching implications for property owners. For instance, the introduction of tax incentives or the modification of assessment procedures could impact tax liabilities and the overall tax landscape.
5. Community Development and Growth
Property taxes play a vital role in community development and economic growth. The revenue generated from these taxes funds initiatives that enhance the local economy, attract businesses, and improve the overall quality of life. A comprehensive analysis can help identify areas where tax revenue is effectively utilized for community development.
6. Comparative Analysis with Other States
Conducting a comparative analysis with other states can provide valuable insights into Indiana’s property tax system. This analysis can highlight areas where Indiana’s system excels and areas that may require improvement to stay competitive and equitable.
| Performance Metric | Analysis Focus |
|---|---|
| Revenue Generation | Assess revenue trends, identify potential shortfalls, and evaluate effectiveness of tax structures. |
| Tax Burden Distribution | Examine fairness and equity, ensuring that tax liabilities are distributed justly among property owners. |
| Property Values and Market Dynamics | Analyze the impact of tax rates on property values and market trends, identifying potential areas of concern or opportunity. |
| Policy and Regulatory Changes | Stay updated on policy revisions, assess their impact, and recommend adjustments as needed. |
| Community Development | Evaluate the effectiveness of tax revenue in driving community growth and development. |
Conclusion: Navigating Indiana’s Property Tax Landscape
Indiana’s property tax system is a dynamic and complex mechanism that plays a vital role in funding local services and shaping the state’s economic landscape. From the assessment process to the factors influencing tax rates, understanding this system is crucial for property owners, investors, and policymakers alike.
By delving into the intricacies of Indiana's property tax landscape, this guide aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the system's workings. From the initial appraisal of a property to the calculation of tax rates and the various deductions and exemptions available, each step in the process is crucial for determining a property's tax liability.
Moreover, the factors influencing tax rates, such as local government budgets, economic conditions, and policy decisions, highlight the intricate relationship between property taxes and the broader economic and social fabric of the state. These factors, when analyzed collectively, provide valuable insights into the performance and future implications of Indiana's property tax system.
As we move forward, it is essential to stay informed about the ongoing developments and changes in the property tax landscape. By doing so, property owners can make informed decisions, while policymakers can ensure a sustainable and equitable tax system that supports the growth and prosperity of Indiana's communities.
Frequently Asked Questions
How often are property taxes assessed in Indiana?
+Property taxes in Indiana are typically assessed annually. Assessors visit properties and determine their value based on current market conditions. This annual assessment ensures that property taxes reflect the changing values of real estate in the state.
Can I appeal my property tax assessment in Indiana?
+Yes, Indiana provides property owners with the right to appeal their assessments if they believe the value assigned to their property is inaccurate. The appeals process involves submitting documentation and evidence to support the claim. It’s important to understand the timeline and procedures for appeals in your specific county.
Are there any online resources to estimate my property tax in Indiana?
+Yes, several online tools and calculators are available to estimate property taxes in Indiana. These tools consider factors such as property value, location, and applicable tax rates. However, it’s important to note that these estimates are not official and may not reflect the final tax liability.
How can I stay updated on changes to Indiana’s property tax laws and regulations?
+To stay informed about changes in Indiana’s property tax laws and regulations, you can subscribe to newsletters or updates from the Indiana Department of Local Government Finance (DLGF). Additionally, local tax offices often provide information on their websites about any upcoming changes or important deadlines.
What are the consequences of not paying property taxes in Indiana?
+Failure to pay property taxes in Indiana can result in significant penalties and interest charges. In extreme cases, the local government may place a tax lien on the property, which could lead to a tax sale if the taxes remain unpaid. It’s crucial to stay current on property tax payments to avoid these consequences.