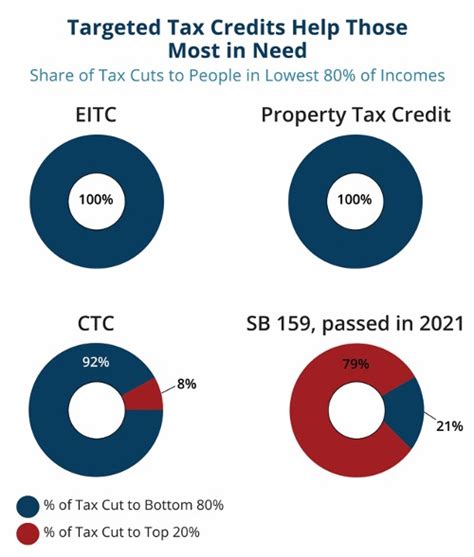
Property Tax Credit

Property tax credits are an essential aspect of the real estate landscape, offering financial relief to homeowners and property owners alike. These credits, often overlooked, can significantly impact an individual's tax liability and overall financial planning. As such, understanding the intricacies of property tax credits is crucial for any homeowner or investor looking to maximize their financial strategies.
Unraveling Property Tax Credits: A Comprehensive Guide
Property tax credits are a type of financial incentive provided by local or state governments to reduce the property tax burden on specific individuals or properties. These credits are designed to encourage certain behaviors, promote economic development, or provide relief to targeted groups. They can take various forms, each with its own set of eligibility criteria and application processes.
Understanding the Basics: Types of Property Tax Credits
Property tax credits can be broadly categorized into two main types: general credits and targeted credits.
General Property Tax Credits
General property tax credits are available to a wide range of property owners, often without specific eligibility requirements. These credits are usually applied uniformly to all qualifying properties within a certain jurisdiction. For instance, some localities may offer a standard credit based on the assessed value of the property, providing a flat-rate reduction in tax liability. This type of credit benefits all homeowners equally, making it a popular choice for governments looking to provide a general incentive for property ownership.
Targeted Property Tax Credits
Targeted property tax credits, on the other hand, are designed to benefit specific groups or promote particular objectives. These credits often come with eligibility criteria that homeowners must meet to qualify. For example, a targeted credit might be offered to homeowners who install energy-efficient improvements, such as solar panels or high-efficiency appliances. Another common targeted credit is the homestead exemption, which provides relief to homeowners who use their property as their primary residence.
Other targeted credits may include:
- Senior Citizen Credits: Many jurisdictions offer reduced property taxes or credits for homeowners who are of a certain age, typically over 65.
- Veteran Credits: These credits are designed to support military veterans, often providing significant tax relief as a way to recognize their service.
- Low-Income Credits: Property tax credits can be targeted towards low-income homeowners, helping to make homeownership more affordable for those who might otherwise struggle.
- Disability Credits: Certain disabilities may qualify homeowners for tax credits, making it easier for them to manage their financial obligations.
The Application Process: Navigating the Red Tape
Applying for property tax credits can be a complex process, often requiring homeowners to submit detailed applications and supporting documentation. While the specifics vary by jurisdiction and credit type, there are some common steps involved.
Researching Eligibility
The first step is to thoroughly research the eligibility criteria for the desired credit. This information is typically available on the website of the local tax assessor’s office or the state’s department of revenue. Understanding the requirements upfront can save time and effort in the long run.
Gathering Necessary Documents
Once eligibility is confirmed, homeowners will need to gather the necessary documents to support their application. This may include proof of ownership, income statements, or documentation of qualifying improvements or characteristics (such as energy-efficient appliances or historical significance of the property). Ensuring all required documents are in order before beginning the application process can streamline the overall experience.
Completing the Application
Applications for property tax credits often involve filling out detailed forms, providing specific information about the property and the homeowner’s circumstances. It’s crucial to read and understand the application thoroughly before submitting it. Many jurisdictions offer online applications, which can simplify the process and reduce the likelihood of errors.
Submitting the Application and Waiting for Approval
After completing the application, homeowners will need to submit it to the appropriate authority, often the local tax assessor’s office or the state’s department of revenue. Processing times can vary, and it’s important to keep track of deadlines to ensure the application is considered for the current tax year. Once submitted, homeowners will need to wait for a decision, which can take several weeks or even months.
Maximizing Your Property Tax Credits: Strategies and Considerations
Property tax credits can provide significant financial relief, but it’s essential to approach them strategically to ensure maximum benefit. Here are some considerations to keep in mind:
Stay Informed about Available Credits
The world of property tax credits is constantly evolving, with new credits being introduced and existing ones being modified or removed. It’s crucial to stay informed about the credits available in your jurisdiction and any changes that might affect your eligibility. Many jurisdictions provide newsletters or updates on their websites to keep taxpayers informed.
Explore Multiple Credit Opportunities
Don’t limit yourself to just one type of credit. Depending on your circumstances, you may qualify for multiple credits. For instance, a homeowner who is over 65, has a low income, and has made energy-efficient improvements might be eligible for a senior citizen credit, a low-income credit, and a green energy credit. Exploring all available options can lead to substantial savings.
Consider the Long-Term Impact
While property tax credits provide immediate financial relief, it’s important to consider their long-term impact. Some credits may require ongoing eligibility checks, and failure to meet the criteria in future years could result in the credit being revoked. Additionally, some credits may affect the property’s assessed value, which could impact future tax liability or the property’s resale value.
Seek Professional Advice
Navigating the complex world of property tax credits can be challenging. Consider seeking advice from a tax professional or financial advisor who specializes in real estate. They can provide personalized guidance based on your specific circumstances and help you understand the potential benefits and drawbacks of different credit options.
Real-World Examples: How Property Tax Credits Work in Practice
To illustrate the impact and application of property tax credits, let’s explore a few real-world examples.
Senior Citizen Credit in Florida
In the state of Florida, homeowners who are 65 or older may be eligible for a Senior Citizen Exemption, which reduces the assessed value of their property by up to $50,000. This exemption can lead to substantial savings on property taxes, especially in areas with high property values. To qualify, homeowners must meet certain income requirements and use the property as their primary residence.
Green Energy Credit in California
California offers a Solar Energy System Credit, which provides a property tax exclusion for the increased value of a property resulting from the installation of a solar energy system. This credit encourages homeowners to invest in renewable energy, reducing their carbon footprint and providing long-term savings on energy costs. The credit is available for both residential and commercial properties.
Homestead Exemption in Texas
Texas provides a Residential Homestead Exemption, which exempts a portion of the home’s value from property taxes. This credit is available to homeowners who use their property as their primary residence and can provide significant savings. The exemption amount varies by county but can be substantial, especially for homeowners in high-tax areas.
| State | Credit Name | Eligibility Criteria | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Florida | Senior Citizen Exemption | Age 65+, Income Limits, Primary Residence | Up to $50,000 reduction in assessed value |
| California | Solar Energy System Credit | Solar Energy System Installation | Exclusion of solar system value from property taxes |
| Texas | Residential Homestead Exemption | Primary Residence | Varies by county, up to substantial savings |

FAQ

Can I apply for multiple property tax credits at the same time?
+Yes, it’s possible to apply for multiple credits if you meet the eligibility criteria for each. However, it’s important to carefully review the requirements and ensure that the credits do not conflict with each other. Some credits may have specific rules about combining with other incentives.
How often do property tax credits change or expire?
+Property tax credits can change or expire at any time, as they are often subject to legislative changes or budget constraints. It’s crucial to stay updated with local and state tax laws to ensure you’re aware of any modifications or new credits that might become available.
Are property tax credits available for rental properties?
+Some property tax credits are specifically designed for rental properties, such as those aimed at encouraging affordable housing or promoting economic development. However, the availability and eligibility criteria for these credits can vary widely by jurisdiction. It’s important to research the specific credits in your area and consult with a tax professional if you own rental properties.