Philadelphia Tax

Welcome to a comprehensive guide on understanding the tax landscape in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. This city, rich in history and culture, presents a unique set of tax considerations for its residents and businesses. As we delve into the intricacies of Philadelphia's tax system, we will explore the various taxes levied, the processes involved, and the strategies to navigate this complex landscape efficiently.
The Diverse Tax Structure of Philadelphia

Philadelphia, the birthplace of American democracy, has a tax system as diverse and dynamic as its vibrant neighborhoods. Understanding this system is crucial for both individuals and businesses to ensure compliance and optimize their financial strategies.
Property Taxes: A Pillar of Philadelphia’s Revenue
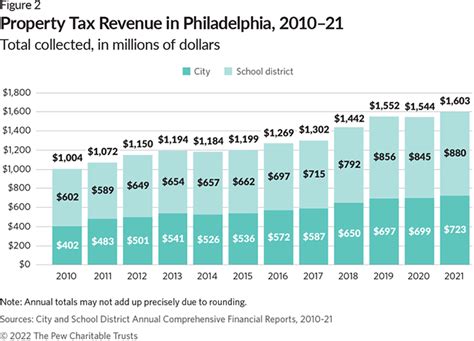
One of the primary sources of revenue for the city is property taxes. These taxes are levied on real estate properties within Philadelphia County, contributing significantly to the city’s budget. The Philadelphia Property Tax system is designed to ensure fairness and efficiency, with assessments based on the property’s value and the city’s fiscal needs.
The property tax rate in Philadelphia is currently set at 1.436% of the property's assessed value. This rate, while seemingly straightforward, can vary based on the property's use and its location within the city. For instance, commercial properties may face different rates compared to residential ones, and properties in certain development zones might benefit from tax abatements or incentives.
| Property Type | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Residential | 1.436% |
| Commercial | Varies (1.436% base rate) |
To illustrate, consider a residential property in Center City with an assessed value of $250,000. The annual property tax bill for this homeowner would be calculated as: $250,000 x 1.436% = $3,590. This example demonstrates how a seemingly simple tax rate can impact homeowners significantly.
The City Wage Tax: A Key Revenue Stream
Another significant tax levied in Philadelphia is the City Wage Tax. This tax is a critical revenue source for the city, contributing to essential services and infrastructure projects. The City Wage Tax is imposed on individuals working or earning income within Philadelphia city limits, regardless of where they reside.
The current wage tax rate in Philadelphia is 3.8416% for residents and 3.4416% for non-residents. This tax is applied to wages, salaries, commissions, bonuses, and other forms of compensation. For those who work in the city but reside elsewhere, this tax can be a significant consideration when evaluating their financial situation.
Let's take the example of a Philadelphia resident earning a yearly salary of $75,000. Their City Wage Tax liability would be calculated as: $75,000 x 3.8416% = $2,881.20. This tax, while essential for the city's functioning, can impact individuals' take-home pay and financial planning.
Philadelphia’s Net Profits Tax: A Business Perspective
For businesses operating in Philadelphia, the Net Profits Tax is a crucial consideration. This tax is imposed on the net profits of businesses, both sole proprietorships and corporations, and is a significant source of revenue for the city. The Net Profits Tax rate varies based on the type of business and its legal structure.
| Business Type | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Sole Proprietorships | 1.4416% |
| Partnerships | 6.35% |
| Corporations | 8.528% (first $30,000), 6.4416% (over $30,000) |
For instance, a sole proprietorship with net profits of $50,000 would owe a Net Profits Tax of $50,000 x 1.4416% = $720.80. This tax, while seemingly small, can significantly impact a business's bottom line, especially for smaller enterprises.
Philadelphia Sales and Use Tax: Consumer Considerations
Philadelphia also levies a Sales and Use Tax on retail sales and certain services provided within the city. This tax is an essential revenue stream, contributing to the city’s general fund and specific projects like transportation infrastructure.
The current Sales and Use Tax rate in Philadelphia is 8%, which includes the state and local tax rates. This tax is applied to the purchase price of goods and services, with certain exemptions and special considerations for specific items.
When purchasing a new laptop for $1,000, for example, the sales tax component would be: $1,000 x 8% = $80. This tax is a critical consideration for consumers and businesses alike, as it directly impacts the cost of goods and services.
Navigating the Complexities: Strategies and Insights

Understanding the various taxes in Philadelphia is the first step; optimizing one’s financial strategies is the next. Here are some expert insights to navigate this complex tax landscape efficiently.
Maximizing Property Tax Abatements and Incentives
Philadelphia offers various property tax abatements and incentives to encourage development and revitalization. These programs can significantly reduce property tax liabilities for qualifying properties. For instance, the Keystone Opportunity Improvement Zone (KOIZ) program provides a 10-year tax abatement for new construction or substantial rehabilitation projects.
Businesses and homeowners should explore these opportunities to reduce their tax burden and contribute to the city's development goals. Working with tax professionals and staying updated on these programs can ensure one doesn't miss out on valuable tax savings.
Efficient Wage Tax Management for Employees and Employers
For individuals working in Philadelphia, efficient wage tax management is crucial. This involves understanding the tax withholding process, ensuring accurate filings, and exploring potential deductions and credits. Employers, too, have a responsibility to withhold and remit wage taxes accurately.
Employers should stay informed about wage tax requirements, including any changes in rates or regulations. Offering employees guidance and resources on tax management can improve overall financial literacy and reduce the risk of errors.
Optimizing Business Tax Strategies
Businesses operating in Philadelphia have a range of tax considerations, from Net Profits Tax to Sales and Use Tax. To optimize their tax strategies, businesses should consider the following:
- Entity Structure: Choose the most tax-efficient legal structure for your business, considering factors like liability protection, tax rates, and administrative burden.
- Tax Credits and Incentives: Explore Philadelphia's business tax credits and incentives, such as the Keystone Innovation Zone (KIZ) program, which offers tax credits for eligible businesses.
- Sales Tax Compliance: Ensure compliance with Philadelphia's Sales and Use Tax by accurately collecting and remitting taxes. Consider using sales tax automation tools to simplify this process.
The Future of Philadelphia’s Tax Landscape
As Philadelphia continues to evolve, its tax landscape will likely undergo changes and reforms. The city’s leadership and policymakers are constantly evaluating the tax system to ensure it remains fair, efficient, and supportive of the city’s growth and development goals.
One potential area of focus is tax equity. Philadelphia has a history of advocating for progressive tax policies, and future reforms may aim to reduce the tax burden on lower-income individuals and businesses while ensuring adequate revenue for essential services.
Additionally, with the ongoing digital transformation, Philadelphia may explore more efficient tax collection methods, such as digital tax filing and payment systems. These advancements could improve tax compliance, reduce administrative burdens, and enhance transparency.
Conclusion: A Comprehensive Approach to Philadelphia Taxes
Navigating Philadelphia’s tax system requires a comprehensive understanding of the various taxes levied, their rates, and the strategies to optimize one’s financial position. Whether you’re a homeowner, employee, business owner, or resident, staying informed and proactive is key to effective tax management.
As Philadelphia continues to thrive and evolve, its tax system will adapt to meet the city's needs. By staying engaged and informed, individuals and businesses can ensure they contribute to the city's growth while effectively managing their tax liabilities.
How often are property taxes assessed in Philadelphia?
+Property taxes in Philadelphia are assessed annually. The Office of Property Assessment conducts regular assessments to determine the market value of properties, which forms the basis for property tax calculations.
Are there any tax incentives for businesses in Philadelphia?
+Yes, Philadelphia offers various tax incentives for businesses, including tax abatements, tax credits, and special programs like the Keystone Opportunity Improvement Zone (KOIZ) and Keystone Innovation Zone (KIZ) initiatives. These programs aim to encourage business growth and development in specific areas of the city.
What happens if I don’t pay my City Wage Tax on time?
+Late payment of the City Wage Tax can result in penalties and interest. It’s important to ensure timely payments to avoid these additional charges and maintain compliance with Philadelphia’s tax regulations.
How can I stay updated on Philadelphia’s tax regulations and changes?
+Staying informed about Philadelphia’s tax landscape is crucial. You can subscribe to updates from the Philadelphia Department of Revenue, follow reputable tax news sources, and consult tax professionals or accountants for the latest information and guidance.



