Ohio Tax Brackets
Welcome to an in-depth exploration of Ohio's tax brackets, a complex yet essential topic for residents and businesses navigating the state's tax landscape. In this comprehensive guide, we'll dive into the intricacies of Ohio's tax system, offering a clear understanding of how it operates and how it affects individuals and entities.
Understanding Ohio's Progressive Tax Structure
Ohio employs a progressive tax system, which means the state tax rate increases as your income rises. This approach ensures fairness, as those with higher incomes contribute a greater proportion of their earnings towards the state's revenue. The tax brackets are divided into different income ranges, each carrying a corresponding tax rate. It's crucial to note that Ohio's tax structure is separate from federal taxes, and residents must file both state and federal tax returns annually.
The Current Tax Brackets in Ohio
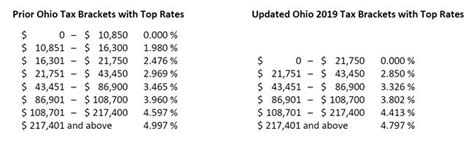
As of 2024, Ohio has six tax brackets, each with a specific tax rate. Here's a breakdown of these brackets:
| Tax Bracket | Tax Rate | Income Range |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.4797% | $0 - $5,000 |
| 2 | 1.5492% | $5,001 - $10,000 |
| 3 | 2.5987% | $10,001 - $20,000 |
| 4 | 3.5482% | $20,001 - $40,000 |
| 5 | 4.5478% | $40,001 - $80,000 |
| 6 | 5.5473% | $80,001 and above |
These tax brackets are applicable for both single filers and married couples filing jointly. However, it's important to note that tax laws and brackets can change annually, so it's essential to refer to the Ohio Department of Taxation's website for the most up-to-date information.
Taxable Income and Exemptions
When calculating your taxable income, several factors come into play. Firstly, you need to consider your gross income, which includes all income sources like wages, investments, and business profits. From this, you can deduct certain exemptions and deductions, such as the standard deduction or itemized deductions for eligible expenses like medical costs, charitable donations, and certain taxes.
Ohio also offers various tax credits, which can further reduce your taxable income. These credits include the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) for low- and moderate-income workers, the Child and Dependent Care Credit, and the Credit for School Supplies and Fees, among others. These credits can significantly impact your tax liability and should be carefully considered when filing your taxes.
Tax Strategies and Planning

Navigating Ohio's tax system requires careful planning and an understanding of the various strategies available. One common strategy is maximizing deductions and credits to lower your taxable income. This could involve contributing to a retirement account like a 401(k) or IRA, which can reduce your taxable income in the current year. Additionally, timing your income and expenses strategically can also impact your tax liability.
For businesses, Ohio offers various incentives and tax breaks, such as the Job Creation Tax Credit and the Research and Development Tax Credit. These incentives aim to encourage economic growth and job creation within the state. Understanding these incentives and how they apply to your business can be a crucial part of your tax planning strategy.
Tax Deadlines and Filing Requirements
Ohio's tax filing deadlines align with the federal tax calendar. Typically, taxes are due on April 15th of each year. However, if this date falls on a weekend or a holiday, the deadline is extended to the next business day. It's crucial to ensure your tax returns are filed on time to avoid penalties and interest charges.
When filing your Ohio state tax return, you'll need to complete Form IT 1040, the Ohio Individual Income Tax Return. This form is available on the Ohio Department of Taxation's website, along with detailed instructions and guidance. If you're filing jointly with a spouse, you'll need to include their information as well.
Online Filing and Payment Options
Ohio offers convenient online filing and payment options. You can use the Ohio Department of Taxation's eFile system to submit your tax return electronically. This system is secure and provides a faster refund process. Additionally, you can choose to pay your taxes online using a credit or debit card, electronic check, or through a third-party payment processor.
For those who prefer traditional methods, paper filing is still an option. You can download and print the necessary forms from the Ohio Department of Taxation's website and mail them to the appropriate address. However, it's worth noting that online filing is generally more efficient and reduces the risk of errors.
Conclusion
Ohio's tax brackets provide a progressive system that ensures fairness and contributes to the state's revenue. Understanding these brackets and the overall tax landscape is crucial for individuals and businesses operating within Ohio. By staying informed and utilizing available resources, you can navigate the tax system effectively and make the most of the deductions, credits, and incentives offered.
Frequently Asked Questions
When are Ohio state tax returns due in 2024?
+
Ohio state tax returns are typically due on April 17, 2024. This date aligns with the federal tax deadline and accounts for any weekend or holiday adjustments.
Can I e-file my Ohio state tax return?
+
Yes, Ohio offers an e-filing system for state tax returns. You can access the eFile system on the Ohio Department of Taxation’s website and submit your return securely online.
What is the standard deduction for Ohio state taxes in 2024?
+
The standard deduction for Ohio state taxes in 2024 is 1,100 for single filers and 2,200 for married couples filing jointly. This deduction reduces your taxable income, providing a significant benefit for many taxpayers.
Are there any tax incentives for starting a business in Ohio?
+
Yes, Ohio offers several tax incentives for businesses, including the Job Creation Tax Credit and the Research and Development Tax Credit. These incentives aim to promote economic growth and job creation within the state.
Can I file an extension for my Ohio state tax return?
+
Yes, you can file for an extension to extend the deadline for filing your Ohio state tax return. To do this, you’ll need to complete Form IT 40-EXT and submit it by the original filing deadline. This grants you an additional six months to file your return.



