North Dakota State Tax

North Dakota, known for its vibrant economy and diverse industries, maintains a unique tax system that impacts both residents and businesses within the state. Understanding the intricacies of North Dakota's state tax structure is crucial for individuals and businesses operating in this dynamic region.
The North Dakota State Tax System: An Overview
North Dakota’s tax system plays a vital role in funding essential public services and infrastructure, while also contributing to the state’s economic growth. The state’s tax structure is designed to promote fairness and economic development, offering a balanced approach to taxation.
North Dakota imposes a progressive income tax system, meaning that higher-income earners pay a larger proportion of their income in taxes. This approach ensures that the tax burden is distributed equitably across different income levels.
The state also levies various taxes on businesses, including corporate income taxes, sales and use taxes, and property taxes. These taxes contribute to the state's revenue stream, enabling it to invest in critical areas such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure development.
Income Tax: A Progressive Approach
North Dakota’s income tax system is structured with six tax brackets, ranging from 1.1% to 5.54%. This progressive tax structure ensures that individuals with higher incomes contribute a larger share to the state’s revenue. The income thresholds for each bracket are adjusted annually to account for inflation and changes in the cost of living.
For instance, in the tax year 2023, the income tax brackets for single filers are as follows:
| Tax Bracket | Income Range | Tax Rate |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | $0 - $2,699 | 1.1% |
| 2 | $2,700 - $5,399 | 2.05% |
| 3 | $5,400 - $11,699 | 2.56% |
| 4 | $11,700 - $44,999 | 3.99% |
| 5 | $45,000 - $204,999 | 4.95% |
| 6 | $205,000 and above | 5.54% |

These brackets are adjusted for married couples filing jointly, head of household, and qualifying widow(er) status.
Sales and Use Taxes: A Key Revenue Source
North Dakota imposes a state-wide sales and use tax of 5%, which applies to the sale or lease of tangible personal property and certain services. The state also allows local governments to levy additional sales taxes, resulting in varying tax rates across different regions.
For instance, the city of Fargo has a local sales tax rate of 1.75%, bringing the total sales tax rate to 6.75% within the city limits. This additional revenue is often utilized for local infrastructure projects and community development.
Property Taxes: Supporting Local Communities
Property taxes are a significant source of revenue for local governments in North Dakota. The state’s property tax system is administered by county assessors, who are responsible for valuing properties and setting tax rates. These taxes support essential services such as education, public safety, and infrastructure maintenance at the local level.
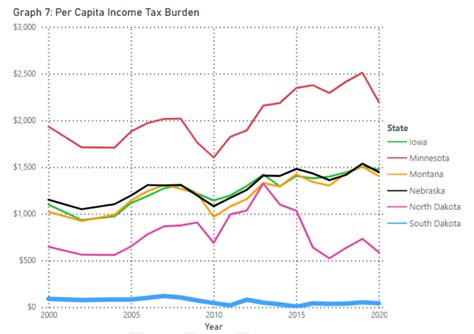
The median effective property tax rate in North Dakota is 1.04%, which is relatively lower compared to many other states. However, it's important to note that property tax rates can vary significantly across different counties and municipalities within the state.
Tax Incentives and Credits: Promoting Economic Growth

North Dakota offers a range of tax incentives and credits to attract businesses and stimulate economic growth. These incentives are designed to encourage investment, job creation, and innovation within the state.
Research and Development Tax Credit
Businesses engaged in research and development activities in North Dakota may be eligible for a tax credit of up to 10% of qualified research expenses. This credit is aimed at fostering innovation and technological advancement within the state’s economy.
Job Creation Tax Credits
The state offers tax credits to businesses that create new jobs, with the credit amount varying based on the number of full-time equivalent (FTE) jobs created and the average annual wage. This incentive is particularly beneficial for businesses in sectors such as manufacturing, agriculture, and energy.
Tax Increment Financing (TIF)
North Dakota’s TIF program allows local governments to finance public improvements and infrastructure projects by capturing a portion of the increased property tax revenue generated by the project. This mechanism encourages economic development and urban revitalization, particularly in distressed areas.
Future Implications and Conclusion
North Dakota’s tax system is designed to support the state’s economic growth while ensuring a fair distribution of the tax burden. The state’s progressive income tax structure, combined with various business incentives, creates a balanced approach to taxation. However, the state’s reliance on sales and property taxes, which can be regressive, warrants careful consideration to maintain fairness across different income levels.
As North Dakota continues to evolve and adapt to changing economic landscapes, the state's tax policies will play a crucial role in shaping its future. A careful balance between revenue generation and economic development will be essential to ensure the state's long-term prosperity and the well-being of its residents.
What is the current state income tax rate in North Dakota for the 2023 tax year?
+The current state income tax rates for the 2023 tax year range from 1.1% to 5.54%, with six tax brackets based on income levels.
Are there any tax incentives for businesses in North Dakota?
+Yes, North Dakota offers various tax incentives, including Research and Development Tax Credits, Job Creation Tax Credits, and Tax Increment Financing (TIF) for public improvements.
How does North Dakota’s property tax system work?
+Property taxes in North Dakota are administered by county assessors, who value properties and set tax rates. These taxes support local governments and essential services.