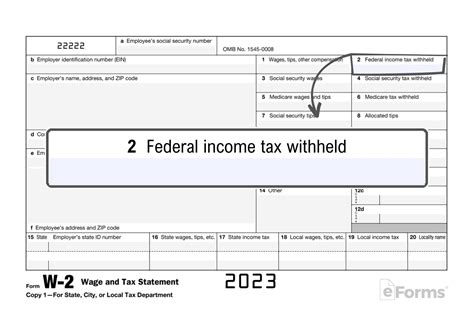
No Federal Income Tax Withheld
Welcome to an in-depth exploration of the topic "No Federal Income Tax Withheld." In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of this concept, its implications, and its significance in the world of taxation. Whether you're a business owner, an employee, or simply interested in understanding tax withholding practices, this article will provide you with valuable insights and expert analysis.
Understanding No Federal Income Tax Withheld

The phrase “No Federal Income Tax Withheld” refers to a specific situation where an employer does not deduct and remit federal income taxes from an employee’s wages or compensation. This scenario can occur under certain circumstances and has important legal and financial implications for both employers and employees.
In the United States, federal income tax is typically withheld from an individual's paycheck to ensure that they pay their fair share of taxes throughout the year. However, there are instances where an employer may choose not to withhold federal income tax, and this decision can be influenced by various factors.
Reasons for No Federal Income Tax Withholding
There are several reasons why an employer might opt to not withhold federal income tax from an employee’s wages. Here are some common scenarios:
- Exempt Employees: Certain employees, particularly those with low incomes or specific tax situations, can claim exemption from federal income tax withholding. This exemption is typically granted when an individual's expected tax liability is below a certain threshold or if they meet specific criteria set by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
- Non-Resident Aliens: Individuals who are not considered U.S. citizens or permanent residents may fall under the category of non-resident aliens. In some cases, these individuals may not be subject to federal income tax withholding, especially if they are working in the U.S. temporarily and meet specific visa requirements.
- Independent Contractors: For employees classified as independent contractors or self-employed individuals, the withholding of federal income tax is not mandatory. Instead, they are responsible for making estimated tax payments directly to the IRS to cover their tax obligations.
- Special Tax Situations: In unique circumstances, such as when an employee has significant tax credits or deductions that significantly reduce their tax liability, an employer might choose to withhold a lower amount or no federal income tax at all. This is often done with careful consideration and in compliance with IRS guidelines.
Implications and Considerations
While “No Federal Income Tax Withheld” can provide certain benefits to employees, such as a higher net pay, it also comes with responsibilities and potential drawbacks:
- Tax Obligations: Employees whose federal income tax is not withheld still have a legal obligation to pay their taxes. They must ensure that they calculate and pay their tax liabilities accurately, either through quarterly estimated tax payments or by settling their taxes at the end of the year.
- Penalty Risks: Failing to pay the correct amount of taxes can result in penalties and interest charges imposed by the IRS. Employees must be aware of their tax obligations and take proactive measures to avoid non-compliance.
- Record-Keeping: Employees should maintain detailed records of their income, expenses, and tax payments to facilitate accurate tax reporting. This practice is crucial for avoiding audit risks and potential disputes with the IRS.
The Role of Withholding Allowances
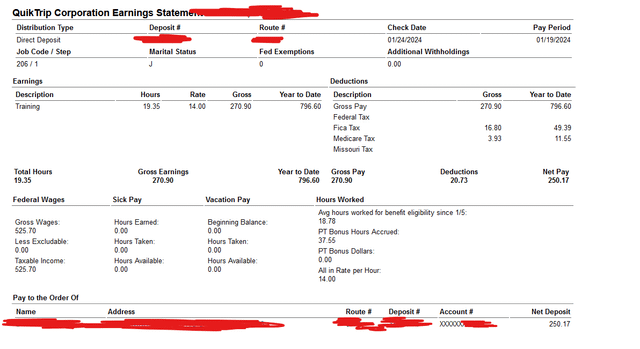
Withholding allowances play a crucial role in determining the amount of federal income tax that an employer withholds from an employee’s paycheck. These allowances are set by the IRS and allow employees to adjust their withholding based on their personal circumstances.
Personal Allowances
Employees can claim personal allowances on their W-4 form, which is used to determine the appropriate amount of federal income tax to withhold. These allowances are typically based on factors such as marital status, number of dependents, and other tax-related deductions.
By claiming the appropriate number of allowances, employees can ensure that their withholding aligns with their expected tax liability. This helps prevent under-withholding, which can lead to penalties, or over-withholding, which results in a larger tax refund but a reduced take-home pay throughout the year.
Additional Withholding
In some cases, employees may opt to have additional federal income tax withheld from their paychecks. This is often done when an individual expects a significant increase in income or has complex tax situations that make accurate withholding challenging. Additional withholding ensures that employees are not caught off guard by a large tax bill at the end of the year.
Employer Responsibilities
Employers have a critical role in ensuring proper tax withholding practices. They are responsible for complying with federal and state tax laws, including the accurate calculation and remittance of payroll taxes.
Withholding Requirements
Employers must adhere to IRS guidelines regarding tax withholding. This includes understanding the different tax forms, such as Form W-4, and ensuring that employees provide accurate and up-to-date information. Employers should also be aware of their obligations regarding backup withholding, which applies when an employee fails to provide a valid taxpayer identification number.
Payroll Management
Effective payroll management is essential for employers to maintain compliance and avoid penalties. This involves regularly reviewing and updating employee information, including tax withholding status, and accurately calculating and remitting taxes to the appropriate authorities. Modern payroll software can greatly assist employers in streamlining these processes.
Tax Planning and Strategy
For both employers and employees, understanding tax withholding and planning strategies can be advantageous. Here are some key considerations:
Employer Tax Planning
- Compliance: Employers should prioritize tax compliance to avoid penalties and legal issues. This includes staying updated with tax law changes and ensuring accurate payroll processing.
- Employee Education: Providing employees with resources and education about tax withholding can empower them to make informed decisions regarding their allowances and tax obligations.
- Payroll Software: Utilizing advanced payroll software can simplify tax calculations, ensure accuracy, and reduce the risk of errors.
Employee Tax Strategy
- Review Allowances: Employees should periodically review their W-4 form to ensure that their withholding allowances accurately reflect their current life circumstances and tax situation.
- Estimated Tax Payments: For those with no federal income tax withheld, making estimated tax payments throughout the year can help avoid a large tax bill at the end of the year and reduce the risk of penalties.
- Tax Professional Advice: Consulting with a tax professional can provide personalized guidance on tax planning, deductions, and credits to optimize an individual’s tax situation.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples

To illustrate the practical implications of “No Federal Income Tax Withheld,” let’s explore a few case studies and real-world scenarios:
Scenario 1: Independent Contractor
Sarah, an independent graphic designer, works with multiple clients and has chosen to be classified as an independent contractor. As a result, her clients do not withhold federal income tax from her payments. Sarah understands her responsibility to make estimated tax payments and has set up a dedicated savings account to cover her quarterly tax obligations.
Scenario 2: Exempt Employee
John, a part-time college student working at a local cafe, has claimed exemption from federal income tax withholding. With a limited income and few deductions, John’s tax liability is expected to be minimal. He plans to file his taxes at the end of the year and is prepared to make a small payment if necessary.
Scenario 3: Non-Resident Alien
Maria, a foreign exchange student working at a campus bookstore, is classified as a non-resident alien. Her employer has determined that, based on her visa status and income, federal income tax withholding is not required. Maria maintains careful records of her income and expenses to ensure accurate tax reporting when she files her taxes.
Future Implications and Trends
The landscape of tax withholding is constantly evolving, and it’s essential to stay informed about potential changes and trends. Here are some future implications to consider:
- Tax Law Updates: Keep an eye on any proposed changes or updates to tax laws, as they can impact withholding requirements and practices.
- Technological Advancements: The use of advanced payroll software and digital tools can streamline tax withholding processes and enhance accuracy.
- Remote Work Trends: With the rise of remote work, employers must navigate tax withholding complexities across different jurisdictions, ensuring compliance with state and local tax laws.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the concept of “No Federal Income Tax Withheld” is a critical aspect of understanding tax withholding practices. Whether you’re an employer, employee, or tax professional, staying informed and proactive is essential to ensure compliance and optimize tax strategies. By comprehending the implications, responsibilities, and potential challenges, individuals and businesses can navigate the world of tax withholding with confidence and expertise.
Can an employer refuse to withhold federal income tax if an employee requests it?
+No, employers are generally required to withhold federal income tax based on the information provided by employees on their W-4 form. Refusing to withhold taxes can lead to legal consequences for employers.
What happens if an employee’s federal income tax is not withheld, and they owe taxes at the end of the year?
+If an employee’s federal income tax is not withheld and they owe taxes, they are responsible for paying the full amount owed, including any penalties and interest. It’s crucial to plan and make estimated tax payments to avoid such situations.
Are there any advantages to having no federal income tax withheld?
+While having no federal income tax withheld can result in a higher net pay, it also comes with the responsibility of accurate tax reporting and timely payments. Employees must carefully consider their tax obligations and plan accordingly.
How often should employees review their withholding allowances?
+Employees should review their withholding allowances at least annually, especially if there are significant life changes such as marriage, childbirth, or a change in income. Regular reviews ensure accurate withholding and avoid surprises at tax time.
What resources are available to help employees understand tax withholding and planning?
+The IRS website provides extensive resources and guides on tax withholding and planning. Additionally, tax professionals and financial advisors can offer personalized advice to help individuals navigate their tax obligations.



