Nevada Sales Tax Rate
Understanding the Nevada sales tax rate is essential for both businesses and consumers within the state. The sales tax is a crucial component of Nevada's revenue system, and it plays a significant role in the state's economy. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of the Nevada sales tax rate, covering its history, current structure, exemptions, and its impact on various industries and consumers.
The Evolution of Nevada’s Sales Tax

The history of the Nevada sales tax dates back to the early 20th century, with the state implementing its first sales tax law in 1933 as a means to generate revenue during the Great Depression. Since then, the sales tax has undergone several revisions and amendments, adapting to the evolving economic landscape and the needs of the state.
Initially, the sales tax rate in Nevada was set at 2%, a modest figure compared to the rates seen in other states. Over the decades, the rate has gradually increased to meet the growing demands of the state's budget and infrastructure development. As of 2023, Nevada's sales tax rate stands at 6.85%, a rate that applies uniformly across the state.
The Current Sales Tax Structure in Nevada

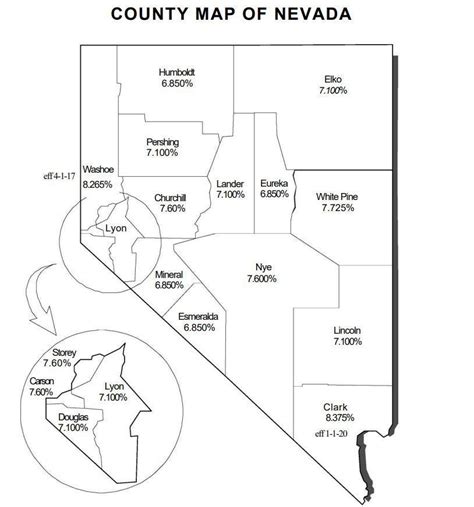
Nevada’s sales tax is a state-level tax, which means that there is a single sales tax rate that applies consistently across all counties and municipalities within the state. This uniformity simplifies the tax system for both businesses and consumers, making it easier to understand and calculate sales tax obligations.
The 6.85% sales tax rate in Nevada is composed of two primary components: the state sales tax and the local sales tax. The state sales tax, set at 6.85%, is a fixed rate that applies to all taxable sales and transactions within the state. This rate is mandated by the Nevada Department of Taxation, which oversees the administration and collection of sales tax.
In addition to the state sales tax, there is also a local sales tax component, which varies depending on the specific jurisdiction. While the state sales tax is a uniform rate, local governments, such as counties and cities, have the authority to impose their own sales tax rates. These local sales taxes are typically lower than the state rate and are used to fund local projects and services. For instance, Clark County, which includes the city of Las Vegas, has a local sales tax rate of 2.25%, bringing the total sales tax rate in this area to 9.1%.
To illustrate the impact of these rates, consider the purchase of a $100 item in different parts of Nevada. In a city like Reno, where the local sales tax rate is 0.75%, the total sales tax on the purchase would be $6.93 (6.85% state tax + 0.75% local tax). In contrast, a similar purchase in Las Vegas would incur a total sales tax of $9.10 (6.85% state tax + 2.25% local tax). These variations in local sales tax rates can significantly affect the final price of goods and services, especially for businesses and consumers operating across multiple jurisdictions.
Sales Tax Exemptions and Special Considerations
While the Nevada sales tax applies to a wide range of goods and services, there are certain categories that are exempt from sales tax. These exemptions are designed to alleviate the tax burden on specific industries or to promote certain economic activities.
Food and Grocery Items
One notable exemption in Nevada is for food and grocery items. The state recognizes the essential nature of food and, therefore, exempts most food products from sales tax. This exemption includes staple foods like bread, milk, eggs, and produce, as well as prepared foods sold in grocery stores. However, it’s important to note that this exemption does not extend to restaurant meals or catered food, which are generally subject to the standard sales tax rate.
To provide a real-world example, consider a customer purchasing $50 worth of groceries at a local supermarket in Nevada. Since these items are exempt from sales tax, the customer would only pay the listed price of $50, without any additional tax. This exemption can lead to significant savings for consumers, especially those with large families or those who rely heavily on grocery shopping.
Manufacturing and Production
Nevada also offers sales tax exemptions for certain manufacturing and production activities. This is done to encourage economic development and investment in the state’s manufacturing sector. Specifically, the state exempts the sale of machinery and equipment used directly in manufacturing or production processes. This exemption can provide significant cost savings for businesses, making Nevada an attractive location for manufacturing operations.
For instance, a company specializing in semiconductor manufacturing purchases $1 million worth of specialized equipment for its Nevada-based facility. Due to the sales tax exemption for manufacturing equipment, the company would not have to pay any sales tax on this purchase, potentially saving them a substantial amount of money.
Real Estate and Construction
The sales tax treatment of real estate and construction activities in Nevada is somewhat complex. While the sale of residential property is generally not subject to sales tax, the situation becomes more nuanced when it comes to commercial real estate and construction services.
For commercial real estate, the sale or lease of property is subject to sales tax, with the tax applying to the rent or lease payments made by the tenant. This means that businesses occupying commercial spaces in Nevada will typically pay sales tax on their monthly rent or lease payments.
In terms of construction services, the sales tax treatment depends on the specific project. New construction projects are generally subject to sales tax, with the tax applying to the cost of labor and materials used in the construction process. However, renovation or repair projects may be exempt from sales tax if they meet certain criteria, such as being deemed essential repairs or maintenance activities.
Consider a scenario where a commercial property owner in Nevada undertakes a $500,000 renovation project on their office building. If this project is classified as essential repairs, the owner may be exempt from paying sales tax on the labor and materials used in the renovation. This exemption can provide significant cost savings for businesses investing in their commercial properties.
The Impact of Nevada’s Sales Tax on Businesses and Consumers
The sales tax rate in Nevada has a direct and significant impact on both businesses and consumers within the state. For businesses, the sales tax rate affects their cost of doing business, their pricing strategies, and their overall profitability. On the other hand, consumers experience the sales tax rate through the prices they pay for goods and services, which can influence their purchasing decisions and overall financial well-being.
Businesses: Cost of Doing Business and Pricing Strategies
For businesses operating in Nevada, the sales tax rate is a crucial factor in their cost structure. The sales tax is imposed on the sale of goods and services, which means that businesses must factor it into their cost of goods sold and operating expenses. This can significantly impact their profit margins and financial performance, especially for businesses with thin margins or those selling low-cost items.
Moreover, the sales tax rate can influence a business's pricing strategy. To maintain their profit margins, businesses may need to raise prices to compensate for the sales tax. This can be a delicate balance, as higher prices may deter customers, especially in a competitive market. As such, businesses often have to carefully consider the impact of the sales tax rate on their pricing, taking into account factors like consumer demand, market dynamics, and competitor pricing.
Consider a retail business selling a range of products in Nevada. If the business's cost of goods sold is $10,000 and the sales tax rate is 6.85%, the business will need to generate $10,685 in sales to cover its costs. This means that the business must carefully consider its pricing to ensure it can cover its costs and generate a profit. For instance, if the business sells a $100 item, it may need to mark up the price to $106.85 to cover the sales tax, a decision that could impact customer demand and sales volume.
Consumers: Purchasing Decisions and Financial Considerations
For consumers in Nevada, the sales tax rate is a key factor in their purchasing decisions and financial planning. The sales tax directly affects the prices they pay for goods and services, which can influence their disposable income and overall financial well-being. As such, consumers often consider the sales tax rate when making purchasing decisions, especially for big-ticket items or when comparing prices across states.
Additionally, the sales tax rate can impact consumer behavior and shopping patterns. Some consumers may choose to shop across state lines or online to avoid the sales tax in Nevada, especially if they live near the state border or have access to online retailers that don't charge sales tax. This can lead to a loss of sales for Nevada-based businesses and impact the state's revenue.
For instance, a consumer in Nevada planning to purchase a new car may compare prices across states. If they find a similar car at a lower price in a neighboring state with a lower sales tax rate, they may choose to make the purchase there, saving money on the sales tax. This decision can significantly impact the consumer's finances and the local economy, as it leads to a loss of sales tax revenue for Nevada.
The Future of Nevada’s Sales Tax

As with any tax system, the sales tax in Nevada is subject to ongoing review and potential changes. The state’s legislators and policymakers regularly assess the sales tax rate and its impact on the economy, considering factors such as revenue needs, economic growth, and tax fairness.
In recent years, there have been discussions and proposals to modify the sales tax rate in Nevada. Some of these proposals aim to raise the sales tax rate to generate additional revenue for specific purposes, such as education or infrastructure development. Other proposals suggest lowering the sales tax rate to boost economic activity and make Nevada more attractive for businesses and consumers.
Additionally, the future of Nevada's sales tax may involve modernizing the tax system to adapt to the changing economic landscape. This could include expanding the sales tax base to include more services, implementing new technologies for tax collection and enforcement, and addressing tax avoidance through online sales and remote transactions.
Furthermore, the growing trend of e-commerce and online sales presents a challenge for Nevada's sales tax system. As more consumers shop online, it becomes increasingly difficult to collect sales tax on these transactions. Nevada, like many other states, is exploring ways to tax online sales more effectively, potentially through legislative action or partnerships with online retailers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Nevada sales tax rate is a critical component of the state’s tax system, impacting both businesses and consumers. The current rate of 6.85% is a uniform state-level tax, with additional local sales taxes varying across jurisdictions. The sales tax has a significant influence on the cost of doing business for companies and the prices paid by consumers, shaping the economic landscape of the state.
Understanding the intricacies of Nevada's sales tax, including its exemptions and special considerations, is essential for businesses and consumers alike. As the state's economy continues to evolve, so too will its sales tax system, adapting to meet the changing needs of the state and its residents. By staying informed about these changes, businesses and consumers can make more informed decisions and navigate the tax landscape effectively.
What is the current sales tax rate in Nevada?
+The current sales tax rate in Nevada is 6.85%, which includes the state sales tax rate and the local sales tax rate. The state sales tax rate is a fixed 6.85%, while local sales tax rates can vary depending on the jurisdiction.
Are there any sales tax exemptions in Nevada?
+Yes, Nevada offers sales tax exemptions for certain categories. These include food and grocery items, manufacturing and production equipment, and some real estate and construction activities. The state exempts these categories to encourage economic development and alleviate the tax burden on specific industries.
How does the sales tax rate affect businesses in Nevada?
+The sales tax rate directly impacts businesses’ cost of doing business and their pricing strategies. It can affect their profit margins and financial performance, especially for businesses with thin margins. Businesses must carefully consider the sales tax rate when setting their prices to ensure they can cover costs and remain competitive.
What is the impact of the sales tax rate on consumers in Nevada?
+The sales tax rate influences consumers’ purchasing decisions and financial planning. It directly affects the prices they pay for goods and services, impacting their disposable income and overall financial well-being. Consumers may consider the sales tax rate when comparing prices across states or when making significant purchases.
How might the sales tax rate change in the future in Nevada?
+The future of Nevada’s sales tax rate is subject to ongoing review and potential changes. There have been discussions and proposals to modify the rate, either by raising or lowering it to meet the state’s revenue needs and economic goals. Additionally, the growing trend of e-commerce may prompt changes to effectively tax online sales.



