Nc Property Tax Rate

The North Carolina property tax system is an essential component of the state's revenue structure, playing a crucial role in funding various public services and infrastructure. Understanding the property tax rates and their implications is vital for homeowners, investors, and anyone interested in the real estate market within the state. This comprehensive guide aims to delve into the intricacies of the Nc Property Tax Rate, providing an in-depth analysis and practical insights.
Understanding the Nc Property Tax Rate Structure
In North Carolina, the property tax system operates on a local level, with each county setting its own tax rates. This decentralized approach allows for a certain level of flexibility, enabling counties to adapt tax policies to their unique economic and demographic conditions. However, it also means that property tax rates can vary significantly across the state.
The property tax rate is typically expressed as a percentage and is applied to the assessed value of a property. This assessed value is determined by the county tax assessor's office, which evaluates the property's worth based on factors such as its location, size, and market conditions. The assessed value is then multiplied by the tax rate to calculate the annual property tax bill.
For instance, if a property is valued at $200,000 and the county's tax rate is set at 0.8%, the annual property tax due would be $1,600. This calculation is a simplified example, as many counties in North Carolina utilize tiered tax rates and offer various exemptions and deductions, which can further impact the final tax amount.
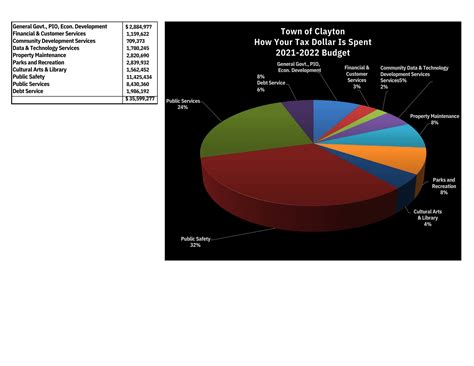
| County | Tax Rate (%) | Assessed Value ($) | Annual Property Tax ($) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mecklenburg | 0.87 | 300,000 | 2,580 |
| Wake | 0.86 | 250,000 | 2,150 |
| Guilford | 0.85 | 400,000 | 3,400 |
Factors Influencing Nc Property Tax Rates
The tax rates in North Carolina are influenced by a variety of factors, each playing a unique role in shaping the overall property tax landscape.
- County Revenue Needs: Counties rely on property taxes as a primary source of revenue to fund essential services such as education, public safety, and infrastructure maintenance. As such, the tax rate may be adjusted to meet the county's financial requirements.
- Economic Conditions: Local economic factors, including employment rates, income levels, and the overall health of the real estate market, can impact property values and, consequently, the tax base. Counties may adjust tax rates to accommodate these economic fluctuations.
- Population Growth: Rapid population growth can put a strain on county resources, leading to increased demand for public services. In such cases, counties might consider raising tax rates to generate additional revenue.
- Statewide Policies: While counties have autonomy in setting tax rates, the state government also plays a role through legislation and funding distribution. State policies can indirectly influence local tax rates and assessment practices.
Exemptions and Deductions
North Carolina offers various exemptions and deductions that can reduce the taxable value of a property, thereby lowering the property tax bill. These include:
- Homestead Exemption: Available to homeowners who use their property as their primary residence, this exemption reduces the assessed value by a set amount, resulting in lower taxes.
- Senior Citizen Exemption: Seniors who meet certain age and income criteria may be eligible for a partial or full exemption, significantly reducing their property taxes.
- Veteran's Exemption: Veterans and their surviving spouses may qualify for an exemption, offering relief from property taxes.
- Agricultural and Forestland Exemption: Properties used for agricultural or forestry purposes may be assessed at a lower value, benefiting landowners engaged in these industries.
The Impact of Nc Property Tax Rates

The property tax rates in North Carolina have a wide-ranging impact on both individuals and the state as a whole. Here’s a closer look at some of the key implications:
Homeownership
Property taxes are a significant consideration for potential homeowners. High tax rates can make homeownership less affordable, particularly for first-time buyers or those on fixed incomes. On the other hand, counties with lower tax rates may be more attractive to homebuyers, leading to increased property values and a healthier real estate market.
Business and Investment
For businesses and investors, property taxes are a critical factor in decision-making. Higher tax rates can deter investment and business expansion, while lower rates can encourage economic growth and development. It’s a delicate balance that counties must consider when setting their tax policies.
Public Services and Infrastructure
Property taxes are a primary funding source for essential public services, including education, healthcare, and public safety. Counties with higher tax rates may be able to invest more in these services, potentially leading to improved outcomes. However, it’s important to strike a balance to ensure that the tax burden is manageable for residents and businesses.
Statewide Economic Growth
The property tax system in North Carolina contributes to the state’s overall economic health. By funding local services and infrastructure, property taxes play a crucial role in supporting economic growth and development. Counties with well-managed tax systems and efficient public services can attract businesses and talent, further boosting the state’s economy.
Comparative Analysis: Nc Property Tax Rates vs. Other States
To gain a broader perspective, it’s beneficial to compare North Carolina’s property tax rates with those of other states. While each state has its unique tax system, some general trends can be observed.
According to recent data, North Carolina's property tax rates are relatively moderate compared to many other states. For instance, Texas and New Jersey are known for their high property tax rates, with some counties exceeding 2% of the assessed value. On the other end of the spectrum, states like Hawaii and Alabama have lower rates, often below 0.5%.
It's important to note that these comparisons should be taken with a grain of salt, as each state's tax system is shaped by its unique circumstances and priorities. Additionally, factors like the quality of public services, cost of living, and economic opportunities can significantly influence the overall appeal of a state for homeowners and investors.
Future Outlook and Considerations
As North Carolina continues to evolve, its property tax system will likely undergo changes and adjustments to meet the evolving needs of its residents and businesses. Here are some key considerations for the future:
Economic Trends
The state’s economic health will remain a crucial factor in shaping property tax rates. As North Carolina continues to attract businesses and experience population growth, counties may need to adapt their tax policies to accommodate these changes. This could involve adjusting tax rates, offering additional exemptions, or exploring alternative revenue sources.
Public Opinion and Political Landscape
The political climate and public sentiment towards property taxes can significantly influence tax policy. If residents or businesses feel that tax rates are too high, there may be pressure for reform or reductions. Conversely, if public services require additional funding, there could be support for higher tax rates.
Technological Advancements
The integration of technology in property assessment and tax administration can lead to more efficient and accurate processes. For instance, the use of drone technology for property assessments or the implementation of digital tax payment systems can streamline operations and potentially reduce administrative costs.
Environmental Considerations
With increasing focus on environmental sustainability, counties may explore tax incentives or exemptions for properties that incorporate green technologies or follow sustainable practices. This could encourage more eco-friendly developments and reduce the environmental impact of the real estate sector.
Conclusion

The Nc Property Tax Rate is a dynamic and multifaceted aspect of North Carolina’s real estate landscape. Understanding the rate structure, its influences, and its impact is crucial for anyone involved in the state’s real estate market. By staying informed and engaging with local authorities, individuals and businesses can navigate the property tax system effectively and make informed decisions about their financial strategies.
How often are property tax rates reviewed and adjusted in North Carolina?
+Property tax rates in North Carolina are typically reviewed annually by county commissioners or the county board of equalization. Adjustments can be made based on various factors, including the county’s financial needs and economic conditions. However, significant changes to tax rates are often made with careful consideration to avoid drastic impacts on residents and businesses.
Are there any online tools to estimate property tax rates in North Carolina?
+Yes, several online tools and property tax calculators are available to estimate property tax rates in North Carolina. These tools often consider factors such as the property’s location, assessed value, and applicable exemptions. However, it’s important to note that these estimates are not official and should be used as a guide only.
Can property tax rates vary within a county in North Carolina?
+In some cases, yes. While counties set their overall tax rates, there can be variations within the county due to different tax districts or special tax areas. These variations can be based on factors such as school district boundaries or infrastructure improvement zones. It’s essential to check with the county tax assessor’s office for specific information on any variations within a county.