Nc Capital Gains Tax
Welcome to a comprehensive guide on the North Carolina (NC) Capital Gains Tax, a critical aspect of financial planning and investment strategies within the state. This article aims to provide an in-depth analysis of the tax implications associated with capital gains in North Carolina, offering valuable insights for investors, business owners, and individuals alike. By understanding the intricacies of NC's capital gains tax structure, you can make informed decisions to optimize your financial portfolio and minimize tax liabilities.
Understanding Capital Gains Tax in North Carolina
Capital gains tax refers to the levy imposed by the government on profits made from the sale of certain types of assets, including investments and real estate. In North Carolina, like many other states, capital gains tax is an essential component of the state’s revenue stream, contributing to the overall economic health and development of the region.
The state of North Carolina recognizes two primary types of capital gains: short-term and long-term capital gains. Short-term capital gains result from the sale of assets held for a year or less, while long-term capital gains apply to assets held for more than a year. The distinction between these two categories is crucial as they are taxed differently, with long-term capital gains often enjoying more favorable tax rates.
Tax Rates and Brackets
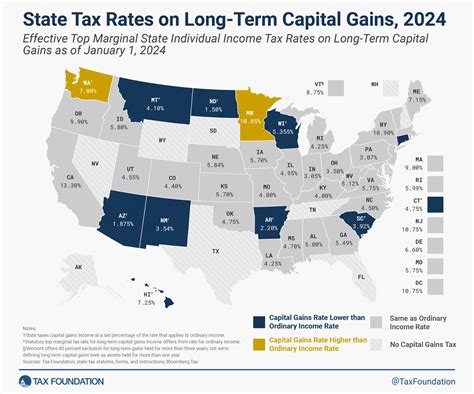
North Carolina operates on a progressive tax system for capital gains, meaning that higher income levels are subject to higher tax rates. As of the latest tax year, the state’s capital gains tax rates range from 5.25% to 5.75%, depending on the individual’s taxable income.
| Taxable Income Range | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| $35,000 or less | 5.25% |
| $35,001 - $135,000 | 5.45% |
| Over $135,000 | 5.75% |
Exemptions and Deductions
North Carolina offers certain exemptions and deductions to mitigate the impact of capital gains tax on taxpayers. One notable exemption is the personal exemption, which allows individuals to deduct a specific amount from their taxable income. This exemption helps reduce the overall tax burden and provides a certain level of financial relief.
Additionally, North Carolina recognizes the capital gains deduction, which allows taxpayers to deduct a portion of their capital gains from their taxable income. This deduction is particularly beneficial for investors who have held their assets for a long time and are looking to minimize the tax implications of their profits.
Strategies for Minimizing NC Capital Gains Tax

Navigating the complexities of capital gains tax in North Carolina requires a strategic approach. Here are some key strategies to consider when planning your investments and managing your tax liabilities:
Hold Assets for the Long Term
One of the most effective ways to reduce your capital gains tax bill is to hold your assets for an extended period. As mentioned earlier, long-term capital gains are taxed at a lower rate compared to short-term gains. By adopting a long-term investment strategy, you can take advantage of this tax benefit and potentially save a significant amount in taxes.
Utilize Tax-Advantaged Accounts
North Carolina offers various tax-advantaged accounts that can help reduce your tax liability. For instance, retirement accounts like IRAs and 401(k)s allow you to defer taxes on investment gains until you withdraw funds during retirement. This strategy not only minimizes your current tax burden but also provides a tax-efficient way to save for the future.
Employ Tax-Loss Harvesting
Tax-loss harvesting is a strategy where you sell losing investments to offset gains and reduce your overall tax liability. By strategically timing your sales, you can balance your portfolio while minimizing the tax impact of your investment decisions. This technique is particularly useful for investors who actively manage their portfolios and aim to optimize their tax efficiency.
Consider Cost Basis Adjustments
The cost basis of an asset refers to its original purchase price, which plays a crucial role in determining capital gains. By making cost basis adjustments, such as through wash sales or basis adjustments for stock dividends, you can potentially lower your capital gains and reduce your tax liability. However, it’s important to consult a tax professional to ensure you comply with the relevant regulations.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Let’s delve into some real-world examples to illustrate the impact of NC’s capital gains tax and the strategies that can be employed to optimize financial outcomes.
Case Study: Long-Term Investment in Real Estate
Imagine an investor who purchases a residential property in North Carolina for 250,000 and holds it for 10 years. During this period, the property appreciates in value to 400,000. When the investor decides to sell the property, they would be subject to long-term capital gains tax on the profit of 150,000. Assuming a tax rate of 5.75%, the investor would owe approximately 8,625 in capital gains tax.
However, if the investor had held the property for an additional year, their tax rate would have dropped to 5.45%, resulting in a savings of $656 on their tax bill. This case study highlights the importance of holding assets for the long term to benefit from lower tax rates.
Case Study: Retirement Account Strategy
Consider an individual who contributes $5,000 annually to a traditional IRA. Over a period of 30 years, this individual’s contributions and investment gains grow to a substantial amount. When they withdraw funds during retirement, the distributions are taxed as ordinary income. By utilizing a traditional IRA, the investor can defer taxes on their investment gains until a lower tax bracket in retirement, potentially saving thousands in taxes over their lifetime.
Future Implications and Tax Reform
As with any tax system, North Carolina’s capital gains tax structure is subject to potential reforms and changes. While the current progressive tax system provides a balanced approach, future legislative actions could bring about modifications to tax rates, brackets, or even the classification of capital gains. Staying informed about any proposed or enacted tax reforms is crucial for investors and taxpayers to adapt their financial strategies accordingly.
Furthermore, the ongoing discussion around federal tax reforms and their potential impact on state-level taxation adds another layer of complexity. Changes at the federal level could influence the way states structure their tax systems, including capital gains taxation. Staying abreast of these developments is essential for long-term financial planning.
How does North Carolina's capital gains tax compare to other states?
+North Carolina's capital gains tax rates are generally in line with many other states. However, it's important to note that each state has its own unique tax structure, and some states may offer more favorable rates or have no capital gains tax at all. It's advisable to compare NC's tax rates with those of neighboring states or regions to make informed decisions.
Are there any exceptions or special considerations for certain types of assets?
+Yes, North Carolina, like many states, recognizes certain exceptions and special considerations for specific assets. For instance, the sale of a primary residence may be exempt from capital gains tax if certain criteria are met. Additionally, some types of investments, such as certain securities or collectibles, may be subject to different tax treatments. It's crucial to consult a tax professional to understand the specific implications for your assets.
Can I offset capital gains with losses from other investments?
+Absolutely! North Carolina allows taxpayers to offset capital gains with capital losses, which can significantly reduce their overall tax liability. By strategically managing your investment portfolio and timing your sales, you can take advantage of this tax benefit to minimize your capital gains tax bill.
In conclusion, understanding the intricacies of North Carolina’s capital gains tax is essential for anyone with investment interests or business ventures within the state. By adopting strategic approaches and staying informed about tax regulations, individuals and businesses can optimize their financial portfolios and minimize their tax liabilities. Remember, seeking professional advice is always recommended to navigate the complexities of tax laws and ensure compliance.



