Mn Income Tax Rate
The Minnesota Income Tax is a crucial component of the state's revenue system, contributing significantly to the funding of various public services and infrastructure. This tax, levied on the taxable income of individuals and businesses, plays a vital role in shaping the state's economy and overall financial health.
Understanding Minnesota’s Progressive Tax Structure
Minnesota employs a progressive income tax system, which means that higher incomes are taxed at progressively higher rates. This approach ensures that individuals with higher earning capacities contribute a larger share of their income to the state’s coffers, promoting economic fairness and stability.
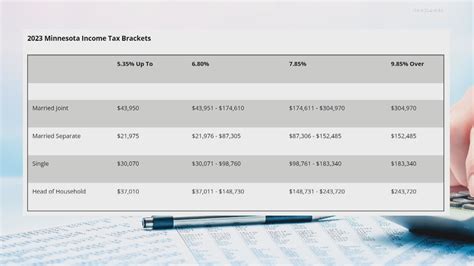
The state's income tax rates are categorized into seven brackets, each corresponding to a specific income range. As of my last update in January 2023, these brackets and their associated tax rates are as follows:
| Income Bracket | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Up to $11,950 | 5.35% |
| $11,951 - $25,000 | 7.05% |
| $25,001 - $40,000 | 7.15% |
| $40,001 - $75,000 | 7.85% |
| $75,001 - $238,500 | 7.875% |
| $238,501 - $397,200 | 9.85% |
| Over $397,200 | 9.875% |

Impact of Tax Brackets on Individual Taxpayers
The bracket system ensures that individuals with varying income levels are taxed proportionally. For instance, a taxpayer with an annual income of 30,000 would fall into the <strong>third bracket</strong> and be taxed at a rate of <strong>7.15%</strong>. This means that for every dollar earned above 25,000, they would pay a tax of 7.15 cents to the state. Conversely, an individual earning 500,000 annually would be taxed at <strong>9.875%</strong> for the portion of their income exceeding 397,200, illustrating the progressive nature of Minnesota’s tax system.
Key Factors Influencing Income Tax Rates

Minnesota’s income tax rates are subject to periodic adjustments, influenced by various economic and legislative factors. These adjustments are typically proposed by the state’s Department of Revenue and approved by the Minnesota Legislature.
Economic Considerations
Economic conditions play a pivotal role in determining income tax rates. During periods of economic growth, when state revenues are robust, tax rates might remain stable or even decrease to encourage continued economic activity. Conversely, economic downturns or budget shortfalls could lead to rate increases or the introduction of new tax brackets to generate additional revenue.
Legislative Decisions
The Minnesota Legislature wields significant influence over income tax rates. Through the enactment of new laws or amendments to existing ones, legislators can adjust tax rates to align with the state’s fiscal goals and priorities. For instance, they might opt to lower tax rates to stimulate economic growth or increase rates to fund specific initiatives or programs.
Historical Perspective
A review of Minnesota’s tax history reveals a dynamic landscape. Over the years, the state has implemented various tax reforms, including the introduction of new brackets, rate adjustments, and the expansion of tax credits and deductions. These changes have often been driven by the need to address budget deficits, promote economic growth, or ensure fairness in the tax system.
The Role of Income Tax in State Revenue
Income tax is a substantial contributor to Minnesota’s state revenue. In the 2021 fiscal year, for instance, individual income taxes accounted for approximately 37.3% of the state’s total revenue, underscoring its critical role in funding essential services such as education, healthcare, infrastructure development, and social welfare programs.
Impact on Public Services
The revenue generated from income taxes directly influences the quality and accessibility of public services. For instance, higher tax revenues can lead to increased funding for schools, resulting in improved educational outcomes. Similarly, well-funded healthcare systems can provide better access to quality medical care for residents.
Economic Development and Job Creation
Income tax revenues also play a crucial role in fostering economic development. These funds can be utilized to support small businesses, encourage innovation, and create job opportunities. Additionally, they can be channeled towards infrastructure projects, such as road improvements or public transportation initiatives, which not only enhance the quality of life but also attract businesses and investment.
Addressing Budget Deficits
In times of economic hardship or unexpected expenses, income tax revenues can serve as a critical tool to address budget deficits. By adjusting tax rates or implementing temporary tax increases, the state can generate additional revenue to maintain essential services and avoid cuts that could negatively impact residents.
Comparative Analysis: Minnesota’s Income Tax vs. Other States
Minnesota’s income tax rates are generally competitive when compared to other states. However, it’s essential to note that each state has its unique tax system, which might include different brackets, rates, and exemptions.
Tax Rates Across the Nation
As of my last update, Minnesota’s tax rates are relatively moderate compared to some of its neighboring states. For instance, Wisconsin has a flat income tax rate of 7.65%, while Iowa’s rates range from 5.5% to 8.98%. On the other hand, states like California and New York have higher top tax rates, with California’s reaching 13.3% and New York’s 8.82%.
It's important to remember that tax rates are just one aspect of a state's tax system. Other factors, such as tax credits, deductions, and the overall cost of living, should also be considered when comparing states.
Impact on Taxpayers
The variation in tax rates across states can significantly impact individuals and businesses. For instance, a high-income earner might consider relocating to a state with lower tax rates to reduce their tax liability. Conversely, states with higher tax rates might offer more comprehensive public services, which could be attractive to certain taxpayers.
Minnesota’s Tax Incentives and Credits
In addition to the standard income tax rates, Minnesota offers various tax incentives and credits to promote specific behaviors or support particular industries. These incentives can significantly reduce an individual’s or business’s tax liability, making them an essential aspect of the state’s tax landscape.
Common Tax Incentives
- Research and Development Tax Credit: This credit encourages businesses to invest in research and development activities by providing a tax credit for qualified expenses.
- Angel Investment Tax Credit: Aimed at promoting entrepreneurship, this credit provides a tax benefit to individuals who invest in qualifying Minnesota startups.
- Historic Preservation Tax Credit: This credit incentivizes the rehabilitation and preservation of historic properties by offering a tax credit for qualified expenses.
Impact of Tax Incentives
Tax incentives can have a significant impact on Minnesota’s economy. By encouraging investment in research, entrepreneurship, and historic preservation, these incentives foster economic growth, job creation, and the preservation of cultural heritage. They also contribute to a more diverse and resilient business landscape, which is beneficial for the state’s long-term economic health.
The Future of Minnesota’s Income Tax
The future of Minnesota’s income tax system is likely to be shaped by a range of factors, including economic trends, demographic shifts, and political ideologies. While it’s challenging to predict specific changes, certain trends and potential scenarios can be explored.
Economic Factors
Economic growth and prosperity could lead to calls for tax rate reductions, especially if the state’s revenue exceeds expectations. Conversely, economic downturns or budget constraints might necessitate rate increases or the introduction of new tax brackets to generate additional revenue.
Demographic Changes
Shifts in Minnesota’s demographic landscape, such as an aging population or changes in income distribution, could influence tax policy. For instance, an aging population might require increased funding for healthcare and social services, potentially leading to adjustments in tax rates or the introduction of new taxes to support these services.
Political Landscape
Political ideologies and party dynamics play a significant role in shaping tax policy. Changes in legislative leadership or shifts in political leanings could result in significant tax reforms, with some advocating for lower taxes to stimulate economic growth and others prioritizing social programs and public services, which might require higher tax rates.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements, such as the increasing adoption of digital technologies and remote work, could impact tax policy. For instance, the state might need to reconsider its tax system to accommodate the changing nature of work and ensure that it captures revenue from remote workers and digital businesses.
National and Global Trends
National and global economic trends, such as trade policies, interest rates, or international tax reforms, could also influence Minnesota’s tax landscape. For example, changes in federal tax policies could impact the state’s tax system, especially if they lead to significant shifts in individual or corporate tax liabilities.
Environmental Considerations
Environmental concerns and the transition to a greener economy might also impact tax policy. The state could introduce tax incentives or disincentives to promote sustainable practices, encourage the adoption of renewable energy, or address environmental challenges, such as carbon emissions.
How often are Minnesota’s income tax rates updated?
+Minnesota’s income tax rates are typically updated annually, based on legislative decisions and economic considerations. The Minnesota Legislature has the authority to adjust tax rates through the enactment of new laws or amendments to existing ones.
Are there any plans to change the number of tax brackets in Minnesota?
+As of my last update, there were no specific plans to change the number of tax brackets in Minnesota. However, tax reforms are an ongoing process, and proposals to adjust the tax system, including the number of brackets, are periodically introduced and considered by the Minnesota Legislature.
What is the process for proposing and implementing tax reforms in Minnesota?
+In Minnesota, tax reforms are typically proposed by the Department of Revenue or other stakeholders and then introduced as bills in the Minnesota Legislature. These bills undergo a rigorous process of committee hearings, public input, and debate before being voted on by legislators. If a tax reform bill is passed, it is then signed into law by the Governor, and the new tax rates or policies become effective on the specified date.



